Your Cambium in plants definition images are ready. Cambium in plants definition are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Cambium in plants definition files here. Find and Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for cambium in plants definition pictures information connected with to the cambium in plants definition keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site always provides you with hints for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
Cambium In Plants Definition. It makes the bark of a plant. A meristem that increases the girth of stems and roots by producing additional xylem and. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening. A cylindrical layer of meristematic tissue that is found between the primary xylem and primary phloem is called vascular cambium.
 Vascular cambium A lateral meristem that forms secondary From virtualplant.ru.ac.za
Vascular cambium A lateral meristem that forms secondary From virtualplant.ru.ac.za
In plants we see a layer of cells that help it to grow and repair called the cambium. Cambium refers to the slender plant membrane located right underneath the bark of a woody tree or plant. By caring for plants and trees each season, they grow healthier and can better resist pests and withstand difficult problems. It makes the bark of a plant. This is the time when the cork cambium develops as a new protective layer. In woody plants, the vascular cambium is displayed as a structured line separating the wood and the bark.
| meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples
The focus is on developing and maintaining healthy plants, so they become less susceptible to problems. This type of cell is taller and oriented towards the axis. In woody plants, cork cambium is the outermost lateral meristem. This hard structure forms the bark, and protects the tree or plant from many forms of damage. This meristem also produces undifferentiated cells, but some will differentiate into phellem cells, becoming the outer bark. The plants which do not possess secondary growth, all cells of the procambium strands mature and develop into vascular tissue.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The primary vascular skeleton is built up by the maturing of the cells of the procambium strands to form xylem and phloem. | meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples The primary vascular skeleton is built up by the maturing of the cells of the procambium strands to form xylem and phloem. Cambium definition, a layer of delicate meristematic tissue between the inner bark or phloem and the wood or xylem, which produces new phloem on the outside and new xylem on the inside in stems, roots, etc., originating all secondary growth. The function of the cork cambium is to develop the cork, which is a tough protective material and secondary cortex.
