Your Cam plants definition images are ready in this website. Cam plants definition are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Cam plants definition files here. Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for cam plants definition pictures information related to the cam plants definition keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site always gives you suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Cam Plants Definition. The c4 plants, evolved from the c3 plants, have high nitrogen and water use efficiency. Crassulacean acid metabolism ( ˌkræsjʊˈleɪʃən) n (botany) the full name for cam 3 Engineering the c3 plants to c4 or cam pathway can help scientist to almost double the biomass yield from the same resources. Examples of cam plants include cactus, pineapple, etc.
 C3 plants overview Sustainable & Refashioned Design by From buddhajeans.com
C3 plants overview Sustainable & Refashioned Design by From buddhajeans.com
Kranz anatomy is one structure within the leaves of the c4 plants that are specialized in nature. This is due to malic acid stored in the vacuoles of the plants� cells during the night and then used up during the day. Crassulacean acid metabolism (cam) a method of photosynthesisfound in certain succulent plants (members of the family crassulaceae) that live in hot, dry climates and close their stomata during the day to avoid excessive transpirationlosses and open them at night. It is primarily caused by the building up of green house gases (ghg) in the atmosphere. Usually, water is one of the two factors required for photosynthesis while the second being carbon dioxide. Photosynthesis is the main process of carbon fixation.
The only agriculturally significant cam plants are the pineapple and an agave species used to make tequila and.
These are cells that are located toward the surface of a plant leaf and are where photosynthesis typically occurs. Cam plant / ( kæm) / noun any plant that undergoes a form of photosynthesis known as crassulacean acid metabolism, in which carbon dioxide is taken up only at night quiz quiz. Any manufacturing process that uses computer software to facilitate, assist or automate parts of the manufacturing process. Cam plants differ from regular plants (called c3 plants) in how they photosynthesize. The diurnal temperatures variation is very high in deserts where many cam plants are found. C3 plants are the most common and the most efficient at photosynthesis in cool, wet climates.
Source: whs-apbio-2011.blogspot.com
The word crassulacean comes from the latin word crassus which means “thick.” there are over 16,000 species of cam plants on earth including cacti, sedum, jade, orchids and agave. Kranz anatomy is one structure within the leaves of the c4 plants that are specialized in nature. Climate change is a serious global problem due to increase the global average surface temperature. They represent about 10% of the plant species and include cacti, orchids, maternity plant, wax plant, pineapple, spanish moss, and some ferns. 44 rows crassulacean acid metabolism, also known as cam photosynthesis, is a carbon fixation pathway that evolved in some plants as an adaptation to arid conditions that allows a plant to photosynthesize during the day, but only exchange gases at night.
 Source: intechopen.com
Source: intechopen.com
The cam pathway is adapted to minimise water loss and photorespiration. Definition crassulacean acid metabolism (cam) cam is a mechanism of photosynthesis involving double fixation of co 2 , which occurs in succulents belonging to crassulaceae, cacti, euphorbias and some other plants of dry habitats where the stomata remain closed during the daytime and open at night. The word crassulacean comes from the latin word crassus which means “thick.” there are over 16,000 species of cam plants on earth including cacti, sedum, jade, orchids and agave. C3 plants are the most common and the most efficient at photosynthesis in cool, wet climates. The c4 plants, evolved from the c3 plants, have high nitrogen and water use efficiency.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Cam plants are the plants, which fix carbon dioxide by cam pathway or crassulacean acid metabolism. Their stomata opens at night. It is a special carbon fixation pathway present in plants that grow under arid conditions. At night stomata are open by pepa and oaa in the presence of pepacarboxylase. Cam plants are a type of plants which utilize cam photosynthesis.
