Your Ascorbic acid for plants images are ready. Ascorbic acid for plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Ascorbic acid for plants files here. Find and Download all royalty-free images.
If you’re looking for ascorbic acid for plants images information connected with to the ascorbic acid for plants interest, you have come to the ideal blog. Our website frequently provides you with suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
Ascorbic Acid For Plants. Ascorbic acid (vitamin c) is an abundant component of plants. In agriculture and animal fodder. The description in 1996 of an mutant deficient in. Ascorbic acid (vitamin c) is an abundant component of plants.
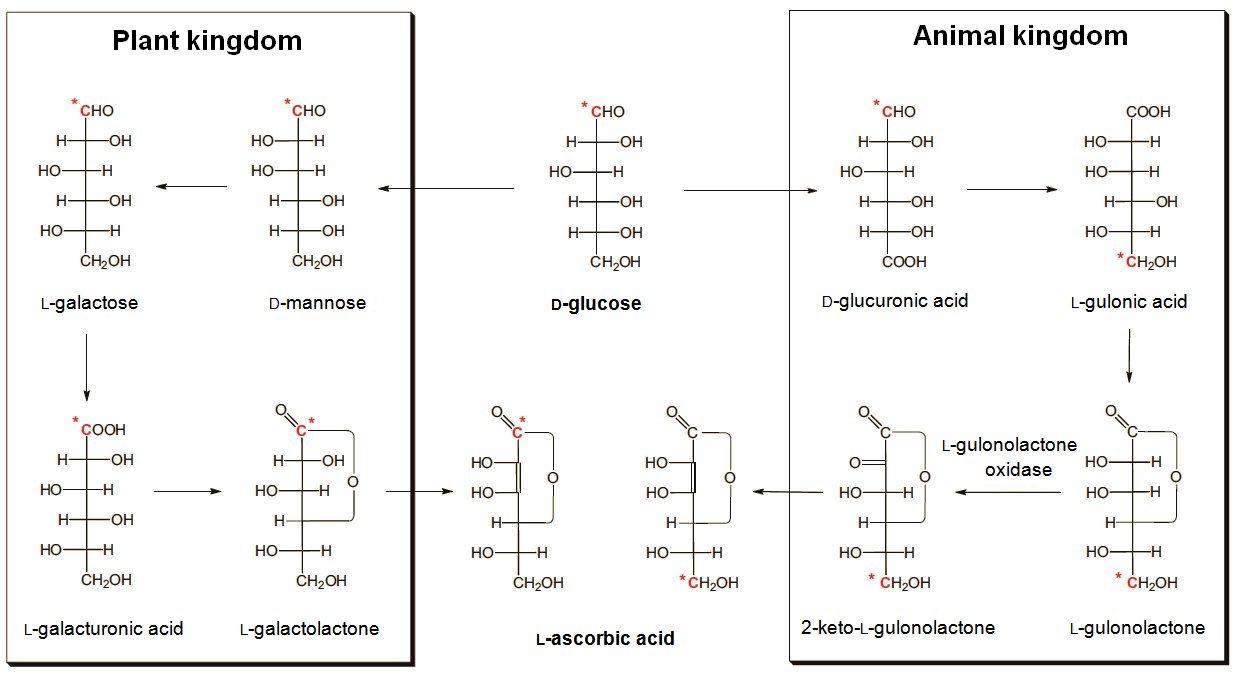 Vitamin C Deficiency Part 4 ChemViews Magazine From chemistryviews.org
Vitamin C Deficiency Part 4 ChemViews Magazine From chemistryviews.org
All plants synthesize ascorbic acid. In higher plants, asa functions as an antioxidant and enzymatic cofactor, playing a crucial role in multiple physiological processes including photoprotection, cell expansion and division, ethylene biosynthesis and abiotic stress. The second group are divided into ascorbic acid group, where the plants roots are presubjected to 0.5 mm asa and let to grow at room temperature, and ascorbic acid with chilling group, where the plants are presubjected to 0.5 mm asa and were exposed to chilling stress (4 °c) for 7 h/day. Ascorbic acid is an antioxidant in plants which play important role in activation of many physiological and defense mechanisms. It became clear from radioisotopic labeling studies in the 1950s that plant ascorbic acid biosynthesis does not proceed in toto via a route similar to that in mammals. Ascorbic acid (vitamin c) is an abundant component of plants.
Since both aa and dha are relatively stable in
Ascorbic acid (asa), vitamin c, a crucial compound is present in most living organisms (laing et al., 2015). It became clear from radioisotopic labeling studies in the 1950s that plant ascorbic acid biosynthesis does not proceed in toto via a route similar to that in mammals. Among a variety of chemical methods, an effective chemical method for chlorination in water treatment plants is the use of ascorbic acid. Considerable evidence has been accruing in the last two decades. Ascorbic acid regulates cell division and growth and is involved in signal transduction. Ascorbic acid (vitamin c) is an abundant component of plants.
