Your Amino acids in plants images are available. Amino acids in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Amino acids in plants files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re searching for amino acids in plants images information related to the amino acids in plants interest, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our website always provides you with suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more informative video content and images that match your interests.
Amino Acids In Plants. Recent studies showed that this statement needs a critical revision. 19, supplement 2, 2019 pp. Amino acids have various prominent functions in plants. Besides their usage during protein biosynthesis, they also represent building blocks for several other biosynthesis pathways and play pivotal roles during signaling processes as well as in.
 Amino Acids and Their Derivatives in Higher Plants by R.M From ebay.com
Amino Acids and Their Derivatives in Higher Plants by R.M From ebay.com
Amino acids are vital building blocks for synthesizing proteins in all organisms. Amino acids have various prominent functions in plants. Some amino acids act as signaling molecules that, during periods of abiotic stress, initiate and activate downstream metabolic pathways that help the plant develop plant defense mechanism in order to ward off or minimize the damage of an external stress point. Amino acids also function as biostimulants for plants. 19, supplement 2, 2019 pp. Accordingly, the efforts to understand the routes and regulation of lys, met, and trp biosynthesis has boosted amino acid research in plants, since these three amino acids are often contained in limiting amounts in staple crops.
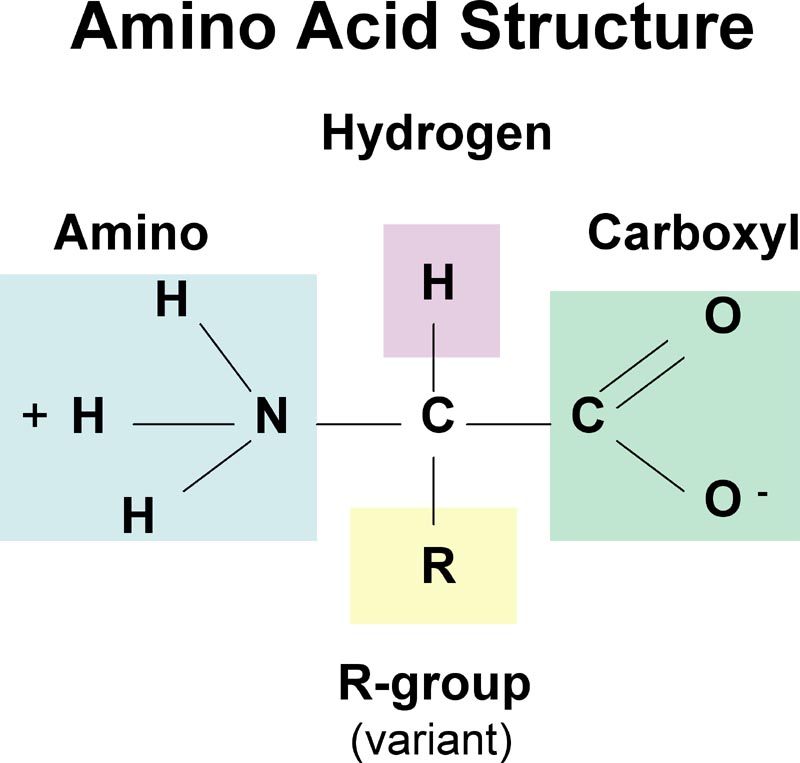
After all, amino acids are primary building blocks in cell machinery.
The process is completely natural and simulates protein hydrolysation, the method living plants use to create amino acids. 19, supplement 2, 2019 pp. The transporters from yeast and plants are related and can be grouped into two large superfamilies. The source of complete eaas are both animal. These functions combined with the ability to be approved for organic use, makes sustainably produced amino acids a smart choice for growers. As a biostimulant, amino acids can play important roles in enhancing plant productivity, especially under abiotic and biotic stress conditions.