 Source: buddhajeans.com
Source: buddhajeans.com
44 rows crassulacean acid metabolism, also known as cam photosynthesis, is a carbon fixation pathway that evolved in some plants as an adaptation to arid conditions that allows a plant to photosynthesize during the day, but only exchange gases at night. It is primarily caused by the building up of green house gases (ghg) in the atmosphere. Examples of cam plants include cactus, pineapple, etc. Their stomata opens at night. Carbon fixation definition “carbon fixation is the process by which plants fix atmospheric carbon to form organic compounds.” all the autotrophs, bacteria, algae and plants fix atmospheric carbon dioxide by the process of photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
 Source: es.slideshare.net
Source: es.slideshare.net
C4 plants are most efficient at photosynthesis in hot, sunny climates. Some plants that are adapted to dry environments, such as cacti and pineapples, use the crassulacean acid metabolism ( cam) pathway to minimize photorespiration. The cam pathway is adapted to minimise water loss and photorespiration. Those rudimentary genes that formed the c4 pathways are also present in plants. Definition crassulacean acid metabolism (cam) cam is a mechanism of photosynthesis involving double fixation of co 2 , which occurs in succulents belonging to crassulaceae, cacti, euphorbias and some other plants of dry habitats where the stomata remain closed during the daytime and open at night.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This is due to malic acid stored in the vacuoles of the plants� cells during the night and then used up during the day. In a plant using full cam, the stomata in the leaves remain shut during the day to reduce evapotranspiration, but they open. Physiological response of c3, c4 and cam plants in changeable climate. It is a special carbon fixation pathway present in plants that grow under arid conditions. Climate change is a serious global problem due to increase the global average surface temperature.
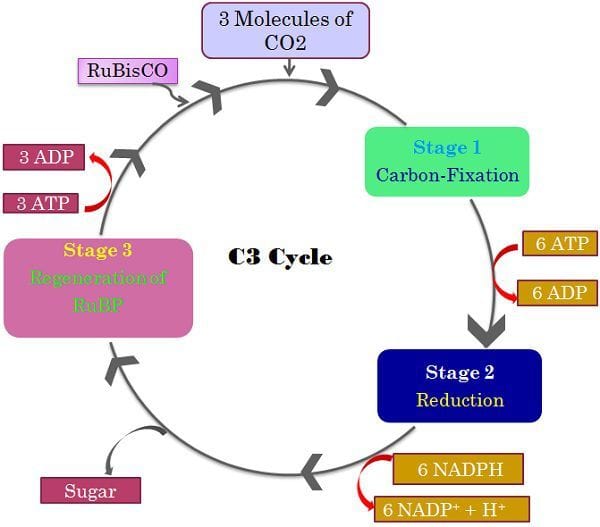 Source: biodifferences.com
Source: biodifferences.com
With the exceptions of pineapple and a few agave species, such as the tequila agave, cam plants are relatively unexploited in terms of human use for food and energy resources. The c4 plants, evolved from the c3 plants, have high nitrogen and water use efficiency. Examples of cam plants include cactus, pineapple, etc. Their stomata opens at night. Therefore, they highly store water inside the plant and become thick.
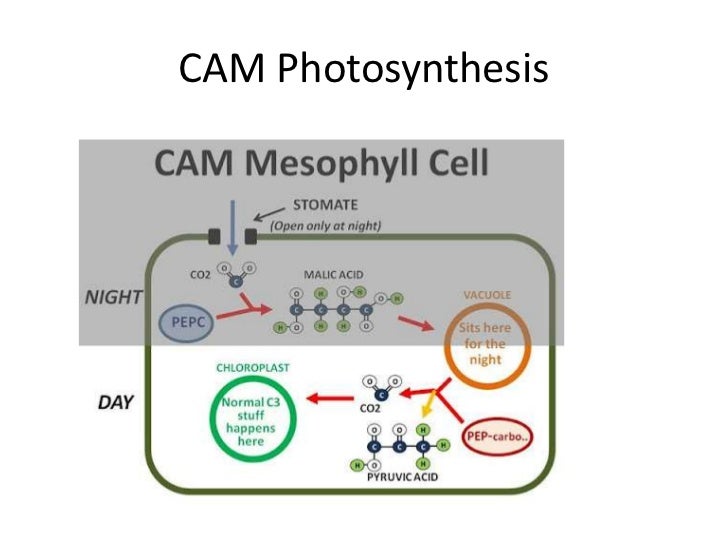 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Physiological response of c3, c4 and cam plants in changeable climate. Plants that use crassulacean acid metabolism, also known as cam plants, are succulents that are efficient at storing water due to the dry and arid climates they live in. The cam pathway is adapted to minimise water loss and photorespiration. It is a special carbon fixation pathway present in plants that grow under arid conditions. Due to excessive heat the stomata remains closed during the day to reduce transpiration.
