Your Aba in plants images are available. Aba in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Aba in plants files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for aba in plants images information linked to the aba in plants topic, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our site always provides you with suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that match your interests.
Aba In Plants. Plant hormones are crucial factors in transducing the stress signal and the main player among them is abscisic acid (aba). Aba is a naturally occurring compound in plants. The canonical aba receptor and signaling pathway appear to have been present and able to respond to aba in the ancestral land plant, despite the absence of a definite xanthoxin dehydrogenase (xd. Abscisic acid (aba) is a plant hormone that regulates numerous aspects of plant growth, development, and stress responses.
 IJMS Free FullText Function of ABA in Stomatal From mdpi.com
IJMS Free FullText Function of ABA in Stomatal From mdpi.com
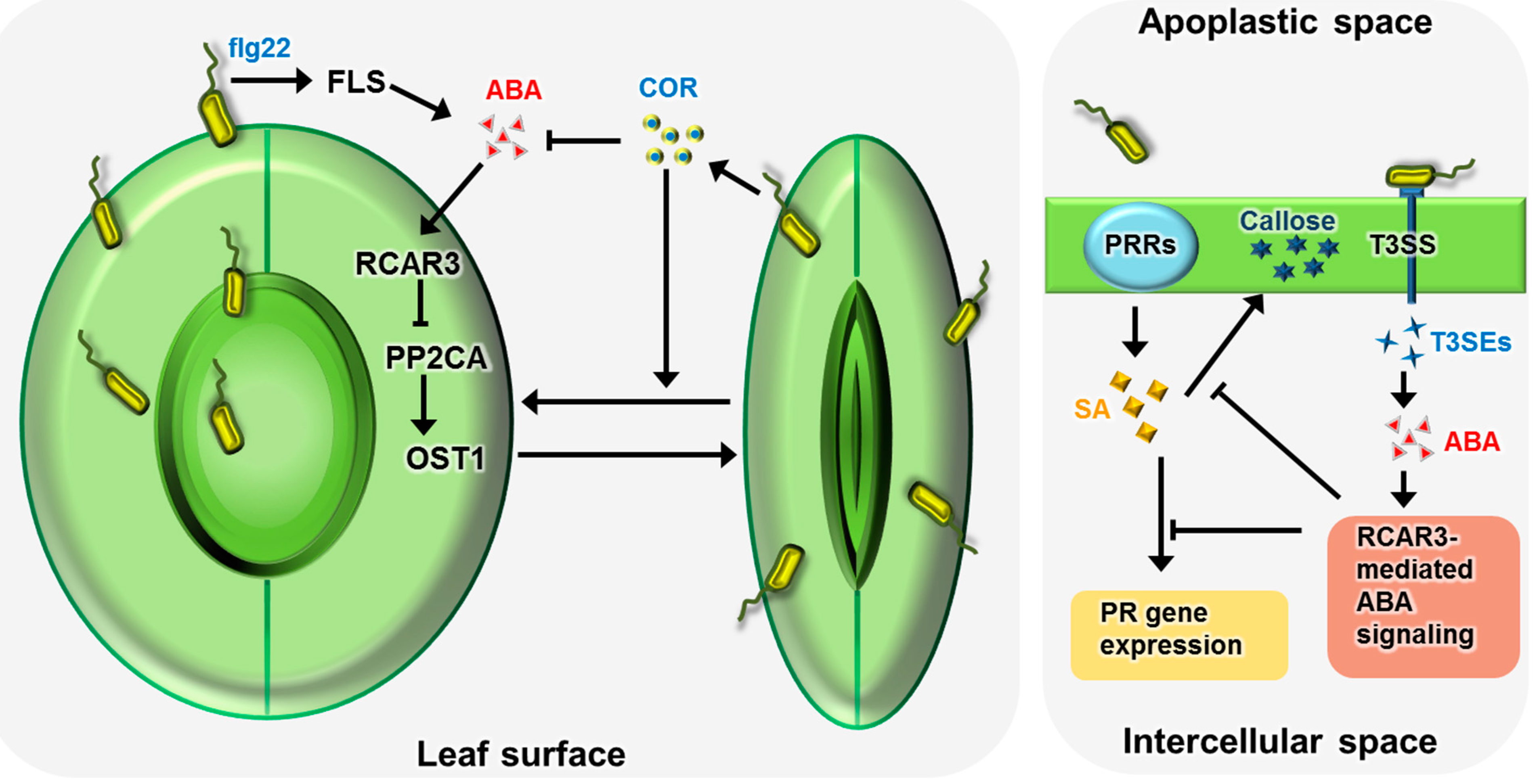
Occurrence and distribution aba is a ubiquitous plant hormone in vascular plants in bryophytes it has been found in mosses but not in liverworts. It has an essential role in multiple physiological processes of plants, such as stomatal closure, cuticular wax accumulation, leaf senescence, bud dormancy, seed germination, osmotic regulation, and growth inhibition among many others. Plants close stomata to limit water loss on water deficit. The canonical aba receptor and signaling pathway appear to have been present and able to respond to aba in the ancestral land plant, despite the absence of a definite xanthoxin dehydrogenase (xd. Abscisic acid (aba) is a plant hormone that regulates numerous aspects of plant growth, development, and stress responses. Aba may be translocated from the sites of biosynthesis, such as roots and leaf vascular tissues, to the guard cells.
Moreover aba is involved in the inhibition of ethylene production, which is a growth inhibitor under stress.
Abscisic acid (aba) regulates various aspects of plant physiology, including promoting seed dormancy and adaptive responses to abiotic and biotic stresses. At the cellular level, aba controls the movement of stomata (pores on the leaf surface) for transpiration and the exchange of co 2 and o 2. Aba regulates multiple developmental stages of plants. It has an essential role in multiple physiological processes of plants, such as stomatal closure, cuticular wax accumulation, leaf senescence, bud dormancy, seed germination, osmotic regulation, and growth inhibition among many others. Occurrence and distribution aba is a ubiquitous plant hormone in vascular plants in bryophytes it has been found in mosses but not in liverworts. The aba hormone has mainly been associated with the regulation of water deficiency in plants.