 Source: hamanol.com
Source: hamanol.com
Amino acids are promoters and catalysts for the synthesis of various enzymes in plants and play an important role in plant metabolism. Other amino acids have been shown as precursor molecules leading to the development of internally. Amino acids have various prominent functions in plants. Fruits rich in amino acids are apples, banana, berries, figs, grapes, melons, oranges, papaya, pineapple, and pomegranates. Amino acids are organic molecules that are part of proteins, playing a key role in most biological processes.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
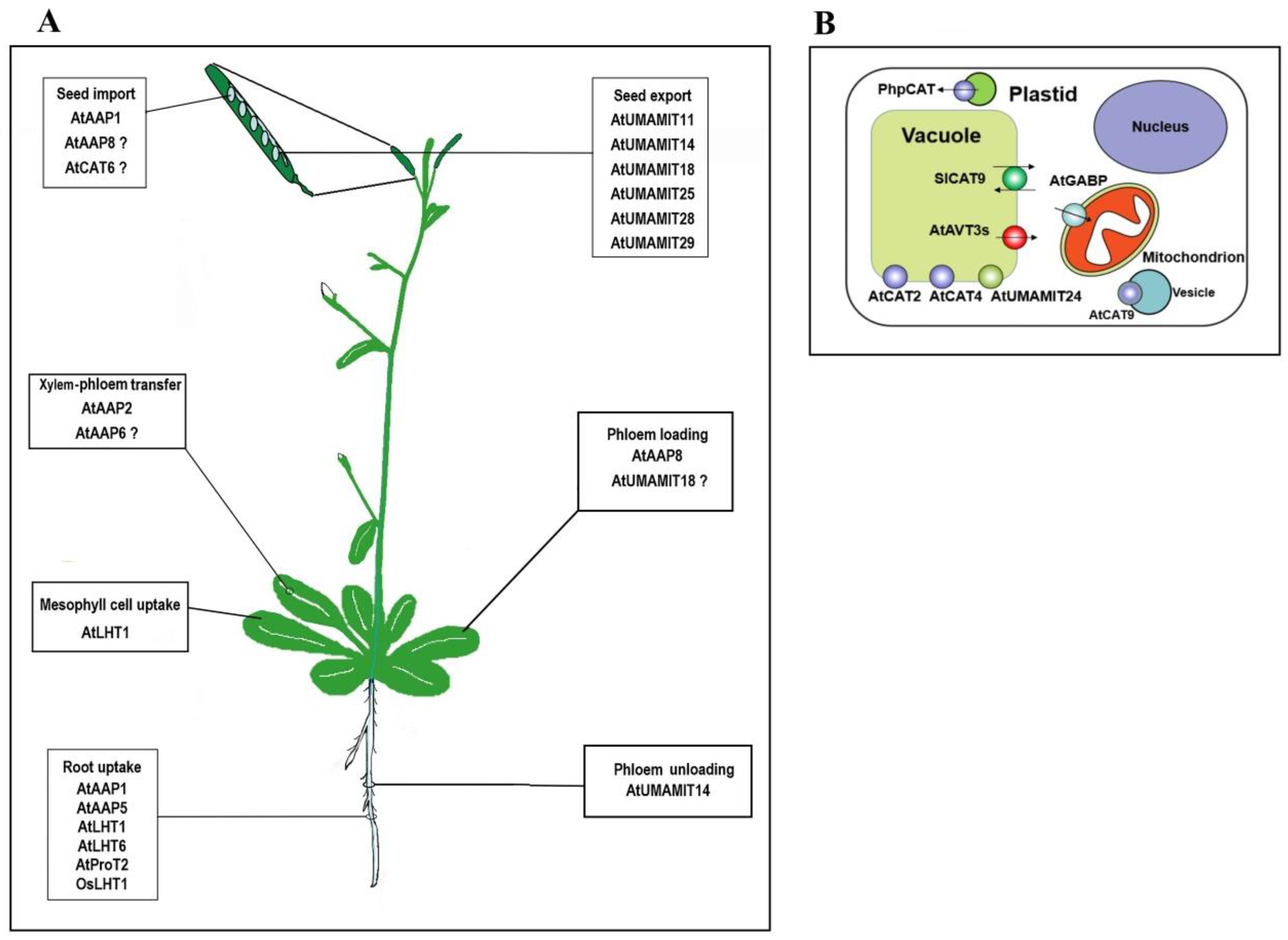
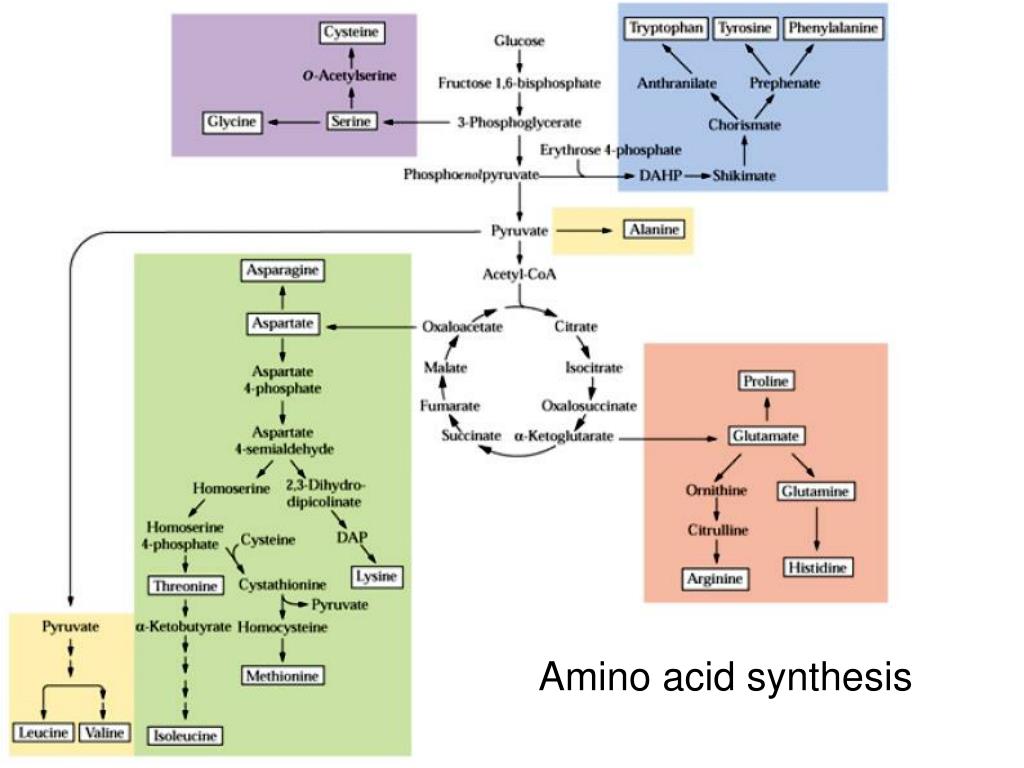
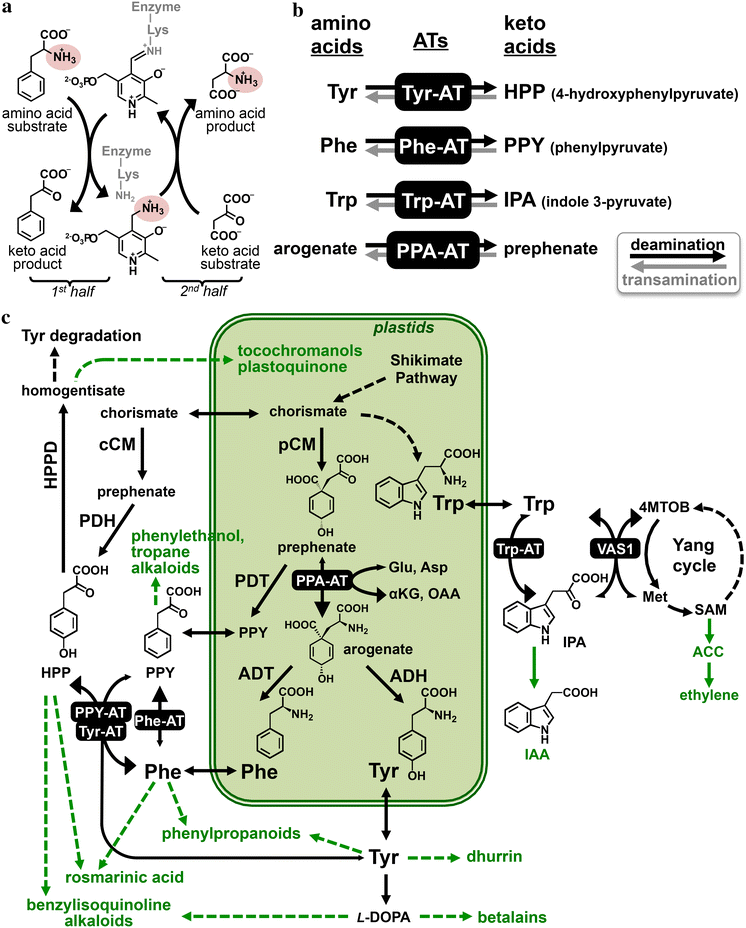
According to their respective precursors, the amino acids are grouped into five families derived from glutamate, serine, pyruvate, aspartate, or chorismate. After all, amino acids are primary building blocks in cell machinery. Novel methods that can detect metabolite export with higher throughput might help the discovery of amino acid exporters in plants (okumoto et al., 2008). 19, supplement 2, 2019 pp. Once inside the plant, the mineral or metal (e.g.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Our amino acid products are derived from an exclusive enzymatic hydrolysis procedure driven by processes used in the latest biotechnology. What essential amino acids are missing from plant based protein? Plant proteins are typically lacking in lycine, tryptophan, methionine, and isoleucine. Let’s look a bit deeper into. Seeds and fruits often represent the harvestable portion of plants.