Source: mnapbiocollection.blogspot.com
Crassulacean acid metabolism (cam) is a photosynthetic adaptation to periodic water supply, occurring in plants in arid regions (e.g., cacti) or in tropical. C3 plants are those which fix and reduce inorganic co2 into organic compounds using only the c3 pathway in photosynthesis while c4 and cam plants employ both c3 and c4 cycles. The c4 plants, evolved from the c3 plants, have high nitrogen and water use efficiency. The cam plants showing clear differences between day and night temperature responses on photosynthesis. Definition crassulacean acid metabolism (cam) cam is a mechanism of photosynthesis involving double fixation of co 2 , which occurs in succulents belonging to crassulaceae, cacti, euphorbias and some other plants of dry habitats where the stomata remain closed during the daytime and open at night.
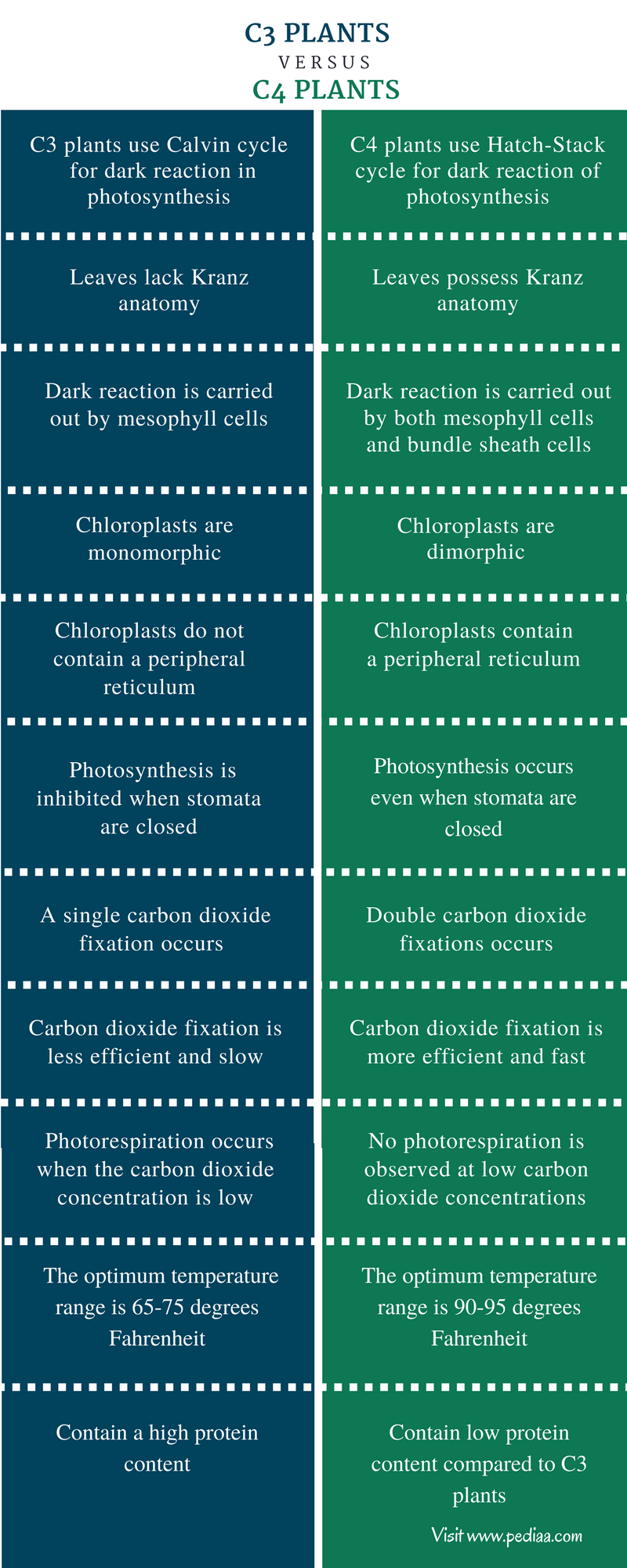 Source: pediaa.com
Source: pediaa.com
They are present in dry and arid environments. It is a special carbon fixation pathway present in plants that grow under arid conditions. Physiological response of c3, c4 and cam plants in changeable climate. It was first discovered in the plants of the crassulaceae family. A broader and simpler definition would be:
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
Cam plant also found in: It is a special carbon fixation pathway present in plants that grow under arid conditions. Crassulacean acid metabolism (cam) a method of photosynthesisfound in certain succulent plants (members of the family crassulaceae) that live in hot, dry climates and close their stomata during the day to avoid excessive transpirationlosses and open them at night. Cam plant / ( kæm) / noun any plant that undergoes a form of photosynthesis known as crassulacean acid metabolism, in which carbon dioxide is taken up only at night quiz quiz. Therefore, they highly store water inside the plant and become thick.
