Your Active transport in plants images are ready in this website. Active transport in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Active transport in plants files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re searching for active transport in plants images information linked to the active transport in plants topic, you have visit the right blog. Our site always provides you with suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Active Transport In Plants. The uptake of minerals can be passive or active and occurs by diffusion or active transport respectively; Complex sugar, ions, large cells, proteins and other particles are transported in this process. There are two types of active transport: © 2016 paul billiet odws phloem made of living cells (sieve tubes and their companion cells) uses active transport to load the phloem.
 PPT Transport in Plants Chapter 36 PowerPoint From slideserve.com
PPT Transport in Plants Chapter 36 PowerPoint From slideserve.com
Two examples of active transport include the root hair cells in plants taking in mineral ions and humans taking in glucose through their intestines. Physical conditions such as oxygen concentration and temperature influence the rate of active transport and there are further evidences from biochemical studies to show that active transport is linked with energy production. Water leaves the xylem and passes to the mesopyll cells by osmosis. Both membranes are selectively permeable. Hence different proteins in the membrane play a major role in both active as well as passive transport. Water evaporates from the surface of the mesophyll cells, to form water vapour, into the air spaces.
Once sugar is unloaded at the sink cells, the ψs increases, causing water to diffuse by osmosis from the phloem back into the xylem.
The energy for active transport comes from atp generated by. Active transport is the net movement of particles against a concentration gradient. Diffusion and active transport are two methods of transporting molecules across the cell membrane. Xylem made of dead cells (xylem vessels) uses physical mechanisms to transport the fluid (the transpiration flow) transports water and mineral salts only from the root to the leaves www.skidmore.edu/academics/biology/plant_bio/. Active transport is the process by which cells expend energy to move atoms or molecules across membranes, requiring the presence of a protein carrier, which is activated by atp. Complex sugar, ions, large cells, proteins and other particles are transported in this process.
 Source: driverlayer.com
Source: driverlayer.com
So, what does this mean? In the cases where energy (such as atp) is required for this process, active transport takes place. Active transport, in which a specific molecule is transported from low concentration to high concentration, that is, against its concentration gradient. Plants taking up nutrients from the soil, endocytosis, exocytosis, sodium/potassium pump, and secretion of a substance into the blood stream are the examples of active transport. The term water potential is defined as “the measure of potential energy in water and.
 Source: quia.com
Source: quia.com
Plants use water potential to transport water to leaves and this helps in carrying out photosynthesis. Xylem made of dead cells (xylem vessels) uses physical mechanisms to transport the fluid (the transpiration flow) transports water and mineral salts only from the root to the leaves www.skidmore.edu/academics/biology/plant_bio/. So, what does this mean? Diffusion is a passive process, but. Active transport requires cellular energy to achieve this movement.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Special proteins within the cell membrane act as specific protein ‘carriers’. Active transport is a mode of transportation in plants, which uses stored energy to move the particles against the concentration gradient. Diffusion and active transport are two methods of transporting molecules across the cell membrane. In a plant cell, it takes place in the root cells by absorbing water and minerals. Hence different proteins in the membrane play a major role in both active as well as passive transport.
Source: researchgate.net
Once sugar is unloaded at the sink cells, the ψs increases, causing water to diffuse by osmosis from the phloem back into the xylem. Two membranes separate these compartments tonoplast around central vacuole and plasmolemma around protoplast and is attached to cell wall. Active transport is the net movement of particles against a concentration gradient. Diffusion is a passive process, but. From low concentration to high concentration.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
So, what does this mean? This movement of water out of the phloem causes. In cellular biology, active transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient. Active transport in plants for plants to take up mineral ions, ions are moved into root hairs, where they are in a higher concentration than in the dilute solutions in the soil. Special proteins within the cell membrane act as specific protein ‘carriers’.