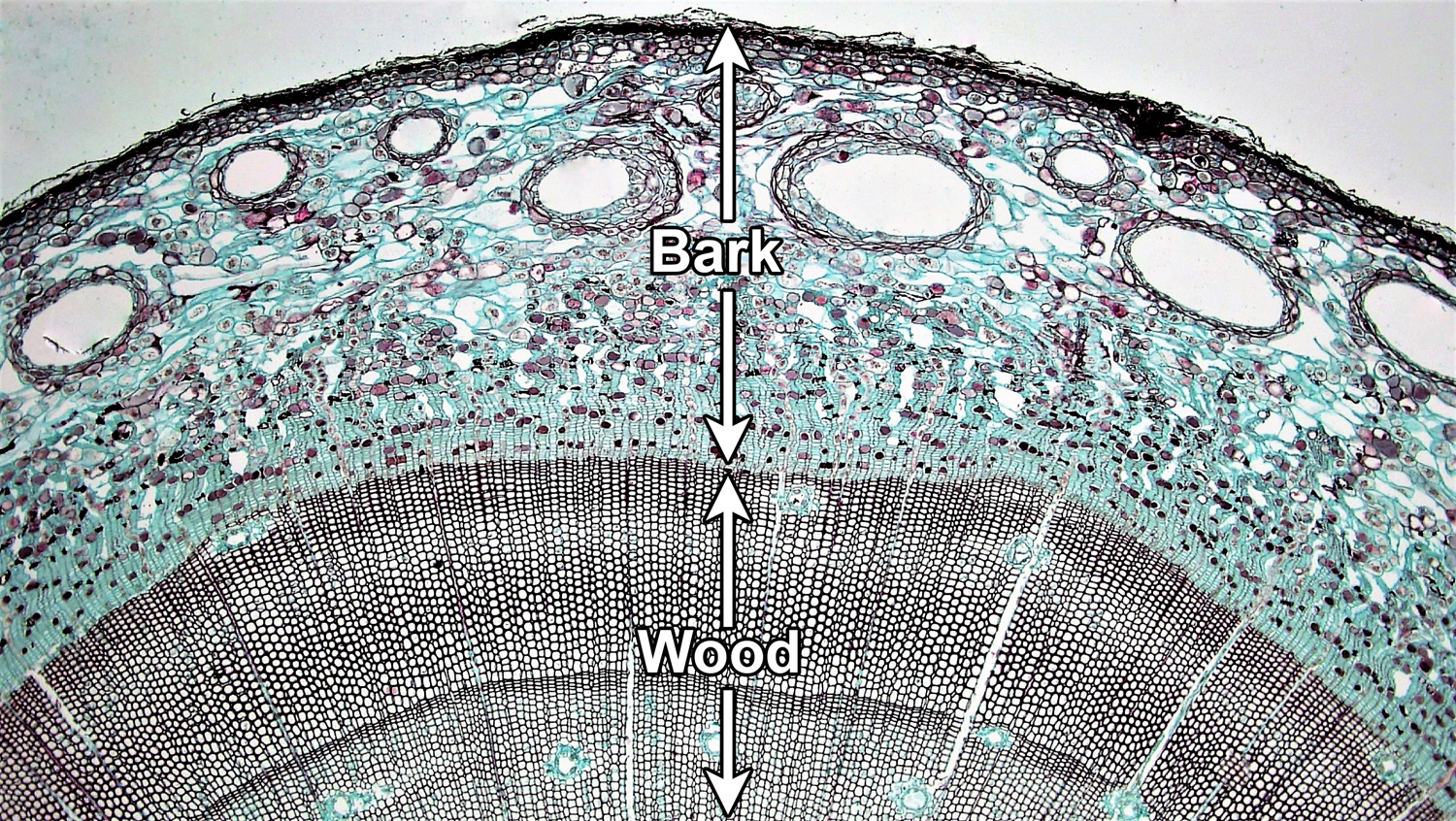 Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
The cambium has several functions. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening. Cambium definition, a layer of delicate meristematic tissue between the inner bark or phloem and the wood or xylem, which produces new phloem on the outside and new xylem on the inside in stems, roots, etc., originating all secondary growth. The meaning of cambium is a thin formative layer between the xylem and phloem of most vascular plants that gives rise to new cells and is responsible for secondary growth. A cambium (plural cambia or cambiums), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Cork cambium, also called phellogen, is another meristematic tissue developed in the cortex region. A plant’s vascular cambium normally consists of two main types of cells: This hard structure forms the bark, and protects the tree or plant from many forms of damage. Cambium, plural cambiums, or cambia, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is responsible for the secondary growth of stems and roots (secondary growth occurs after the first season and results in increase in thickness). The cork cambium is a specialized meristem that forms on the tissue just outside the periderm.
Source: researchgate.net
Cambium definition, a layer of delicate meristematic tissue between the inner bark or phloem and the wood or xylem, which produces new phloem on the outside and new xylem on the inside in stems, roots, etc., originating all secondary growth. | meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples This hard structure forms the bark, and protects the tree or plant from many forms of damage. In woody plants, the vascular cambium is displayed as a structured line separating the wood and the bark. Cambium refers to the slender plant membrane located right underneath the bark of a woody tree or plant.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
It is a vascular tissue of plants. It also encourages the secondary growth of roots and stems. The vascular cambium is also known as main cambium, wood cambium or bifacial cambium. In woody plants, it produces layers of xylem and phloem, consequently enhancing the stem’s diameter. This meristem also produces undifferentiated cells, but some will differentiate into phellem cells, becoming the outer bark.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
In woody plants, the vascular cambium is displayed as a structured line separating the wood and the bark. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. This type of cell is taller and oriented towards the axis. | meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples Cork cambium, also called phellogen, is another meristematic tissue developed in the cortex region.
