Your Cambium in plants images are ready in this website. Cambium in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Cambium in plants files here. Get all free vectors.
If you’re searching for cambium in plants images information connected with to the cambium in plants keyword, you have come to the ideal blog. Our site always gives you suggestions for viewing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Cambium In Plants. A cambium is a layer found in woody stems between the xylem and phloem. Cork cambium, also called phellogen, is another meristematic tissue developed in the cortex region. It is responsible for producing new cells, known as secondary growth, which allows woody plants to grow in diameter. Vascular cambium is a type of cell associated with the primary and secondary growth of plants.
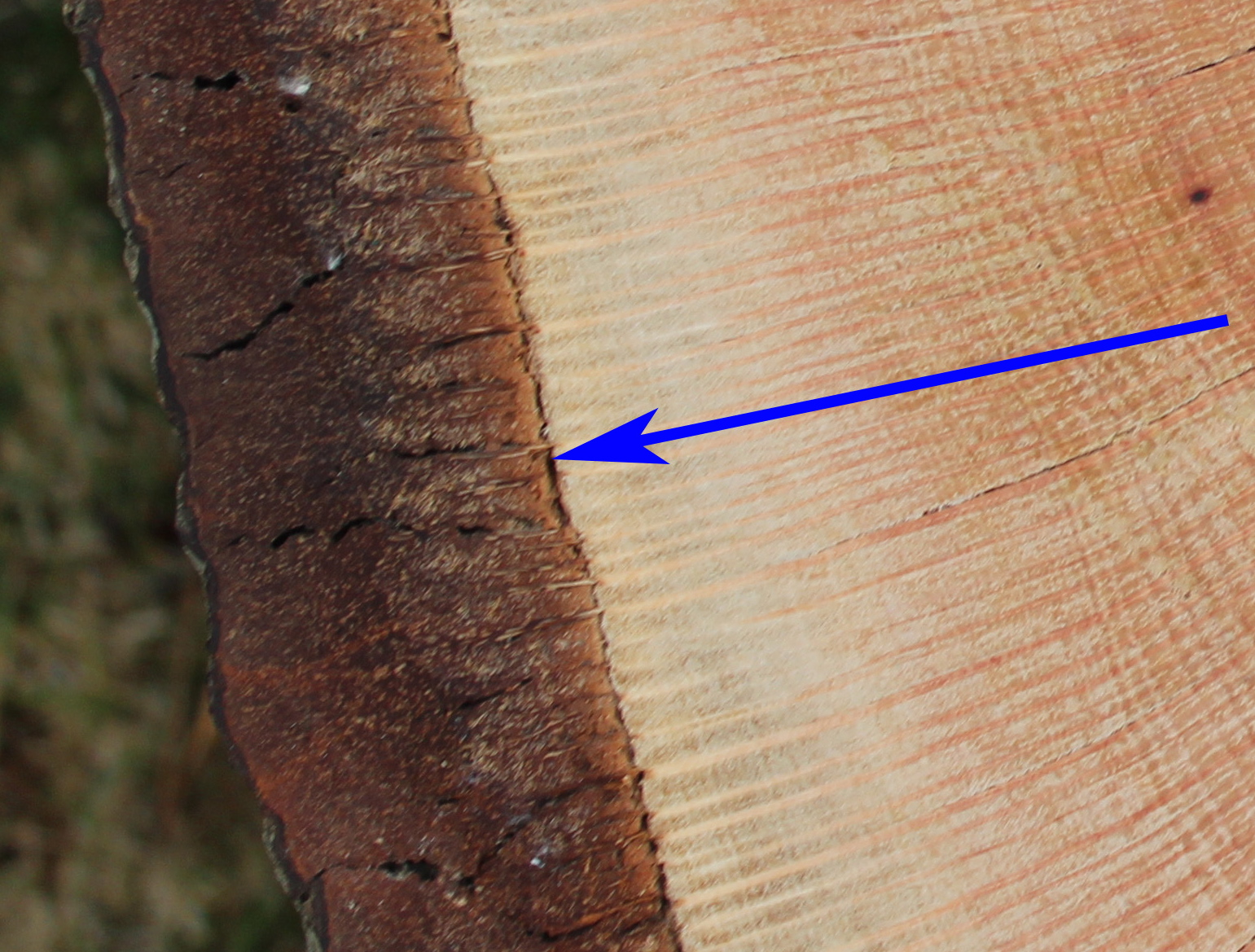 Cambium Learning Among the Oaks From learningamongtheoaks.org
Cambium Learning Among the Oaks From learningamongtheoaks.org
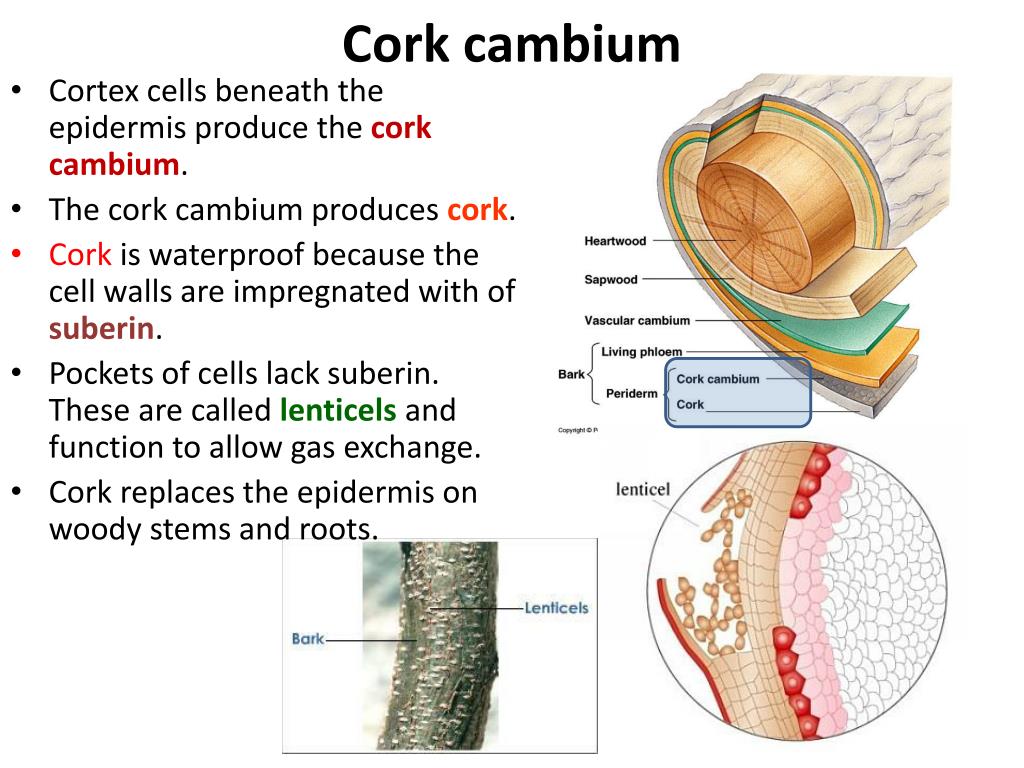
The cambium exists as essentially undifferentiated or blank cells that have no specific purpose until called. A thin formative layer between the xylem and phloem of most vascular plants that gives rise to new cells and is responsible for secondary growth. The vascular cambium and cork cambium are secondary meristems that are formed in stems and roots after the tissues of the primary plant body have differentiated. When wounds occur on plants, a large amount of soft parenchymatous tissue is formed on or below the injured surface; This is the time when the cork cambium develops as a new protective layer. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem.