 Source: gardenandgreenhouse.net
Source: gardenandgreenhouse.net
Recent studies showed that this statement needs a critical revision. Besides their usage during protein biosynthesis, they also represent building blocks for several other biosynthesis pathways and play pivotal roles during signaling processes as well as in. Amino acids are promoters and catalysts for the synthesis of various enzymes in plants and play an important role in plant metabolism. Novel methods that can detect metabolite export with higher throughput might help the discovery of amino acid exporters in plants (okumoto et al., 2008). Besides their usage during protein biosynthesis, they also represent building blocks for several other biosynthesis pathways and play pivotal roles during
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In case of humans there are 9 eaas: Novel methods that can detect metabolite export with higher throughput might help the discovery of amino acid exporters in plants (okumoto et al., 2008). Essential amino acids (eaas) are amino acids which are necessary to build proteins in an organism but can not be synthesized by the organism itself and as such must be provided in the diet. Amino acids have various prominent functions in plants. The most abundant amino acids in plants are glutamic acid and aspartic acid.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by humans and animals. Besides their usage during protein biosynthesis, they also represent building blocks for several other biosynthesis pathways and play pivotal roles during signaling processes as well as in plant stress response. Once inside the plant, the mineral or metal (e.g. Pearson�s correlation analysis among different amino acids showed that there were no negative correlations between the amino acids. These proteins, most of which are uncharacterized, are likely candidates of amino acid exporters in plants.
 Source: lifeextensionaustralia.com
Source: lifeextensionaustralia.com
The process is completely natural and simulates protein hydrolysation, the method living plants use to create amino acids. The carbon skeletons of amino acids are derived from different intermediates of the central carbon metabolism (boxed in blue). Seeds and fruits often represent the harvestable portion of plants. Novel methods that can detect metabolite export with higher throughput might help the discovery of amino acid exporters in plants (okumoto et al., 2008). Accordingly, the efforts to understand the routes and regulation of lys, met, and trp biosynthesis has boosted amino acid research in plants, since these three amino acids are often contained in limiting amounts in staple crops.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The transporters from yeast and plants are related and can be grouped into two large superfamilies. Besides their usage during protein biosynthesis, they also represent building blocks for several other biosynthesis pathways and play pivotal roles during Pearson�s correlation analysis among different amino acids showed that there were no negative correlations between the amino acids. The carbon skeletons of amino acids are derived from different intermediates of the central carbon metabolism (boxed in blue). Seeds and fruits often represent the harvestable portion of plants.
 Source: pt.slideshare.net
Source: pt.slideshare.net
Seeds and fruits often represent the harvestable portion of plants. As a biostimulant, amino acids can play important roles in enhancing plant productivity, especially under abiotic and biotic stress conditions. Amino acids are vital building blocks for synthesizing proteins in all organisms. Amino acids are promoters and catalysts for the synthesis of various enzymes in plants and play an important role in plant metabolism. Amino acids have various prominent functions in plants.