 Source: stemcell.com
Source: stemcell.com
Ascorbic acid functions as a major redox buffer and as a cofactor for enzymes involved in regulating photosynthesis, hormone biosynthesis, and regenerating other antioxidants. It reaches a concentration of over 20 m m in chloroplasts and occurs in all cell compartments, including the cell wall. It is also used to repair and maintain cartilage, bones, and teeth to heal wounds and create scar tissue. Recent studies on asa homeostasis have broadened our understanding of these physiological events. This compound stops the oxidation reactions in various food.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The effect of vitamin c on plants was studied with sterile plant cultures. Ascorbate acid (asa) is an important antioxidant in plants, playing important roles in various physiological processes. The second group are divided into ascorbic acid group, where the plants roots are presubjected to 0.5 mm asa and let to grow at room temperature, and ascorbic acid with chilling group, where the plants are presubjected to 0.5 mm asa and were exposed to chilling stress (4 °c) for 7 h/day. Ascorbic acid is an antioxidant in plants which play important role in activation of many physiological and defense mechanisms. In higher plants, asa functions as an antioxidant and enzymatic cofactor, playing a crucial role in multiple physiological processes including photoprotection, cell expansion and division, ethylene biosynthesis and abiotic stress.
 Source: uky.edu
Source: uky.edu
It reaches a concentration of over 20 mm in chloroplasts and occurs in all cell compartments, including the cell wall. It reaches a concentration of over 20 mm in chloroplasts and occurs in all cell compartments, including the cell wall. This compound stops the oxidation reactions in various food. It has other applications in photo development and in some specialized scientific applications. It reaches a concentration of over 20 m m in chloroplasts and occurs in all cell compartments, including the cell wall.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Since both aa and dha are relatively stable in Ascorbic acid is synthesised by eukaryotes, the known exceptions being primates and some other animal groups which have lost functional gulonolactone oxidase. The effect of vitamin c on plants was studied with sterile plant cultures. The level of ascorbic acid in plants is determinant of its tolerance against the adverse effect of oxidizing pollutants. In most plant tissues ascorbic acid is rapidly oxidized when the structure is disorganized as by homogenizing.
 Source: gulfsupplements.com
Source: gulfsupplements.com
In agriculture and animal fodder. In most plant tissues ascorbic acid is rapidly oxidized when the structure is disorganized as by homogenizing. Among a variety of chemical methods, an effective chemical method for chlorination in water treatment plants is the use of ascorbic acid. It reaches a concentration of over 20 m m in chloroplasts and occurs in all cell compartments, including the cell wall. It has other applications in photo development and in some specialized scientific applications.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
It is also used to repair and maintain cartilage, bones, and teeth to heal wounds and create scar tissue. Of crystalline ascorbic acid was added to the liquid medium. Considerable evidence has been accruing in the last two decades. Ascorbic acid (vitamin c) is an abundant component of plants. 40 mg of crystalline ascorbic acid was added to the liquid medium.
 Source: journal.frontiersin.org
Source: journal.frontiersin.org
In most plant tissues ascorbic acid is rapidly oxidized when the structure is disorganized as by homogenizing. Ascorbic acid in the food industry: It has proposed functions in photosynthesis as an enzyme cofactor (including synthesis of ethylene, gibberellins and anthocyanins) and in control of cell growth. In this article we will discuss about the tests for estimation of ascorbic acid in plants. It is also used to repair and maintain cartilage, bones, and teeth to heal wounds and create scar tissue.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The effect of vitamin c on plants was studied with sterile plant cultures. Ascorbic acid (asa) is considered one of the most important antioxidants in plant tissues, being highly abundant and exerting crucial roles in plant adaptation to unfavourable environments by contributing to a cellular redox state. It has proposed functions in photosynthesis as an enzyme cofactor (including synthesis of ethylene, gibberellins and anthocyanins) and in control of cell growth. Ascorbic acid is an antioxidant in plants which play important role in activation of many physiological and defense mechanisms. Ascorbic acid regulates cell division and growth and is involved in signal transduction.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In plants asa serves as a major redox buffer and regulates various physiological processes controlling growth, development, and stress tolerance. In agriculture and animal fodder. Of crystalline ascorbic acid was added to the liquid medium. It has proposed functions in photosynthesis as an enzyme cofactor (including synthesis of ethylene, gibberellins and anthocyanins) and in control of cell growth. Ascorbic acid (vitamin c) is an abundant component of plants.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Ascorbic acid (vitamin c) is an abundant component of plants. In agriculture and animal fodder. Ascorbic acid (asa), vitamin c, a crucial compound is present in most living organisms (laing et al., 2015). It has proposed functions in photosynthesis as an enzyme cofactor (including synthesis of ethylene, gibberellins and anthocyanins) and in control of cell growth. Recent studies on asa homeostasis have broadened our understanding of these physiological events.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In this article we will discuss about the tests for estimation of ascorbic acid in plants. Ascorbic acid regulates cell division and growth and is involved in signal transduction. The description in 1996 of an mutant deficient in. Ascorbic acid (vitamin c) is an abundant component of plants. It has proposed functions in photosynthesis as an enzyme cofactor (including synthesis of ethylene, gibberellins and anthocyanins) and in control of cell growth.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
It has proposed functions in photosynthesis as an enzyme cofactor (including synthesis of ethylene, gibberellins and anthocyanins) and in control of cell growth. Ascorbate acid (asa) is an important antioxidant in plants, playing important roles in various physiological processes. In contrast to the single pathway responsible for ascorbic acid biosynthesis in animals, plants use multiple pathways to synthesize ascorbic acid, perhaps reflecting the. Ascorbic acid regulates cell division and growth and is involved in signal transduction. The description in 1996 of an mutant deficient in.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Ascorbic acid regulates cell division and growth and is involved in signal transduction. In agriculture and animal fodder. In contrast to the single pathway responsible for ascorbic acid biosynthesis in animals, plants use multiple pathways to synthesize ascorbic acid, perhaps reflecting the. It is also used to repair and maintain cartilage, bones, and teeth to heal wounds and create scar tissue. In higher plants, asa functions as an antioxidant and enzymatic cofactor, playing a crucial role in multiple physiological processes including photoprotection, cell expansion and division, ethylene biosynthesis and abiotic stress.
