Your Anaerobic respiration in plants images are available. Anaerobic respiration in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Anaerobic respiration in plants files here. Download all royalty-free images.
If you’re looking for anaerobic respiration in plants pictures information connected with to the anaerobic respiration in plants interest, you have visit the ideal site. Our site always gives you hints for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Anaerobic Respiration In Plants. Anaerobic respiration is a type of respiration where oxygen is not used as an oxidant and the organic food is broken down incompletely to liberate energy without oxygen being used as an oxidant. Some organisms can respire in the absence of oxygen. This occurs in microorganisms, but is also a temporary response to oxygen. Sometimes animal and plant cells cannot get enough oxygen to carry out aerobic respiration.
Respiration in Plants Types of Respiration Aerobic and From vedantu.com
The conversion of pyruvate into lactic acid (animals) or ethanol and co 2 (plants / yeasts) is reversible. The process of respiration in plants. It is most common in higher organisms (both plants and animals). Anaerobic respiration in plants produces ethanol (c_2h_5oh) whose accumulation may kill the plant, whereas in animals anaerobic respiration produces lactic acid (ch_3ch(oh)cooh) that however cannot cause death of animal but lead to minor muscle. So they cannot use aerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration which is carried out in the lungs of humans, animals are called pulmonary respiration.
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm, therefore plants do experience anaerobic respiration.
The animals and plants that can exist and gain energy even in the lack of oxygen are called anaerobic. In the absence of oxygen, the glucose derived from food is broken down into alcohol and carbon dioxide along with the production of energy. Anaerobic respiration is mainly seen in unicellular organisms like bacteria, fungi, protozoa, etc. Anaerobic respiration is a type of respiration where oxygen is not used as an oxidant and the organic food is broken down incompletely to liberate energy without oxygen being used as an oxidant. Can only synthesise atp in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm, therefore plants do experience anaerobic respiration.
 Source: bankofbiology.com
Source: bankofbiology.com
This is in contrast to the highly efficient process of aerobic respiration , which relies on oxygen to produce energy. So they use an emergency system of reactions, that is anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration in plants and yeast anaerobic respiration also happens in plant cells and some microorganisms. Hence, each part nourishes and fulfils its own energy requirements. 3c pyruvate is then converted into ethanol + carbon dioxide through fermentation.
 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
This process is also called intramolecular respiration. Can only synthesise atp in the presence of oxygen. Beside this other organic matter such as citric acid, oxalic acid, lactic acid, etc are also produced. Anaerobic respiration is respiration without oxygen and this is universal for all pathways. Which is an example of anaerobic respiration in plants?
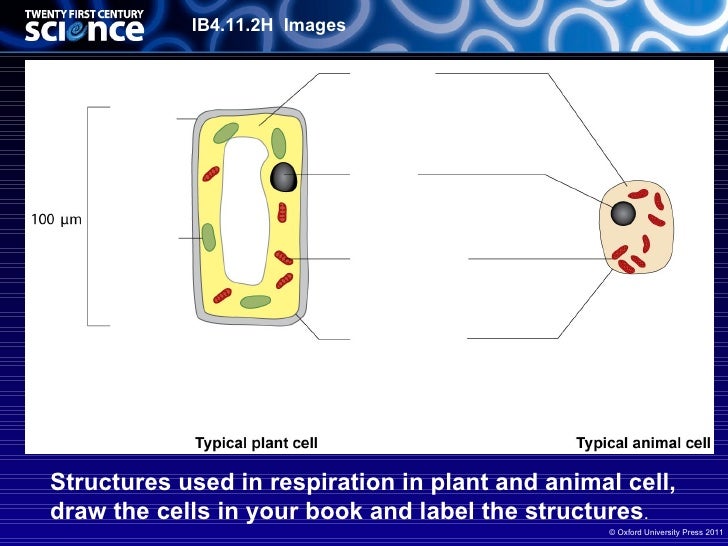 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
This occurs in microorganisms, but is also a temporary response to oxygen. It uses oxygen for breaking the respiratory material into simple substances. Anaerobic respiration in plants and animals is a process where respiration takes place in the absence of molecular oxygen. Some individual cells in obligate anaerobes can be classed as facultative anaerobes, but this is only temporarily as it produces compounds which need to be. Anaerobic respiration is the exclusive mode of respiration in some parasitic worms, many prokaryotes, several unicellular eukaryotes and moulds.