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Moreover aba is involved in the inhibition of ethylene production, which is a growth inhibitor under stress. At the organ level, dry seeds obtain desiccation tolerance via aba. The canonical aba receptor and signaling pathway appear to have been present and able to respond to aba in the ancestral land plant, despite the absence of a definite xanthoxin dehydrogenase (xd. Plant responses to abiotic cues involve changes in metabolism, photosynthesis, gene expression, ion levels, etc., and must be perfectly coordinated by. Aba promotes root stem cell maintenance through abfs together with wox5, and maintains primary root growth by restricting the ethylene production through acs2/5.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Abscisic acid (aba) functions in different stages during plant growth. Occurrence and distribution aba is a ubiquitous plant hormone in vascular plants in bryophytes it has been found in mosses but not in liverworts. The aba hormone has mainly been associated with the regulation of water deficiency in plants. It is synthesized partially in the chloroplasts and the biosynthesis primarily occurs in the leaves. Moreover aba is involved in the inhibition of ethylene production, which is a growth inhibitor under stress.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Aba regulates multiple developmental stages of plants. Abscisic acid (aba) is a phytohormone critical for plant growth and development and plays an important role in integrating various stress signals and controlling downstream stress responses. Plant hormones are crucial factors in transducing the stress signal and the main player among them is abscisic acid (aba). Aba regulates multiple developmental stages of plants. Moreover aba is involved in the inhibition of ethylene production, which is a growth inhibitor under stress.
 Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Aba and metabolites and stomatal apertures sizes in bean leaves. Plants have to adjust aba levels constantly in responce to changing physiological and environmental conditions. Abscisic acid (aba) is a plant hormone that is tightly associated with water availability. Abscisic acid (aba) is a phytohormone critical for plant growth and development and plays an important role in integrating various stress signals and controlling downstream stress responses. Plant hormones are crucial factors in transducing the stress signal and the main player among them is abscisic acid (aba).