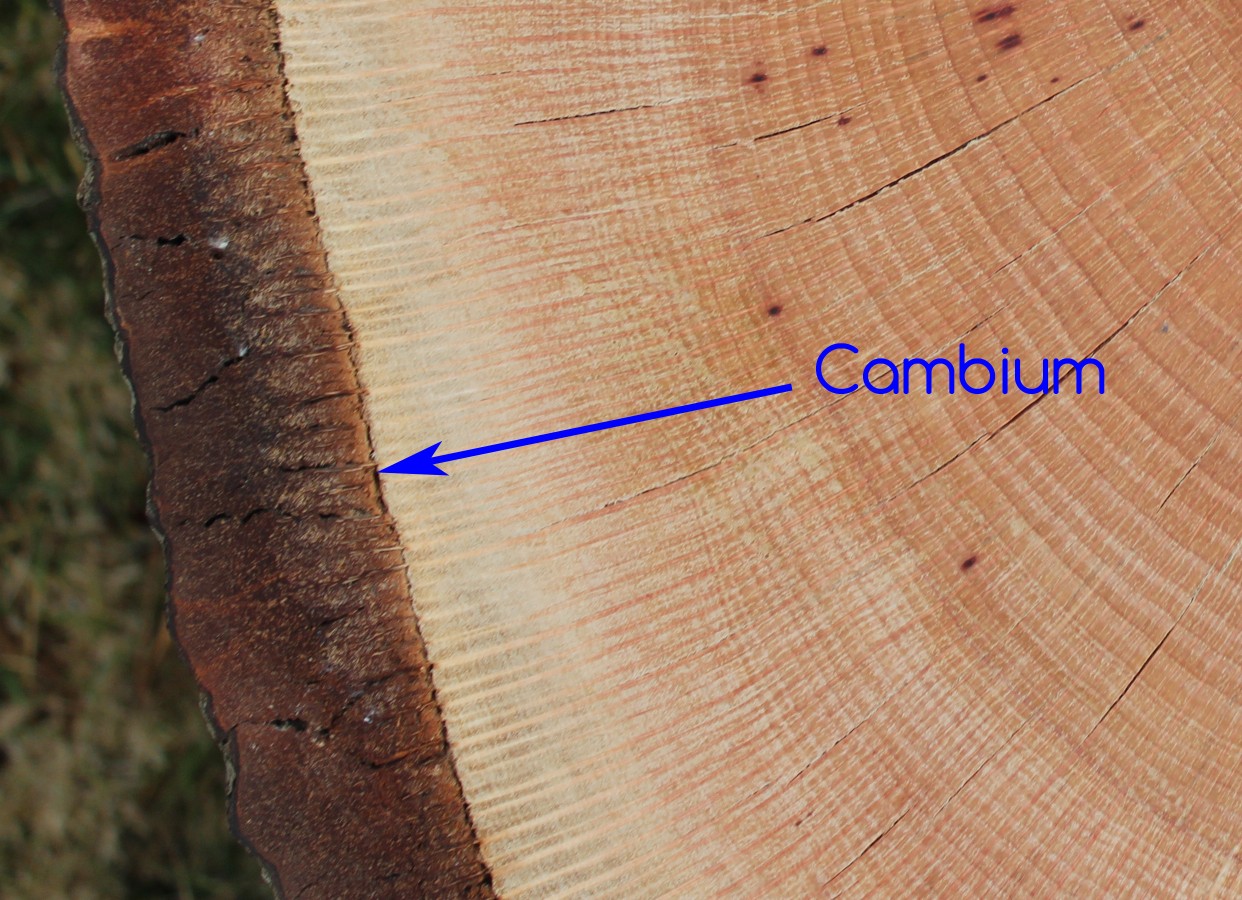
A cambium (plural cambia or cambiums ), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth.