Source: vedantu.com
Respiration in cells can take place anaerobically (without oxygen), to transfer energy; Plants have a similar anaerobic respiration pathway to fungi such as yeast where they break. Aerobic respiration is the release of energy from the complete oxidation of glucose in the presence of oxygen e.g., plant cells, animal cells. Anaerobic respiration in plants and yeast anaerobic respiration also happens in plant cells and some microorganisms. The process of respiration in plants.

This process is also called intramolecular respiration. Beside this other organic matter such as citric acid, oxalic acid, lactic acid, etc are also produced. Anaerobic respiration in plants produces ethanol (c_2h_5oh) whose accumulation may kill the plant, whereas in animals anaerobic respiration produces lactic acid (ch_3ch(oh)cooh) that however cannot cause death of animal but lead to minor muscle. Takes place in complete absence of oxygen. Synthesise atp by aerobic respiration is possible, but can switch to anaerobic respiration is necessary.
 Source: studiousguy.com
Source: studiousguy.com
The respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen is known as anaerobic respiration. Table 12.1 differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. C 6 h 1 2 o 6 + 6 o 2 → 6 c o 2 + 6 h 2 o + e n e r. This process is called fermentation or anaerobic respiration (figure 14.12). Some organisms can respire in the absence of oxygen.
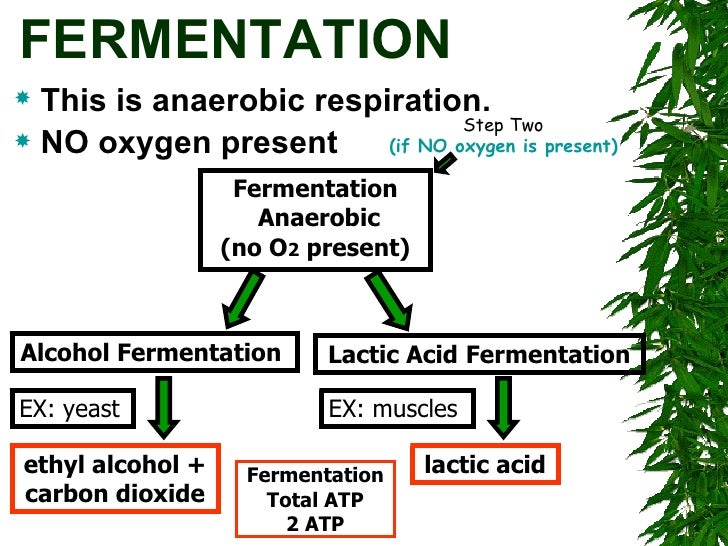 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The anaerobic respiration occurs in organisms like yeast, certain bacteria, and parasitic worms. C 6 h 1 2 o 6 + 6 o 2 → 6 c o 2 + 6 h 2 o + e n e r. Synthesise atp by aerobic respiration is possible, but can switch to anaerobic respiration is necessary. They convert glucose into 3c (3 carbon) pyruvate through glycolysis. Anaerobic respiration is a type of respiration where oxygen is not used as an oxidant and the organic food is broken down incompletely to liberate energy without oxygen being used as an oxidant.
 Source: learncbse.in
Source: learncbse.in
Hence, each part nourishes and fulfils its own energy requirements. C 6 h 1 2 o 6 + 6 o 2 → 6 c o 2 + 6 h 2 o + e n e r. Anaerobic respiration in mammals, plants & fungi in a snap! Anaerobic respiration is a type of respiration where oxygen is not used as an oxidant and the organic food is broken down incompletely to liberate energy without oxygen being used as an oxidant. This is represented by the following overall reaction.