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
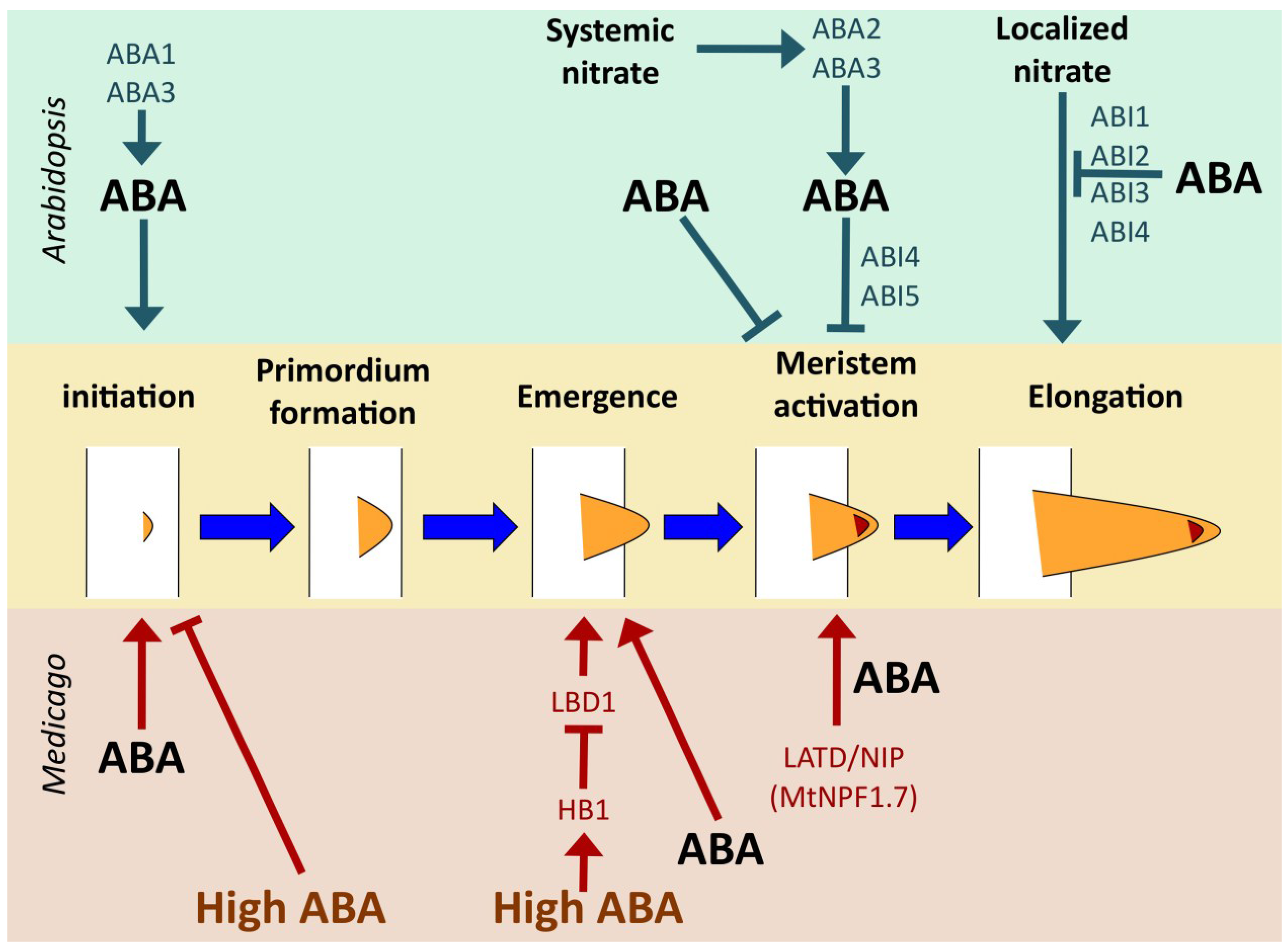
Although it is a relatively simple molecule, some. In higher plants, aba and ga have been reported to antagonistically regulate seed dormancy and germination and respond to environmental cues, such as light, temperature, and abiotic stresses (golldack et al. A plethora of studies have shown the critical roles of aba in regulating genes expression, proteins, and enzymatic activities involved in plant cell dehydration tolerance [ 33, 34 ]. Aba controls plants’ stress response at. Aba may be translocated from the sites of biosynthesis, such as roots and leaf vascular tissues, to the guard cells.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Abscisic acid (aba) is a phytohormone critical for plant growth and development and plays an important role in integrating various stress signals and controlling downstream stress responses. In higher plants, aba and ga have been reported to antagonistically regulate seed dormancy and germination and respond to environmental cues, such as light, temperature, and abiotic stresses (golldack et al. Abscisic acid (aba) regulates various aspects of plant physiology, including promoting seed dormancy and adaptive responses to abiotic and biotic stresses. A plethora of studies have shown the critical roles of aba in regulating genes expression, proteins, and enzymatic activities involved in plant cell dehydration tolerance [ 33, 34 ]. Aba regulates multiple developmental stages of plants.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Occurrence and distribution aba is a ubiquitous plant hormone in vascular plants in bryophytes it has been found in mosses but not in liverworts. Plants have to adjust aba levels constantly in responce to changing physiological and environmental conditions. Out of five characteristic phytohormones, one is aba which helps in controlling many development and growth characteristics of plants such as leaf abscission, inhibition of fruit ripening, etc. Abscisic acid (aba) regulates various aspects of plant physiology, including promoting seed dormancy and adaptive responses to abiotic and biotic stresses. Abscisic acid (aba) is a phytohormone critical for plant growth and development and plays an important role in integrating various stress signals and controlling downstream stress responses.