This is the time when the cork cambium develops as a new protective layer. Plural “cambia”) is a plant tissue located between the xylem and the phloem in the stems and roots of vascular plants. It is a cylinder of unspecialized meristem cells that divide to form secondary vascular tissues. Cambium, plural cambiums, orcambia, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is responsible for the secondary growth of stems and roots (secondary growth occurs after the first season and results in increase in thickness). This is the time when the cork cambium develops as a new protective layer. They are closely intertwined with the xylem and phloem due to the amount of.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Peter barlow, in vascular transport in plants, 2005 final comments the cambium is a zone especially adapted to supply cells that are already of nearly the requisite length for fulfilling the functional demands— vertical transport and mechanical strength and flexibility—of the secondary xylem and phloem tissues. It is usually missing from monocotyledons, such as the grasses. The secondary tissues are formed during the secondary growth which results in. Plural “cambia”) is a plant tissue located between the xylem and the phloem in the stems and roots of vascular plants. Cambium, plural cambiums, orcambia, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is responsible for the secondary growth of stems and roots (secondary growth occurs after the first season and results in increase in thickness).
Source: researchgate.net
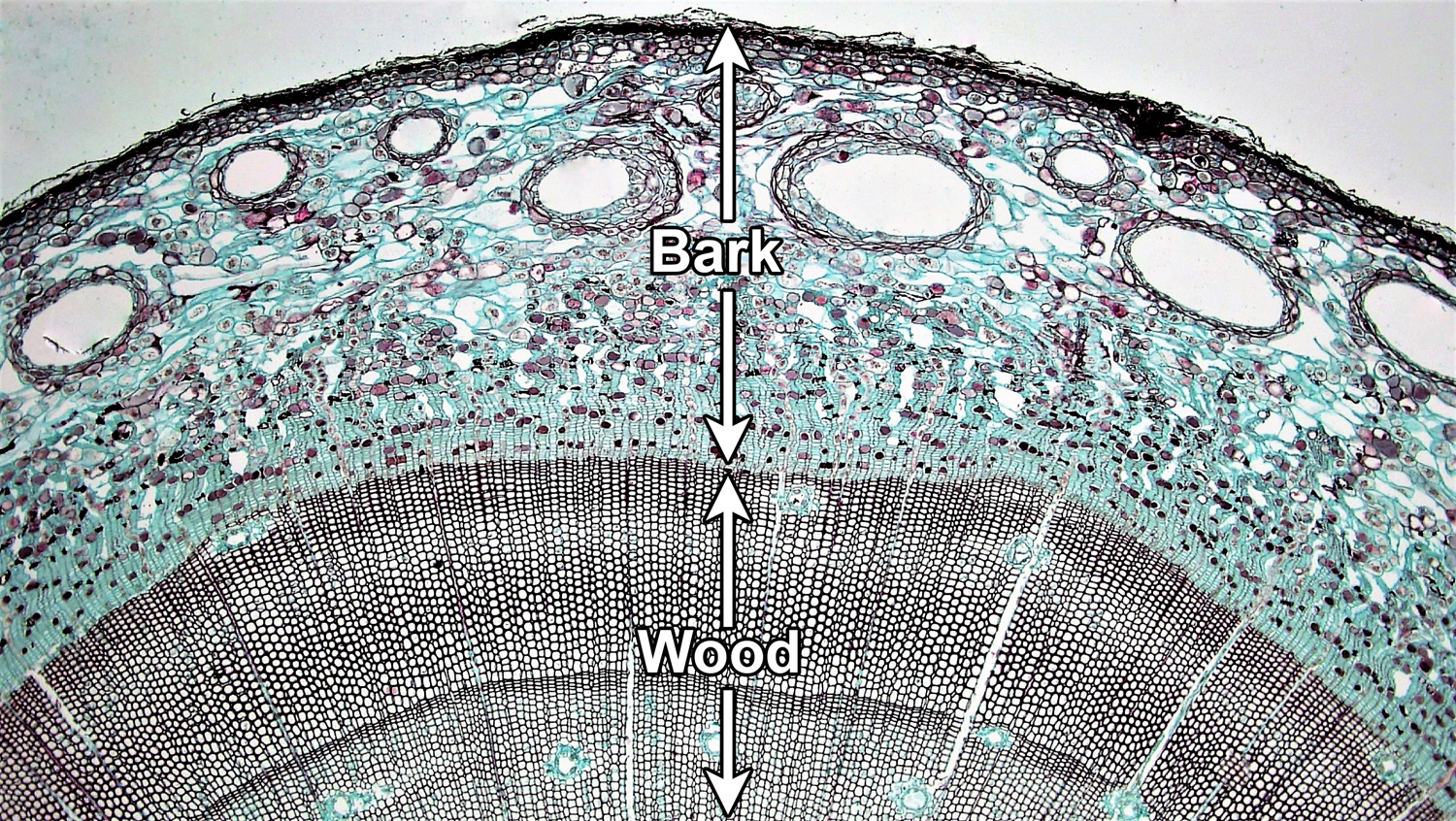
The cambium is a group of meristem cells that are parallel to one another and encircle the stem of a plant. In woody plants, cork cambium is the outermost lateral meristem. Its this cambium which cut secondary xylem called wood on the inside of a stem or root. It produces secondary xylem inwards, towards the pith, and secondary phloem outwards, towards the bark. The vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and oak trees, gymnosperms such as pine trees, as well as in certain other vascular plants.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The vascular cambium is responsible for increasing the diameter of stems and roots and for forming woody tissue. The cambium exists as essentially undifferentiated or blank cells that have no specific purpose until called. It is a cylinder of unspecialized meristem cells that divide to form secondary vascular tissues. In the following two chapters we shall discuss in detail the structure, functions, and the importance to the plant of these tissues which also have great significance for mankind. It is responsible for producing new cells, known as secondary growth, which allows woody plants to grow in diameter.
 Source: learningamongtheoaks.org
Source: learningamongtheoaks.org