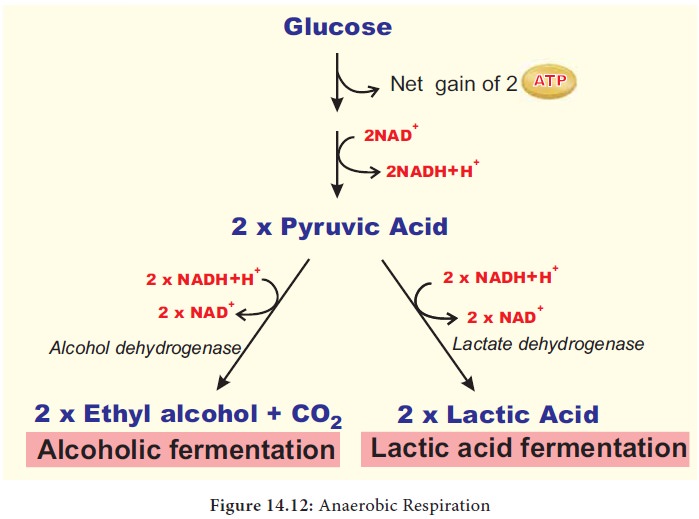 Source: brainkart.com
Source: brainkart.com
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm, therefore plants do experience anaerobic respiration. Synthesise atp by aerobic respiration is possible, but can switch to anaerobic respiration is necessary. Sometimes animal and plant cells cannot get enough oxygen to carry out aerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration is the type of respiration through which cells can break down sugars to generate energy in the absence of oxygen. Energy is liberated during the breaking of bonds between various types of atoms.
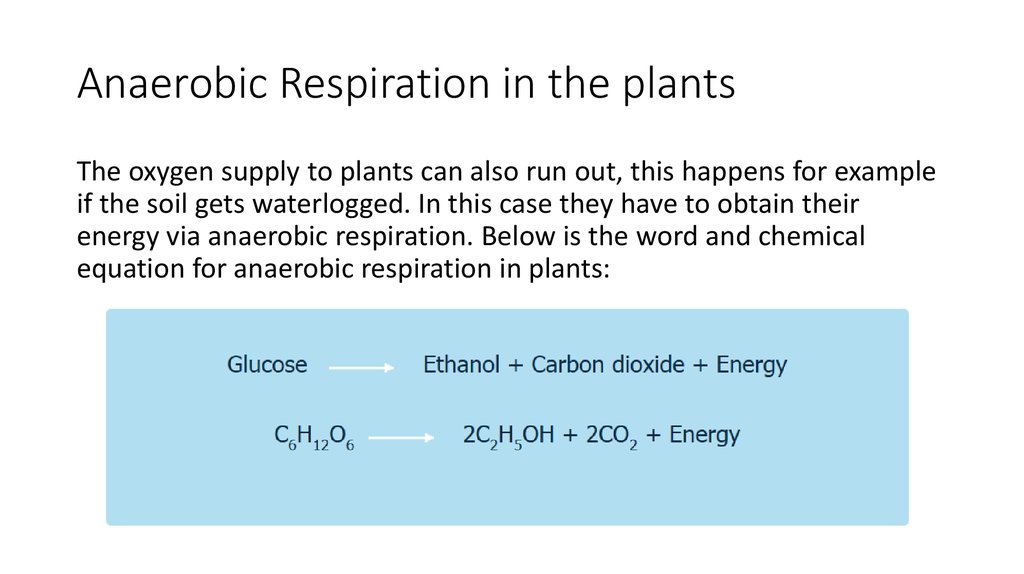 Source: ppt-online.org
Source: ppt-online.org
Energy is liberated during the breaking of bonds between various types of atoms. Plants have a similar anaerobic respiration pathway to fungi such as yeast where they break. Can only synthesise atp in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm, therefore plants do experience anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration in plants and yeast anaerobic respiration also happens in plant cells and some microorganisms.