 Source: chemistryviews.org
Source: chemistryviews.org
Ascorbic acid is found in plants and food, including citrus fruits, tomatoes and green vegetables. Ascorbic acid functions as a cofactor for enzymes involved in photosynthesis, synthesis of plant hormones, as an antioxidant and also regenerator of other antioxidants. This compound stops the oxidation reactions in various food. The level of ascorbic acid in plants is determinant of its tolerance against the adverse effect of oxidizing pollutants. The effect of vitamin c on plants was studied with sterile plant cultures.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
It has other applications in photo development and in some specialized scientific applications. Ascorbic acid (asa), vitamin c, a crucial compound is present in most living organisms (laing et al., 2015). Ascorbate acid (asa) is an important antioxidant in plants, playing important roles in various physiological processes. Among a variety of chemical methods, an effective chemical method for chlorination in water treatment plants is the use of ascorbic acid. In agriculture and animal fodder.
 Source: probasicsnutrition.com
Source: probasicsnutrition.com
It reaches a concentration of over 20 mm in chloroplasts and occurs in all cell compartments, including the cell wall. Among a variety of chemical methods, an effective chemical method for chlorination in water treatment plants is the use of ascorbic acid. Since both aa and dha are relatively stable in The effect of vitamin c on plants was studied with sterile plant cultures. Ascorbic acid is an antioxidant in plants which play important role in activation of many physiological and defense mechanisms.
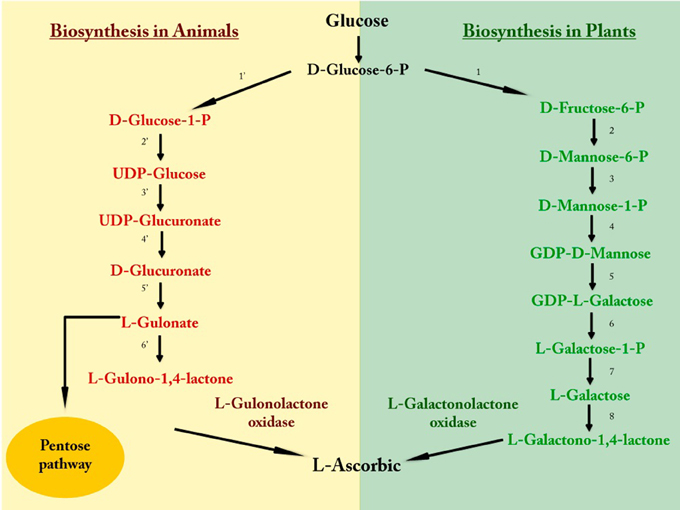 Source: onlinebiologynotes.com
Source: onlinebiologynotes.com
It has other applications in photo development and in some specialized scientific applications. It has proposed functions in photosynthesis as an enzyme cofactor (including synthesis of ethylene, gibberellins and anthocyanins) and in control of cell growth. Recent studies on asa homeostasis have broadened our understanding of these physiological events. The effect of vitamin c on plants was studied with sterile plant cultures. The second group are divided into ascorbic acid group, where the plants roots are presubjected to 0.5 mm asa and let to grow at room temperature, and ascorbic acid with chilling group, where the plants are presubjected to 0.5 mm asa and were exposed to chilling stress (4 °c) for 7 h/day.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
40 mg of crystalline ascorbic acid was added to the liquid medium. Ascorbic acid is an antioxidant in plants which play important role in activation of many physiological and defense mechanisms. Ascorbic acid is synthesised by eukaryotes, the known exceptions being primates and some other animal groups which have lost functional gulonolactone oxidase. All plants synthesize ascorbic acid. The effect of vitamin c on plants was studied with sterile plant cultures.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title ascorbic acid for plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