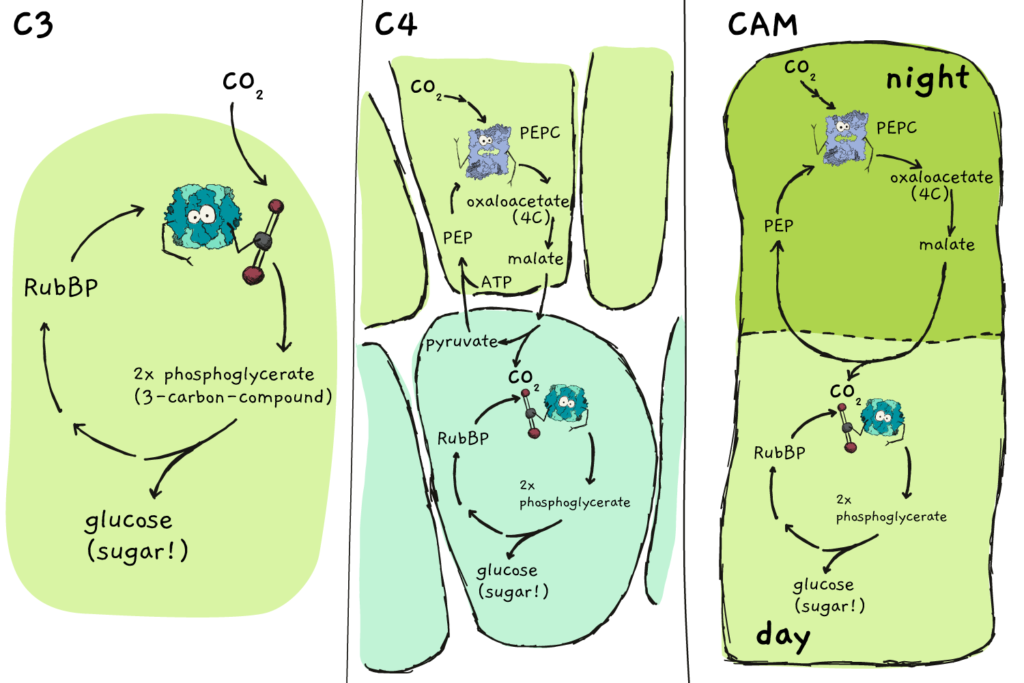 Source: plantsandpipettes.com
Source: plantsandpipettes.com
Physiological response of c3, c4 and cam plants in changeable climate. Kranz anatomy is one structure within the leaves of the c4 plants that are specialized in nature. Crassulacean acid metabolism ( ˌkræsjʊˈleɪʃən) n (botany) the full name for cam 3 C4 plants are most efficient at photosynthesis in hot, sunny climates. Physiological response of c3, c4 and cam plants in changeable climate.