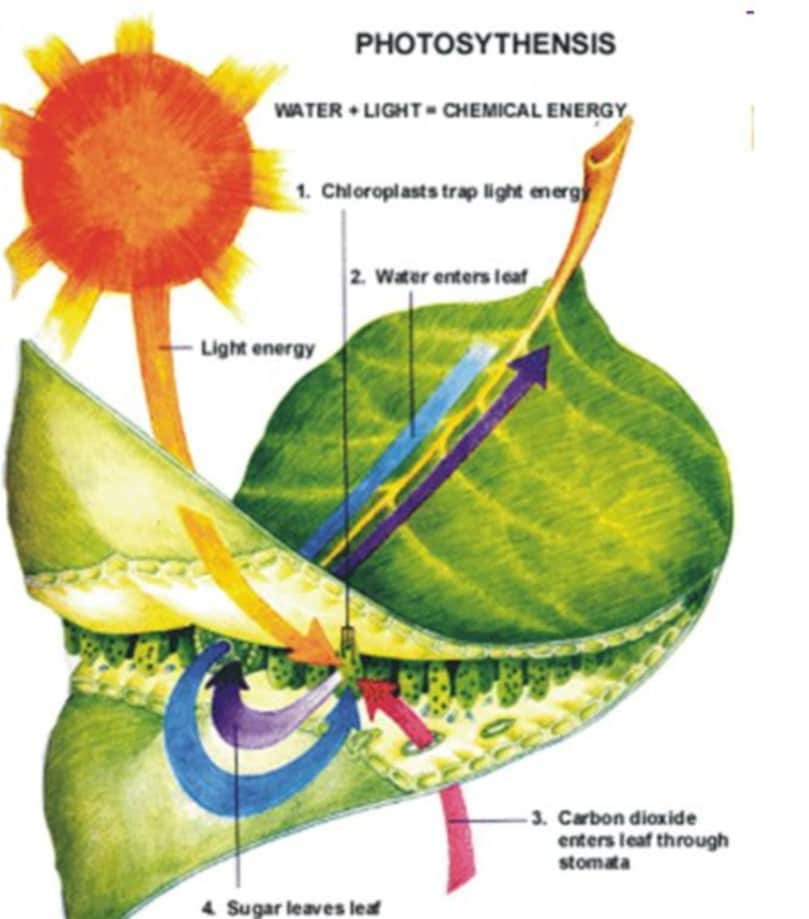 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
Anaerobic respiration in plants and yeast anaerobic respiration also happens in plant cells and some microorganisms. So they use an emergency system of reactions, that is anaerobic respiration. They convert glucose into 3c (3 carbon) pyruvate through glycolysis. Takes place in complete absence of oxygen. It uses oxygen for breaking the respiratory material into simple substances.
 Source: fabiosouza-show.blogspot.com
Source: fabiosouza-show.blogspot.com
This process is also called intramolecular respiration. The process of respiration in plants. Anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm, therefore plants do experience anaerobic respiration. In the absence of oxygen, the glucose derived from food is broken down into alcohol and carbon dioxide along with the production of energy. Plants have a similar anaerobic respiration pathway to fungi such as yeast where they break.
 Source: doubtnut.com
Source: doubtnut.com
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm, therefore plants do experience anaerobic respiration. The respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen is known as anaerobic respiration. In animals when you sprint for a bus, your muscles use so much oxygen that you cannot supply it in time. This occurs in microorganisms, but is also a temporary response to oxygen. By restoring stocks of nad+ via anaerobic pathways, the organism can continue to produce atp via glycolysis.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm, therefore plants do experience anaerobic respiration. Leads to complete oxidation of organic substrate. Table 12.1 differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Energy is liberated during the breaking of bonds between various types of atoms. Aerobic respiration which is carried out in the lungs of humans, animals are called pulmonary respiration.