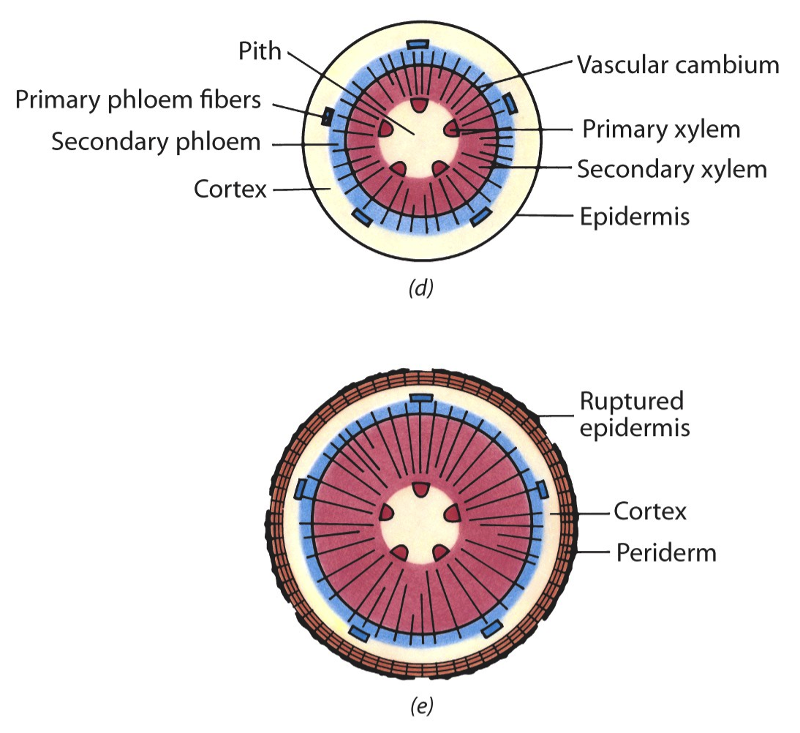 Source: easynotecards.com
Source: easynotecards.com
Cambium, plural cambiums, orcambia, in plants, layer of actively dividing cells between xylem (wood) and phloem (bast) tissues that is responsible for the secondary growth of stems and roots (secondary growth occurs after the. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening. A cambium arborist and tree expert will help predict and prevent problems before they happen. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues. These tend to be on the smaller side and roundish to angular.
 Source: organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu
Source: organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu
The cambium exists as essentially undifferentiated or blank cells that have no specific purpose until called. It is a vascular tissue of plants. The vascular cambium consists of cells within the inside of the plant that is responsible for growth in most plants. This is the time when the cork cambium develops as a new protective layer. The vascular cambium is responsible for increasing the diameter of stems and roots and for forming woody tissue.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The vascular cambium consists of cells within the inside of the plant that is responsible for growth in most plants. The vascular cambium is also known as main cambium, wood cambium or bifacial cambium. In woody plants, cork cambium is the outermost lateral meristem. This meristem also produces undifferentiated cells, but some will differentiate into phellem cells, becoming the outer bark. The vascular cambium consists of cells within the inside of the plant that is responsible for growth in most plants.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
In woody plants, the vascular cambium is displayed as a structured line separating the wood and the bark. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. The vascular cambium is also known as main cambium, wood cambium or bifacial cambium. A cylindrical layer of meristematic tissue that is found between the primary xylem and primary phloem is called vascular cambium. It is a vascular tissue of plants.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This meristem also produces undifferentiated cells, but some will differentiate into phellem cells, becoming the outer bark. They are closely intertwined with the xylem and phloem due to the amount of. This meristem also produces undifferentiated cells, but some will differentiate into phellem cells, becoming the outer bark. A cambium arborist and tree expert will help predict and prevent problems before they happen. Cork cambium, also called phellogen, is another meristematic tissue developed in the cortex region.
 Source: pinterest.co.uk
Source: pinterest.co.uk
It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues. In herbaceous plants, it occurs in the vascular. The focus is on developing and maintaining healthy plants, so they become less susceptible to problems. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues. The cork cambium is a specialized meristem that forms on the tissue just outside the periderm.