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Aba controls plants’ stress response at. Plant hormones are crucial factors in transducing the stress signal and the main player among them is abscisic acid (aba). Abscisic acid (aba) is an important phytohormone regulating plant growth, development, and stress responses. Aba may be translocated from the sites of biosynthesis, such as roots and leaf vascular tissues, to the guard cells. It has an essential role in multiple physiological processes of plants, such as stomatal closure, cuticular wax accumulation, leaf senescence, bud dormancy, seed germination, osmotic regulation, and growth inhibition among many others.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Abscisic acid (aba) regulates various aspects of plant physiology, including promoting seed dormancy and adaptive responses to abiotic and biotic stresses. A plethora of studies have shown the critical roles of aba in regulating genes expression, proteins, and enzymatic activities involved in plant cell dehydration tolerance [ 33, 34 ]. In higher plants, aba and ga have been reported to antagonistically regulate seed dormancy and germination and respond to environmental cues, such as light, temperature, and abiotic stresses (golldack et al. It has an essential role in multiple physiological processes of plants, such as stomatal closure, cuticular wax accumulation, leaf senescence, bud dormancy, seed germination, osmotic regulation, and growth inhibition among many others. Plants have to adjust aba levels constantly in responce to changing physiological and environmental conditions.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Aba limits water loss through promoting wax synthesis and stomatal closure. The aba hormone has mainly been associated with the regulation of water deficiency in plants. Abscisic acid (aba) is an important phytohormone regulating plant growth, development, and stress responses. At the organ level, dry seeds obtain desiccation tolerance via aba. Abscisic acid (aba) regulates many agronomically important aspects of plant development, including the synthesis of seed storage proteins and lipids, the promotion of seed desiccation tolerance and dormancy, and the inhibition of the phase transitions from embryonic to germinative growth and from vegetative to reproductive growth (reviewed.