 Source: discover.hubpages.com
Source: discover.hubpages.com
There are two types of active transport: There are two types of active transport: Both membranes are selectively permeable. Water leaves the xylem and passes to the mesopyll cells by osmosis. Physical conditions such as oxygen concentration and temperature influence the rate of active transport and there are further evidences from biochemical studies to show that active transport is linked with energy production.
 Source: thescienceteacher.co.uk
Source: thescienceteacher.co.uk
Countertransport is active transport that. Water leaves the xylem and passes to the mesopyll cells by osmosis. Active transport can also occur in biological systems that is actively producing energy by respiration. Since they are living, they provide energy to carry out active transport. Plants taking up nutrients from the soil, endocytosis, exocytosis, sodium/potassium pump, and secretion of a substance into the blood stream are the examples of active transport.
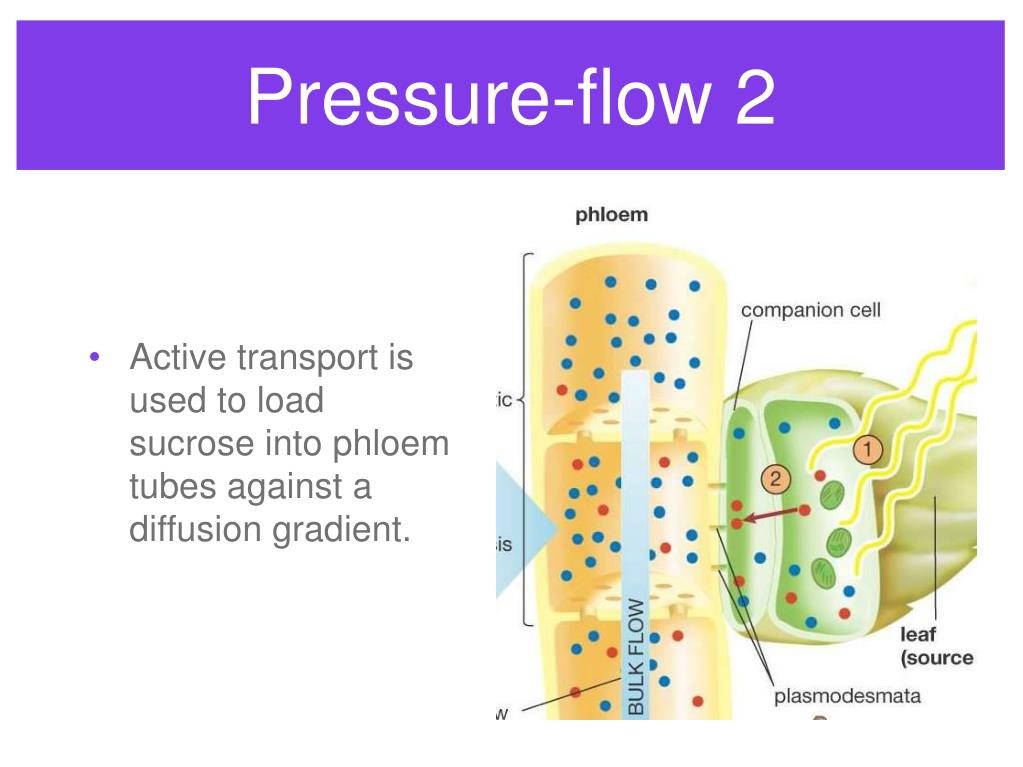 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Plants taking up nutrients from the soil, endocytosis, exocytosis, sodium/potassium pump, and secretion of a substance into the blood stream are the examples of active transport. The uptake of minerals can be passive or active and occurs by diffusion or active transport respectively; Diffusion and active transport are two methods of transporting molecules across the cell membrane. Both membranes are selectively permeable. Special proteins within the cell membrane act as specific protein ‘carriers’.