 Source: pinterest.co.uk
Source: pinterest.co.uk
The focus is on developing and maintaining healthy plants, so they become less susceptible to problems. The focus is on developing and maintaining healthy plants, so they become less susceptible to problems. In plants we see a layer of cells that help it to grow and repair called the cambium. By caring for plants and trees each season, they grow healthier and can better resist pests and withstand difficult problems. This hard structure forms the bark, and protects the tree or plant from many forms of damage.
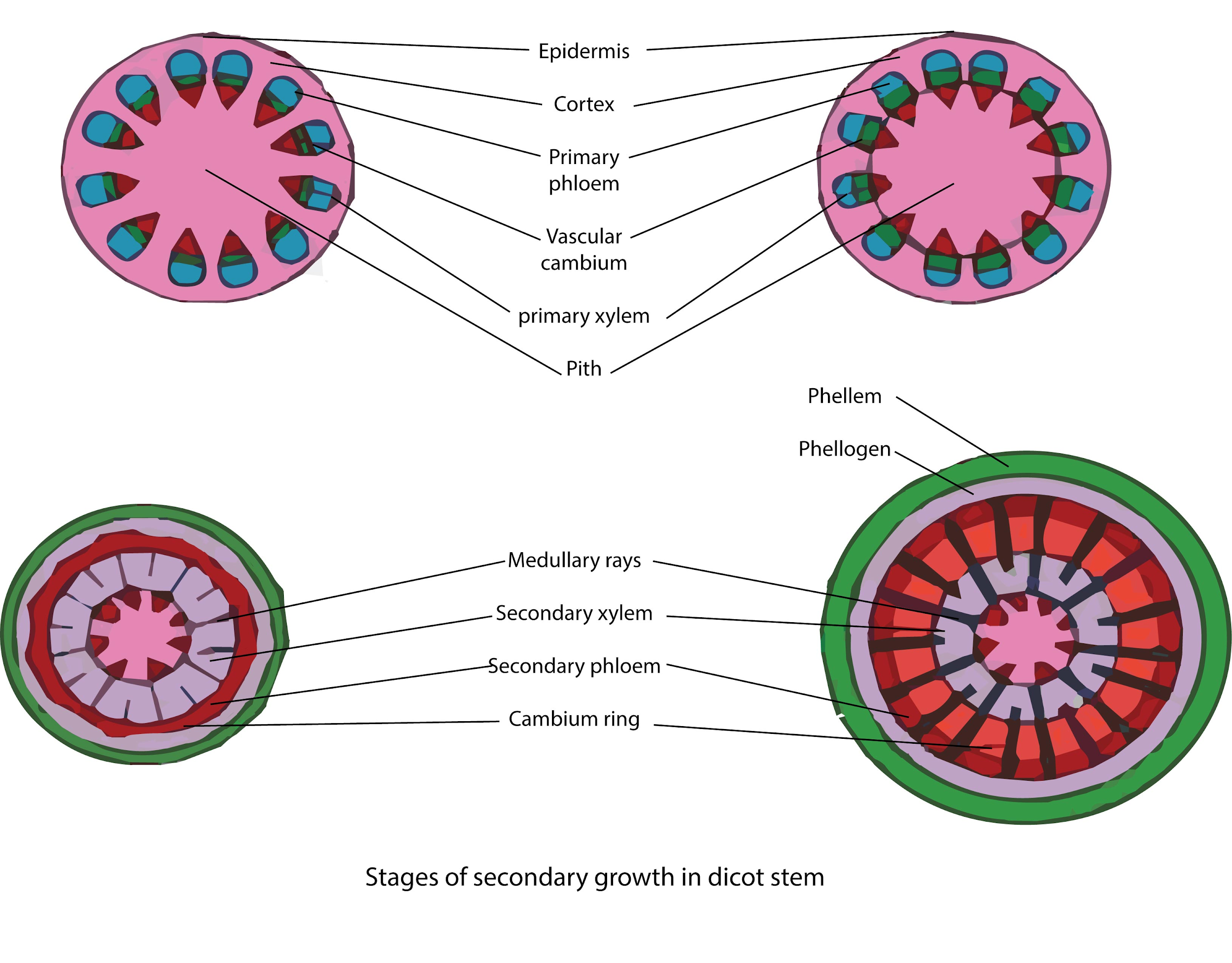 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
| meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples Cambium is a layer of undifferentiated cells between a plant�s phloem and xylem that produces secondary phloem and xylem as the. In woody plants, the vascular cambium is displayed as a structured line separating the wood and the bark. These tend to be on the smaller side and roundish to angular. Cork cambium is one of the plant�s meristems which is a collection of tissues containing a number of embryonic cells for which the growth of plants is responsible.