In plants growing in tropical regions, cambium is active throughout the whole life of plants. Wood is the most abundant biomass produced by land plants and is mainly used for timber, pulping, and paper making. The cambium gives rise to secondary xylem and phloem cells. A cambium is a layer found in woody stems between the xylem and phloem. It is present in stems and roots and in their branches.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
A cambium (plural cambia or cambiums ), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. In woody plants, cork cambium is the outermost lateral meristem. Cambium, wether temporary or permanent represents fast dividing meristematic tissues. Vascular cambium is a type of cell associated with the primary and secondary growth of plants. Cambium (lateral meristem) a plant tissue consisting of actively dividing cells (see meristem) that is responsible for increasing the girth of the plant, i.e.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Other words from cambium example sentences phrases containing cambium learn more about cambium. Due to the cambial ring activity, the outer layers such as cortex cells and epidermis get crushed. Plant bodies are made up of different types of tissues and cells which helps the plant to grow by producing new cells and tissues. One of the important functions of the cambium is the formation of callus or wound tissue, and the healing of the wounds. The vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and oak trees, gymnosperms such as pine trees, as well as in certain other vascular plants.
 Source: biology-forums.com
Source: biology-forums.com
The vascular cambium is one cell thick permanent secondary meristem. The cambium is filled with undifferentiated cells which have the ability to differentiate into many different types of cells, depending on where in the plant they are growing. Vascular cambium is a type of cell associated with the primary and secondary growth of plants. A cambium (plural cambia or cambiums ), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. The cambium is a group of meristem cells that are parallel to one another and encircle the stem of a plant.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
The cambium exists as essentially undifferentiated or blank cells that have no specific purpose until called. The vascular cambium is one cell thick permanent secondary meristem. When wounds occur on plants, a large amount of soft parenchymatous tissue is formed on or below the injured surface; The vascular cambium and cork cambium are secondary meristems that are formed in stems and roots after the tissues of the primary plant body have differentiated. Cambium is the zone of parenchyma cells which periodically divide to form new layers of secondary xylem tissue and secondary phloem tissue.