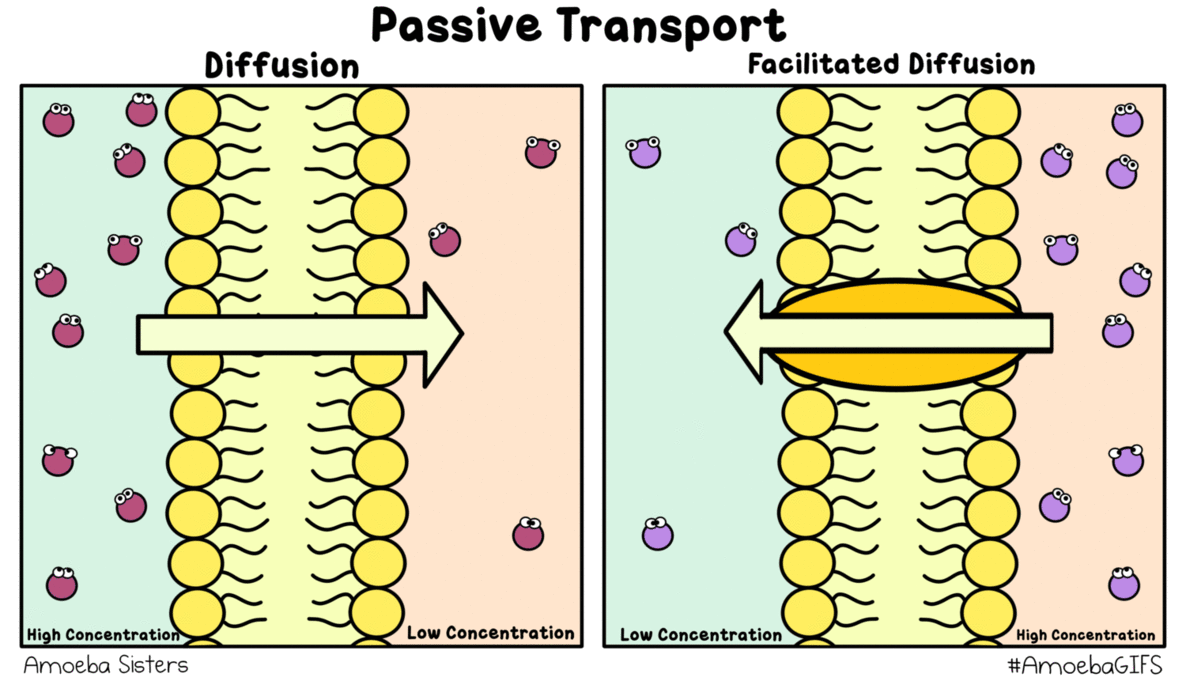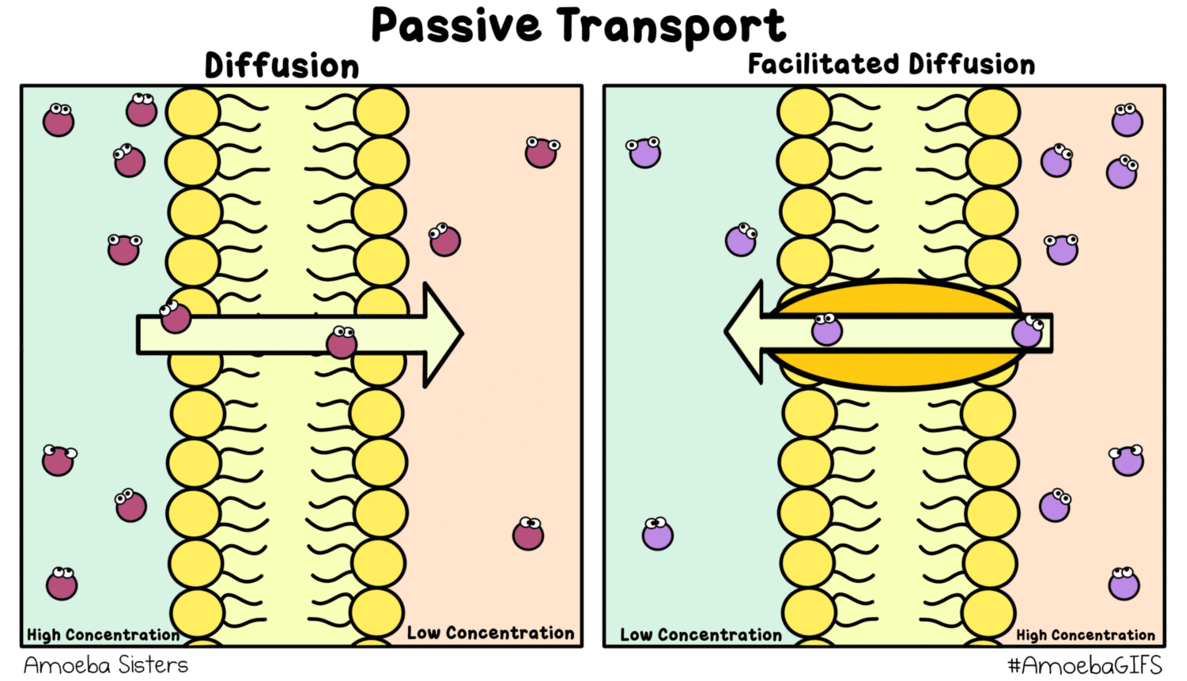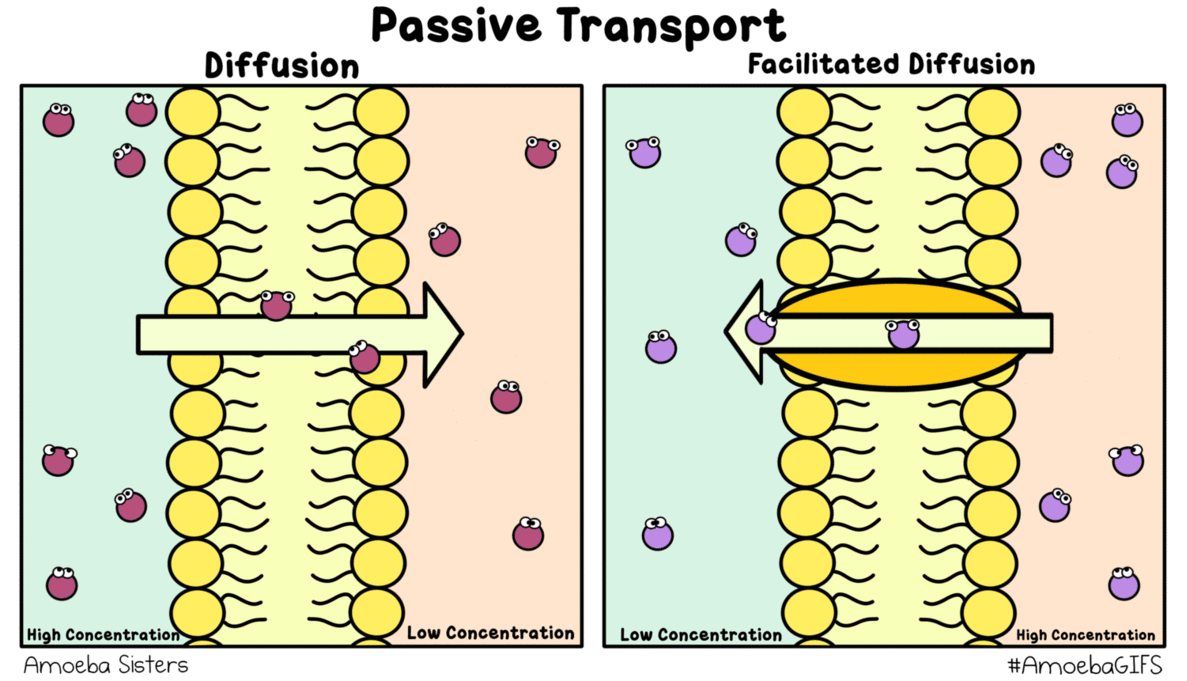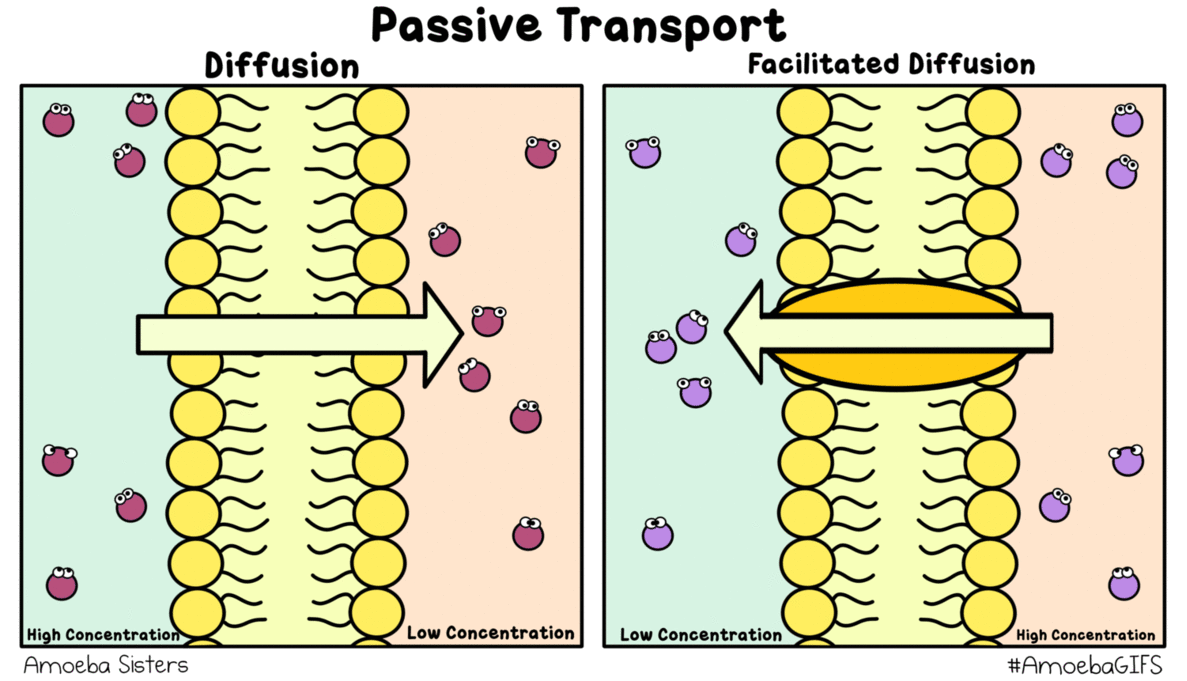 Source: amoebasisters.tumblr.com
Source: amoebasisters.tumblr.com
Primary active transport, also known as direct active transport, carries molecules across a membrane using metabolic energy. Active transport in animals in animals, glucose molecules have. Active transport is the process by which cells expend energy to move atoms or molecules across membranes, requiring the presence of a protein carrier, which is activated by atp. Active transport is a mode of transportation in plants, which uses stored energy to move the particles against the concentration gradient. This means that although the sap solution of the root hair cells is concentrated, yet it absorbs.