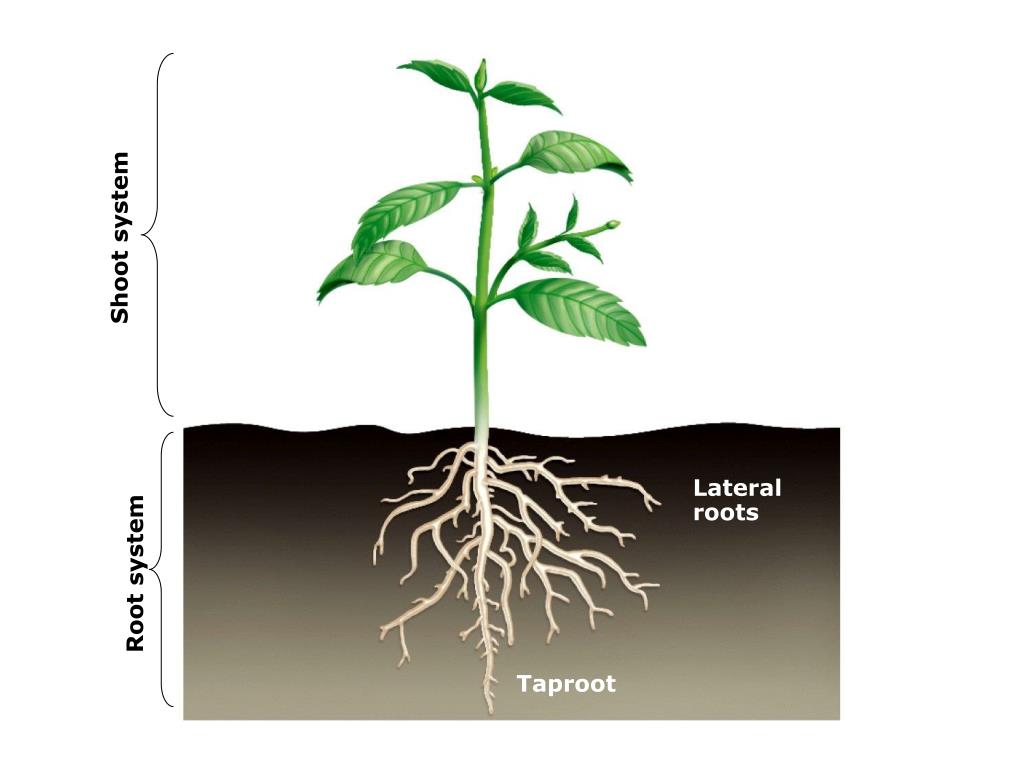 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Climate change is a serious global problem due to increase the global average surface temperature. C3 plants are those which fix and reduce inorganic co2 into organic compounds using only the c3 pathway in photosynthesis while c4 and cam plants employ both c3 and c4 cycles. Cam plant / ( kæm) / noun any plant that undergoes a form of photosynthesis known as crassulacean acid metabolism, in which carbon dioxide is taken up only at night quiz quiz. The cam pathway is adapted to minimise water loss and photorespiration. C3 plants are the most common and the most efficient at photosynthesis in cool, wet climates.
 Source: onlinesciencenotes.com
Source: onlinesciencenotes.com
A broader and simpler definition would be: Therefore, they highly store water inside the plant and become thick. Crassulacean acid metabolism (cam) a method of photosynthesisfound in certain succulent plants (members of the family crassulaceae) that live in hot, dry climates and close their stomata during the day to avoid excessive transpirationlosses and open them at night. In normal photosynthesis, glucose is formed when carbon dioxide (co2), water (h2o), light, and an enzyme called rubisco to work together to create oxygen, water, and two carbon molecules containing three carbons each (hence, the name c3). Definition of cam plants the noteworthy remark which distinguishes this process from the above two is that in this type of photosynthesis the organism absorbs the energy from the sunlight at the day time and uses this energy at the night time for the assimilation of carbon dioxide.
Source: mnapbiocollection.blogspot.com
Also, this mechanism was first found in the plant family crassulaceae. This name comes from the family of plants, the crassulaceae, in which scientists first discovered the pathway. The cam plants showing clear differences between day and night temperature responses on photosynthesis. The cam plants represent a metabolic strategy adapted to extremely hot and dry environments. C3 plants are the most common and the most efficient at photosynthesis in cool, wet climates.