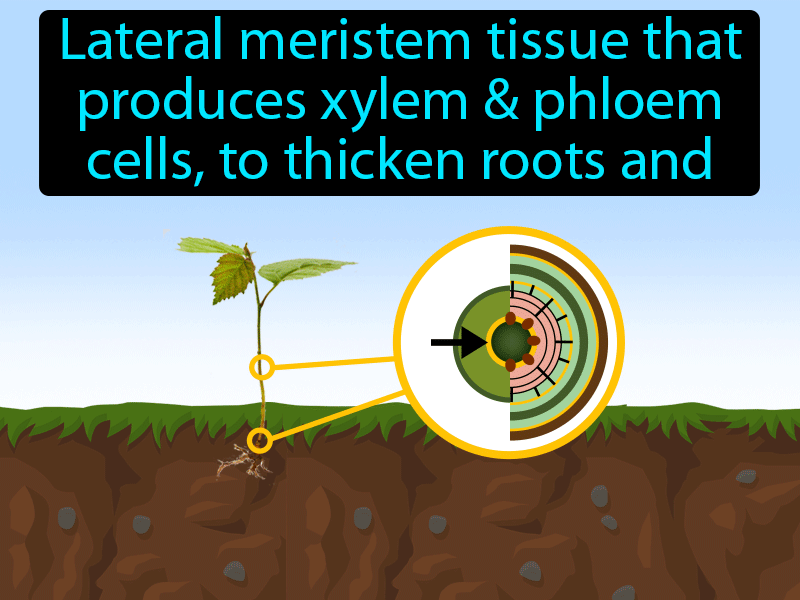 Source: gamesmartz.com
Source: gamesmartz.com
The cambium exists as essentially undifferentiated or blank cells that have no specific purpose until called. The vascular cambium consists of cells within the inside of the plant that is responsible for growth in most plants. By caring for plants and trees each season, they grow healthier and can better resist pests and withstand difficult problems. In plants we see a layer of cells that help it to grow and repair called the cambium. The cambium exists as essentially undifferentiated or blank cells that have no specific purpose until called.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In woody plants, it produces layers of xylem and phloem, consequently enhancing the stem’s diameter. The cork cambium produces some of the bark. It also encourages the secondary growth of roots and stems. It is the availability of photosynthate which makes possible the development of nutritious, edible parts of plants, such as fruits, nuts and grains, bulbs, tubers, other edible roots, and leaves, etc., the source of so much of the food supply of humans and other organisms. In woody plants, it produces layers of xylem and phloem, consequently enhancing the stem’s diameter.
 Source: education-portal.com
Source: education-portal.com
The primary vascular skeleton is built up by the maturing of the cells of the procambium strands to form xylem and phloem. This type of cell is taller and oriented towards the axis. A layer of cells in the roots and stems of some plants that divide to produce new tissue, such…. Cork cambium is one of the plant�s meristems which is a collection of tissues containing a number of embryonic cells for which the growth of plants is responsible. In plants we see a layer of cells that help it to grow and repair called the cambium.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The vascular cambium is also known as main cambium, wood cambium or bifacial cambium. The cambium exists as essentially undifferentiated or blank cells that have no specific purpose until called. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues. In woody plants, cork cambium is the outermost lateral meristem. As it adds layers to the inside ring of the vascular cambium, the outside is pushed outward.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title cambium in plants definition by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