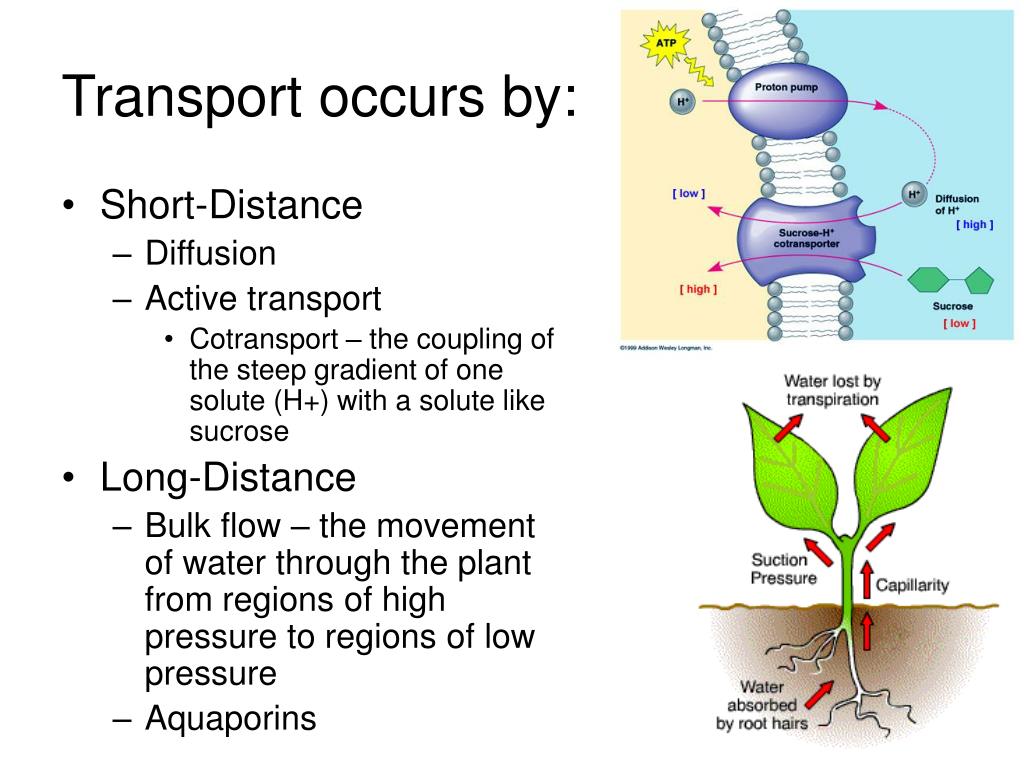 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Plants use water potential to transport water to leaves and this helps in carrying out photosynthesis. Active transport requires cellular energy to achieve this movement. Plants must take in a constant supply of water and dissolved minerals to compensate for the continuous loss of water via transpiration in the leaves, and so that they can photosynthesise and produce proteins Special proteins within the cell membrane act as specific protein ‘carriers’. Plants taking up nutrients from the soil, endocytosis, exocytosis, sodium/potassium pump, and secretion of a substance into the blood stream are the examples of active transport.
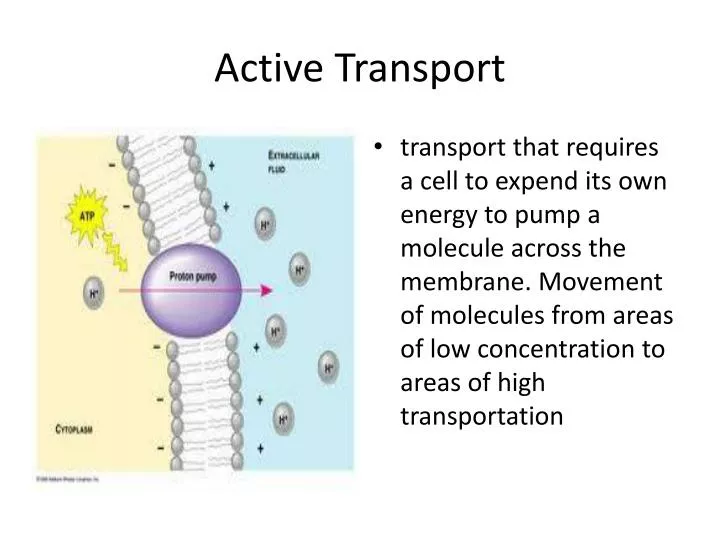 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Active transport is the net movement of particles against a concentration gradient. Ions moving from soil into plant roots Let me tell you that active transport is the movement of molecules from a region of lower concentration to a region of a higher concentration (against the concentration gradient). Water leaves the xylem and passes to the mesopyll cells by osmosis. The term water potential is defined as “the measure of potential energy in water and.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
9.2 transport in the phloem of plants: Active transport is a process that is required to move molecules against a concentration gradient.the process requires energy. These charged ions require ion pumps/channels to cross membranes and distribute throughout the. Primary active transport, also known as direct active transport, carries molecules across a membrane using metabolic energy. 9.2 transport in the phloem of plants:
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Primary active transport, also known as direct active transport, carries molecules across a membrane using metabolic energy. Active transport is a mode of transportation in plants, which uses stored energy to move the particles against the concentration gradient. Active transport in animals in animals, glucose molecules have. Water evaporates from the surface of the mesophyll cells, to form water vapour, into the air spaces. Hence different proteins in the membrane play a major role in both active as well as passive transport.