 Source: intechopen.com
Source: intechopen.com
These results imply that low light stress may inhibit seed germination by decreasing the bioactive ga content in the incubated seeds. Plants have to adjust aba levels constantly in responce to changing physiological and environmental conditions. It has an essential role in multiple physiological processes of plants, such as stomatal closure, cuticular wax accumulation, leaf senescence, bud dormancy, seed germination, osmotic regulation, and growth inhibition among many others. It exhibits inhibitive functions when it is accumulated in large amount under stress to help plant survival through inhibition of processes such as stomatal opening and plant size expansion. Aba and metabolites and stomatal apertures sizes in bean leaves.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Aba regulates multiple developmental stages of plants. Out of five characteristic phytohormones, one is aba which helps in controlling many development and growth characteristics of plants such as leaf abscission, inhibition of fruit ripening, etc. Abscisic acid (aba) is a plant hormone that regulates numerous aspects of plant growth, development, and stress responses. Transport of abscisic acid (aba) in plants as influenced by journal of journal of experimental botany, vol. Aba is commonly known as the “stress hormone” that responds to variety of environmental stresses including both biotic and abiotic stress ( zhang, 2014 ).
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
It exhibits inhibitive functions when it is accumulated in large amount under stress to help plant survival through inhibition of processes such as stomatal opening and plant size expansion. Abscisic acid (aba) is a phytohormone critical for plant growth and development and plays an important role in integrating various stress signals and controlling downstream stress responses. Plants have to adjust aba levels constantly in responce to changing physiological and environmental conditions. Abscisic acid (aba) regulates many agronomically important aspects of plant development, including the synthesis of seed storage proteins and lipids, the promotion of seed desiccation tolerance and dormancy, and the inhibition of the phase transitions from embryonic to germinative growth and from vegetative to reproductive growth (reviewed. Aba and metabolites and stomatal apertures sizes in bean leaves.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Abscisic acid (aba) is a plant hormone that is tightly associated with water availability. Abscisic acid (aba) regulates many agronomically important aspects of plant development, including the synthesis of seed storage proteins and lipids, the promotion of seed desiccation tolerance and dormancy, and the inhibition of the phase transitions from embryonic to germinative growth and from vegetative to reproductive growth (reviewed. Plant responses to abiotic cues involve changes in metabolism, photosynthesis, gene expression, ion levels, etc., and must be perfectly coordinated by. Aba limits water loss through promoting wax synthesis and stomatal closure. It is synthesized partially in the chloroplasts and the biosynthesis primarily occurs in the leaves.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