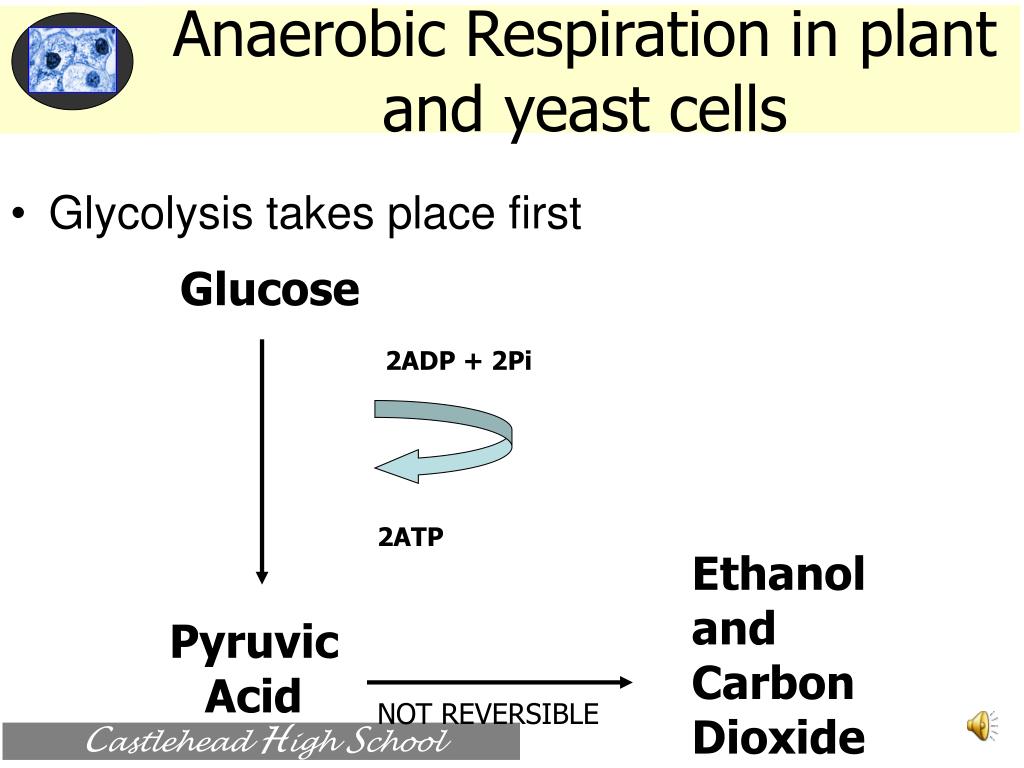 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Takes place in complete absence of oxygen. The upcoming discussion will update you about the differences between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration in plants. Anaerobic respiration is a type of respiration where oxygen is not used as an oxidant and the organic food is broken down incompletely to liberate energy without oxygen being used as an oxidant. Anaerobic respiration usually occurs in lower plants and microorganisms. The process of respiration in plants.
 Source: askiitians.com
Source: askiitians.com
The animals and plants that can exist and gain energy even in the lack of oxygen are called anaerobic. Some individual cells in obligate anaerobes can be classed as facultative anaerobes, but this is only temporarily as it produces compounds which need to be. The animals and plants that can exist and gain energy even in the lack of oxygen are called anaerobic. But they still need to obtain energy to stay alive. Table 12.1 differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
They convert glucose into 3c (3 carbon) pyruvate through glycolysis. In animals when you sprint for a bus, your muscles use so much oxygen that you cannot supply it in time. The upcoming discussion will update you about the differences between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration in plants. Anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm, therefore plants do experience anaerobic respiration. This process is also called intramolecular respiration.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The animals and plants that can exist and gain energy even in the lack of oxygen are called anaerobic. The conversion of pyruvate into lactic acid (animals) or ethanol and co 2 (plants / yeasts) is reversible. The animals and plants that can exist and gain energy even in the lack of oxygen are called anaerobic. This process is also called intramolecular respiration. These include plants that grow in marshes, where oxygen concentrations will be low.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title anaerobic respiration in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