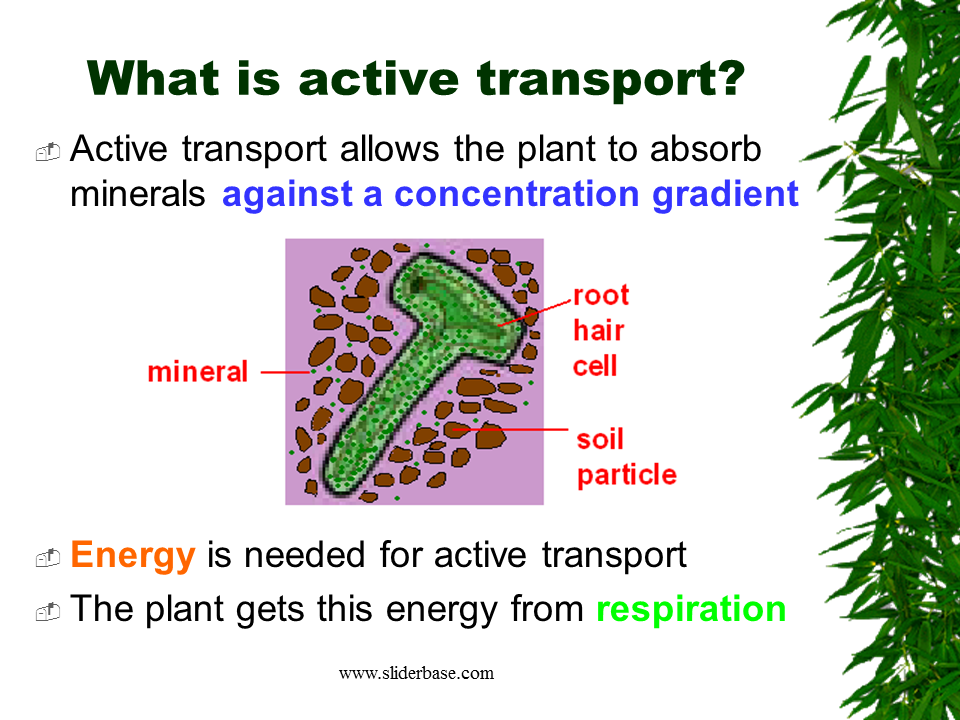
The term water potential is defined as “the measure of potential energy in water and. Water leaves the xylem and passes to the mesopyll cells by osmosis. This means that although the sap solution of the root hair cells is concentrated, yet it absorbs. So, what does this mean? Following figure shows the active transport in cell:
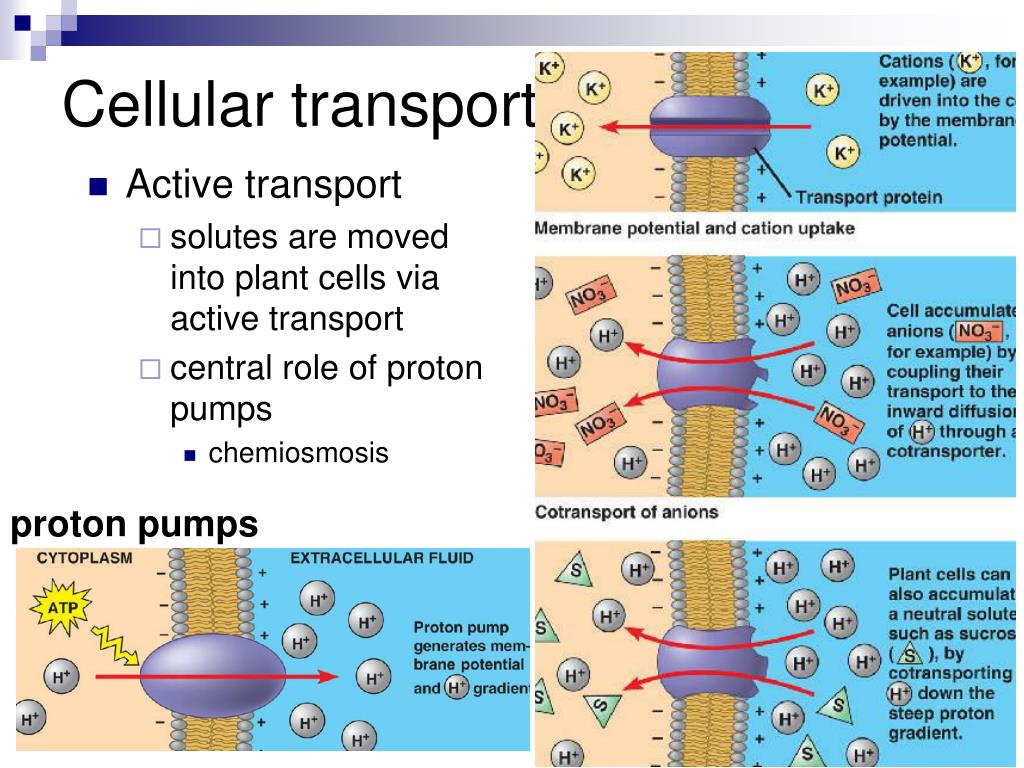 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Examples of such substances that are carried across the cell membrane by primary active transport include metal ions, are na +, k +, mg 2 +, and ca 2 +. The term water potential is defined as “the measure of potential energy in water and. Special proteins within the cell membrane act as specific protein ‘carriers’. Countertransport is active transport that. Active transport in the root hairs of plants allows plants to absorb mineral ions, which are necessary for healthy growth, even though the concentration of minerals is usually lower in the soil than in the root hair.
 Source: phys.org
Source: phys.org
Active transport then occurs across the root so that the plant takes in the ions it needs from the soil around it. Diffusion is a passive process, but. It is usually powered by atp. Active transport requires cellular energy to achieve this movement. Active transport in plants for plants to take up mineral ions, ions are moved into root hairs, where they are in a higher concentration than in the dilute solutions in the soil.
 Source: cronodon.com
Source: cronodon.com
These charged ions require ion pumps/channels to cross membranes and distribute throughout the. These charged ions require ion pumps/channels to cross membranes and distribute throughout the. From low concentration to high concentration. Cotransport is active transport that uses a carrier that must simultaneously transport two substances in the same direction. In cellular biology, active transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Active transport then occurs across the root so that the plant takes in the ions it needs from the soil around it. There are two types of active transport: Examples of such substances that are carried across the cell membrane by primary active transport include metal ions, are na +, k +, mg 2 +, and ca 2 +. Learn about diffusion and active transport in plants, osmosis and the role of the xylem and phloem. Water leaves the xylem and passes to the mesopyll cells by osmosis.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title active transport in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