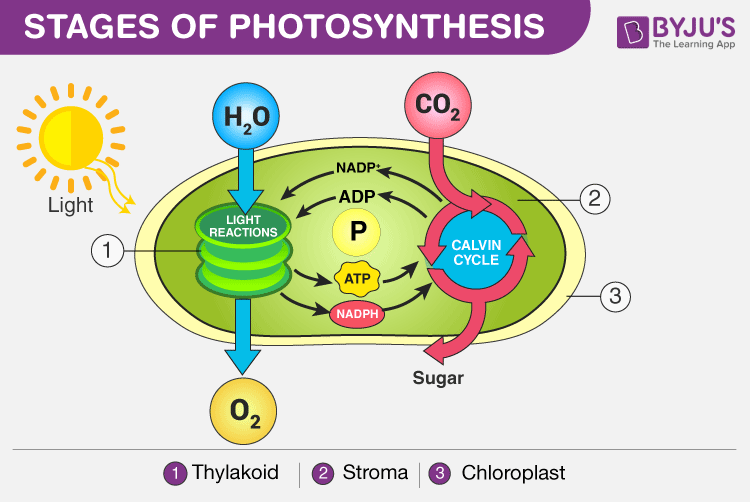 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
Due to excessive heat the stomata remains closed during the day to reduce transpiration. It was first discovered in the plants of the crassulaceae family. However, the water loss of these plants is high. A broader and simpler definition would be: Cam plants are the plants, which fix carbon dioxide by cam pathway or crassulacean acid metabolism.
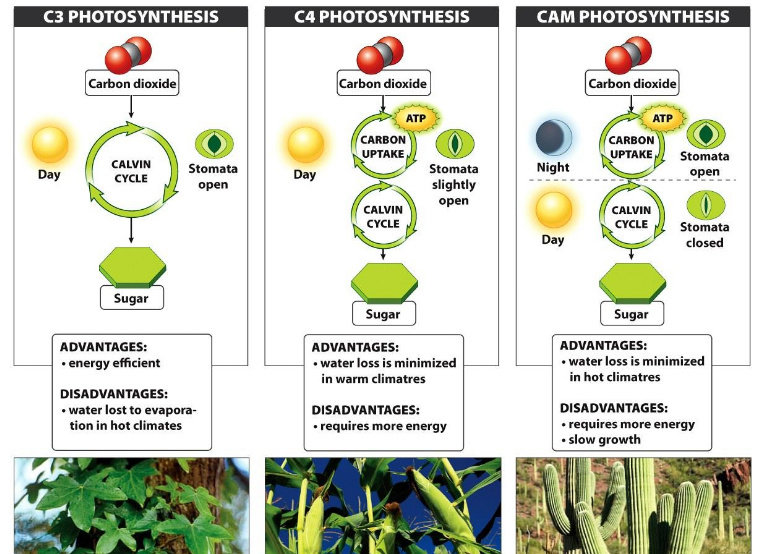 Source: dictio.id
Source: dictio.id
C4 plants are most efficient at photosynthesis in hot, sunny climates. Therefore, they highly store water inside the plant and become thick. Cam plants are adapted to avoid. Engineering the c3 plants to c4 or cam pathway can help scientist to almost double the biomass yield from the same resources. The diurnal temperatures variation is very high in deserts where many cam plants are found.
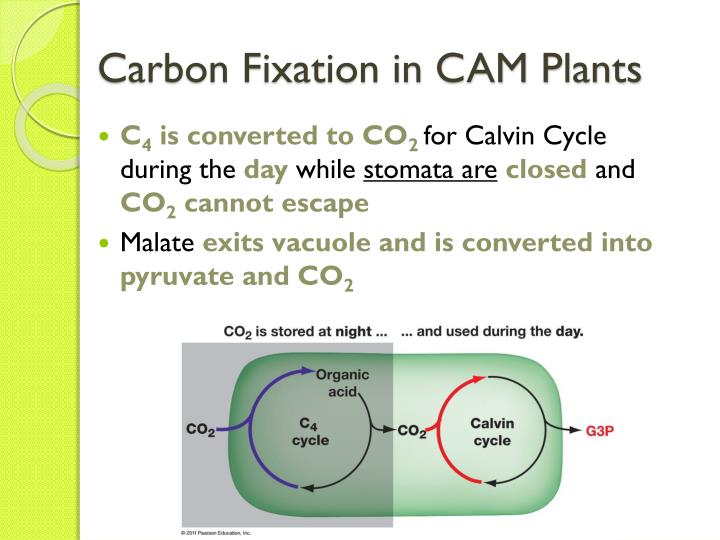 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
C3 plants are the most common and the most efficient at photosynthesis in cool, wet climates. However, the water loss of these plants is high. Kranz anatomy is one structure within the leaves of the c4 plants that are specialized in nature. Examples of cam plants include cactus, pineapple, etc. The cam plants represent a metabolic strategy adapted to extremely hot and dry environments.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title cam plants definition by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