 Source: learningamongtheoaks.org
Source: learningamongtheoaks.org
Cambium, in plants is responsible for. The cambium is a group of meristem cells that are parallel to one another and encircle the stem of a plant. In plants we see a layer of cells that help it to grow and repair called the cambium. The cambium promotes secondary growth of stems and roots, which is the growth that occurs after the first season. Cambium, in plants is responsible for.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Peter barlow, in vascular transport in plants, 2005 final comments the cambium is a zone especially adapted to supply cells that are already of nearly the requisite length for fulfilling the functional demands— vertical transport and mechanical strength and flexibility—of the secondary xylem and phloem tissues. The vascular cambium (also called main cambium, wood cambium, bifacial cambium; The cambium promotes secondary growth of stems and roots, which is the growth that occurs after the first season. As these cells divide and multiply in number, the plants increase their girth. The cork cambium produces some of the bark.
 Source: pinterest.se
Source: pinterest.se
It helps a plant to grow in girth/ width. The cambium exists as essentially undifferentiated or blank cells that have no specific purpose until called. In plants growing in tropical regions, cambium is active throughout the whole life of plants. In the following two chapters we shall discuss in detail the structure, functions, and the importance to the plant of these tissues which also have great significance for mankind. Its this cambium which cut secondary xylem called wood on the inside of a stem or root.
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
Wood is the most abundant biomass produced by land plants and is mainly used for timber, pulping, and paper making. It may even extend into leaf petioles in some woody plants. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. It produces secondary xylem inwards, towards the pith, and secondary phloem outwards, towards the bark. The two most important cambia are the vascular (or fascicular ) cambium and the cork cambium.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In plants we see a layer of cells that help it to grow and repair called the cambium. It is difficult to overemphasize the importance of the vascular cambium which produces secondary xylem and secondary phloem. In plants growing in tropical regions, cambium is active throughout the whole life of plants. Vascular cambium is a type of cell associated with the primary and secondary growth of plants. The vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and oak trees, gymnosperms such as pine trees, as well as in certain other vascular plants.
 Source: virily.com
Source: virily.com
When wounds occur on plants, a large amount of soft parenchymatous tissue is formed on or below the injured surface; In contrast to this, in plants of temperate region, the cambium almost ceases its activity with the commencement of unfavourable season— generally in autumn and this dormant stage remains till the following spring when it is reactivated and produces. The cambium is filled with undifferentiated cells which have the ability to differentiate into many different types of cells, depending on where in the plant they are growing. The vascular cambium consists of cells within the inside of the plant that is responsible for growth in most plants. Cambium, plural cambiums, orcambia, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is responsible for the secondary growth of stems and roots (secondary growth occurs after the.
 Source: education-portal.com
Source: education-portal.com
This tissue is known as callus. It is present in stems and roots and in their branches. The vascular cambium (also called main cambium, wood cambium, bifacial cambium; The vascular cambium and cork cambium are secondary meristems that are formed in stems and roots after the tissues of the primary plant body have differentiated. The cambium is filled with undifferentiated cells which have the ability to differentiate into many different types of cells, depending on where in the plant they are growing.
 Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
Wood is the most abundant biomass produced by land plants and is mainly used for timber, pulping, and paper making. A thin formative layer between the xylem and phloem of most vascular plants that gives rise to new cells and is responsible for secondary growth. It is a cylinder of unspecialized meristem cells that divide to form secondary vascular tissues. It may even extend into leaf petioles in some woody plants. Wood (secondary xylem) is derived from vascular cambium, and its formation encompasses a series of developmental processes.
 Source: pinterest.co.uk
Source: pinterest.co.uk
Cork cambium is the layer of cambium that is usually seen in woody plants. Cork cambium is the layer of cambium that is usually seen in woody plants. The vascular cambium consists of cells within the inside of the plant that is responsible for growth in most plants. A cambium (plural cambia or cambiums ), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. The cork cambium produces some of the bark.

The cambium gives rise to secondary xylem and phloem cells. The vascular cambium consists of cells within the inside of the plant that is responsible for growth in most plants. When wounds occur on plants, a large amount of soft parenchymatous tissue is formed on or below the injured surface; A cambium (plural cambia or cambiums ), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is responsible for producing new cells, known as secondary growth, which allows woody plants to grow in diameter.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title cambium in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