Pearson�s correlation analysis among different amino acids showed that there were no negative correlations between the amino acids. Calcium, zinc, manganese, magnesium, etc.) is released, and the leftover amino acids that formed the protective shell are either used by the plant directly as amino acids or further broken down. The level of these essential amino acids can vary between different plant protein sources. Amino acids have various prominent functions in plants. Unfortunately, since the biosynthesis of amino acids has received less attention in plants than in other organisms (the amides are a notable exception to this statement.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
19, supplement 2, 2019 pp. Amino acid transport has been well characterized in the yeast saccharomyces cerevisiae, and functional complementation has served as an excellent tool for identifying and characterizing amino acid transporters from plants. The amino acids in plants are synthesized from the nitrogen absorbed by the roots, through a process that involves a high energy expenditure. Our amino acid products are derived from an exclusive enzymatic hydrolysis procedure driven by processes used in the latest biotechnology. Whereas the plant can produce all the amino acids it requires, animals and many microorganisms must obtain several of the amino acids preformed, in their food or culture medium.
 Source: ebay.com
Source: ebay.com
Histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Amino acid transport has been well characterized in the yeast saccharomyces cerevisiae, and functional complementation has served as an excellent tool for identifying and characterizing amino acid transporters from plants. Calcium, zinc, manganese, magnesium, etc.) is released, and the leftover amino acids that formed the protective shell are either used by the plant directly as amino acids or further broken down. These functions combined with the ability to be approved for organic use, makes sustainably produced amino acids a smart choice for growers. Besides their usage during protein biosynthesis, they also represent building blocks for several other biosynthesis pathways and play pivotal roles during signaling processes as well as in plant stress response.
 Source: plantphysiol.org
Source: plantphysiol.org
Recent studies showed that this statement needs a critical revision. 19, supplement 2, 2019 pp. The source of complete eaas are both animal. These proteins, most of which are uncharacterized, are likely candidates of amino acid exporters in plants. The most abundant amino acids in plants are glutamic acid and aspartic acid.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Amino acid biosynthesis in plants. Amino acids have various prominent functions in plants. Besides their usage during protein biosynthesis, they also represent building blocks for several other biosynthesis pathways and play pivotal roles during The level of these essential amino acids can vary between different plant protein sources. After all, amino acids are primary building blocks in cell machinery.
 Source: carlagoldenwellness.com
Source: carlagoldenwellness.com
Amino acids have various prominent functions in plants. Besides their usage during protein biosynthesis, they also represent building blocks for several other biosynthesis pathways and play pivotal roles during However, amino acids are easily assimilated and decomposed by bacteria in the soil, so. In case of humans there are 9 eaas: Seeds and fruits often represent the harvestable portion of plants.
 Source: plantphysiol.org
Source: plantphysiol.org
Besides their usage during protein biosynthesis, they also represent building blocks for several other biosynthesis pathways and play pivotal roles during signaling processes as well as in. Whereas the plant can produce all the amino acids it requires, animals and many microorganisms must obtain several of the amino acids preformed, in their food or culture medium. Novel methods that can detect metabolite export with higher throughput might help the discovery of amino acid exporters in plants (okumoto et al., 2008). These functions combined with the ability to be approved for organic use, makes sustainably produced amino acids a smart choice for growers. The source of complete eaas are both animal.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
Seeds and fruits often represent the harvestable portion of plants. As a biostimulant, amino acids can play important roles in enhancing plant productivity, especially under abiotic and biotic stress conditions. Plant proteins are typically lacking in lycine, tryptophan, methionine, and isoleucine. The carbon skeletons of amino acids are derived from different intermediates of the central carbon metabolism (boxed in blue). The process is completely natural and simulates protein hydrolysation, the method living plants use to create amino acids.
 Source: growerssecret.com
Source: growerssecret.com
These proteins, most of which are uncharacterized, are likely candidates of amino acid exporters in plants. Whereas the plant can produce all the amino acids it requires, animals and many microorganisms must obtain several of the amino acids preformed, in their food or culture medium. Amino acids have various prominent functions in plants. The transporters from yeast and plants are related and can be grouped into two large superfamilies. Amino acids have various prominent functions in plants.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title amino acids in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