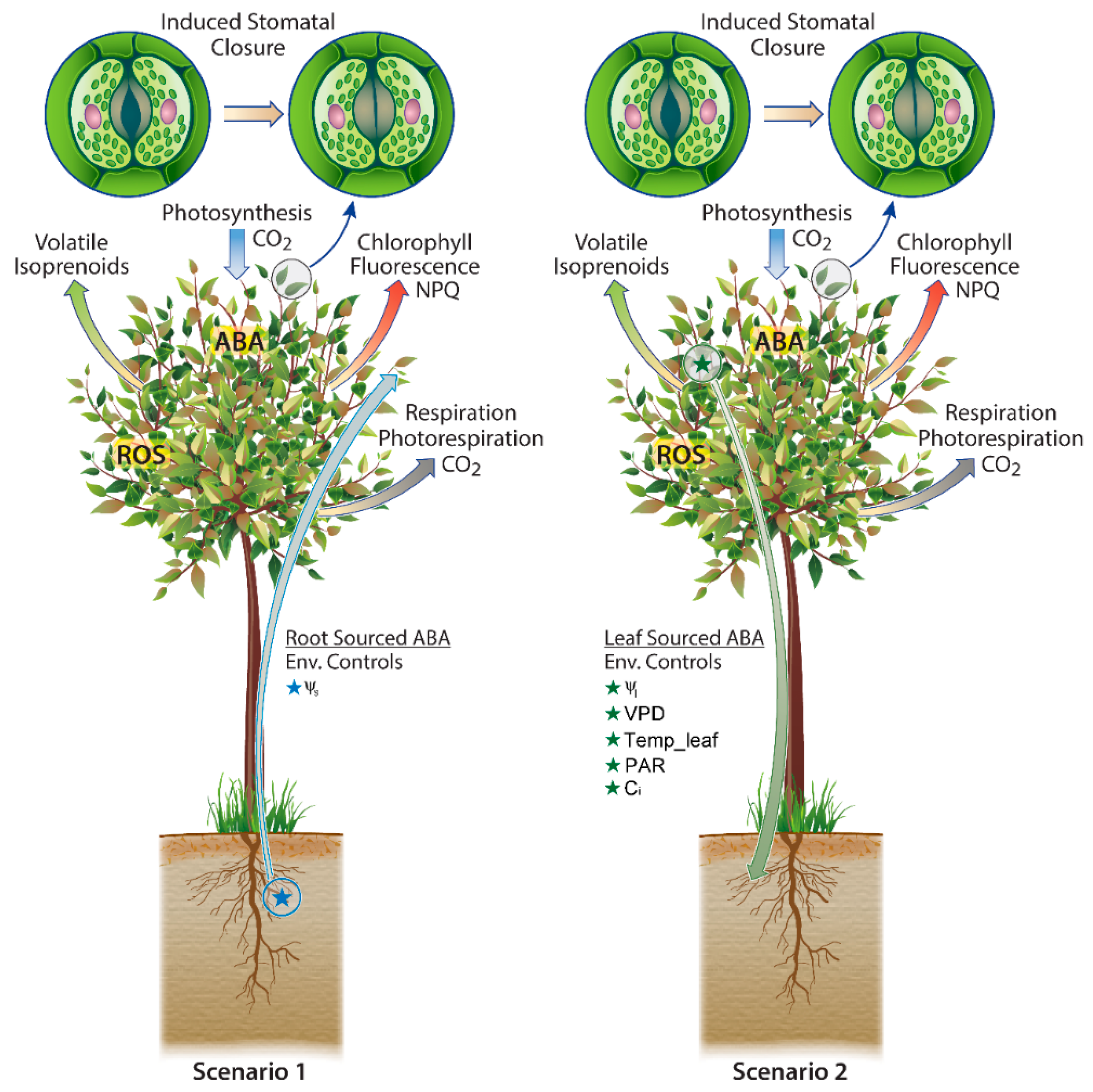
Aba is commonly known as the “stress hormone” that responds to variety of environmental stresses including both biotic and abiotic stress ( zhang, 2014 ). Aba may be translocated from the sites of biosynthesis, such as roots and leaf vascular tissues, to the guard cells. Aba promotes root stem cell maintenance through abfs together with wox5, and maintains primary root growth by restricting the ethylene production through acs2/5. It is evident that aba is required in this process based on the phenotypes of mutants defective in aba biosynthesis or signal transduction. It exhibits inhibitive functions when it is accumulated in large amount under stress to help plant survival through inhibition of processes such as stomatal opening and plant size expansion.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Aba promotes root stem cell maintenance through abfs together with wox5, and maintains primary root growth by restricting the ethylene production through acs2/5. Abscisic acid (aba) is a plant hormone that is tightly associated with water availability. It is synthesized partially in the chloroplasts and the biosynthesis primarily occurs in the leaves. Transport of abscisic acid (aba) in plants as influenced by journal of journal of experimental botany, vol. Aba regulates multiple developmental stages of plants.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Abscisic acid (aba) is an important phytohormone regulating plant growth, development, and stress responses. Abscisic acid (aba) is a plant hormone that is tightly associated with water availability. Abscisic acid (aba) functions in different stages during plant growth. Abscisic acid (aba) is a plant hormone that regulates numerous aspects of plant growth, development, and stress responses. Aba is a naturally occurring compound in plants.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Plants have to adjust aba levels constantly in responce to changing physiological and environmental conditions. Aba and metabolites and stomatal apertures sizes in bean leaves. Out of five characteristic phytohormones, one is aba which helps in controlling many development and growth characteristics of plants such as leaf abscission, inhibition of fruit ripening, etc. Aba controls plants’ stress response at. Aba regulates multiple developmental stages of plants.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title aba in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






