Your Capillary action in plants images are available in this site. Capillary action in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Capillary action in plants files here. Download all royalty-free images.
If you’re searching for capillary action in plants images information connected with to the capillary action in plants interest, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our site always gives you suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
Capillary Action In Plants. It is defined as the movement of water within the spaces of a porous. The difference between the concentration of water and nutrients between the roots of the plant and the soil. Capillary action is defined as the spontaneous flow of a liquid into a narrow tube or porous material. The roots of plants draw water via capillary action from the soil, and thus, supply it to various parts of the plant including the stems, branches, and leaves.
 Capillary Action American Welding Society Education Online From awo.aws.org
Capillary Action American Welding Society Education Online From awo.aws.org
Amaze your toddlers, preschoolers, kindegartners, and grade 1 students with this magical blooming flowers capillary action experiment for kids!this super simple experiment only needs our flower template, markers, and water to make a walking water science experiment. Capillary action pulls water into the soil. The movement of water from the root to other parts of the plant is known as capillary action in plants. In this activity, students see capillary action. Capillary action is sometimes called capillary motion, capillarity, or. The capillary action is a clever trick plants use to transport water from the roots, up the stem and through to the rest of the plant.
For capillary action to work, the adhesion force between the water and plant tissues must be stronger than the cohesion between water molecules.
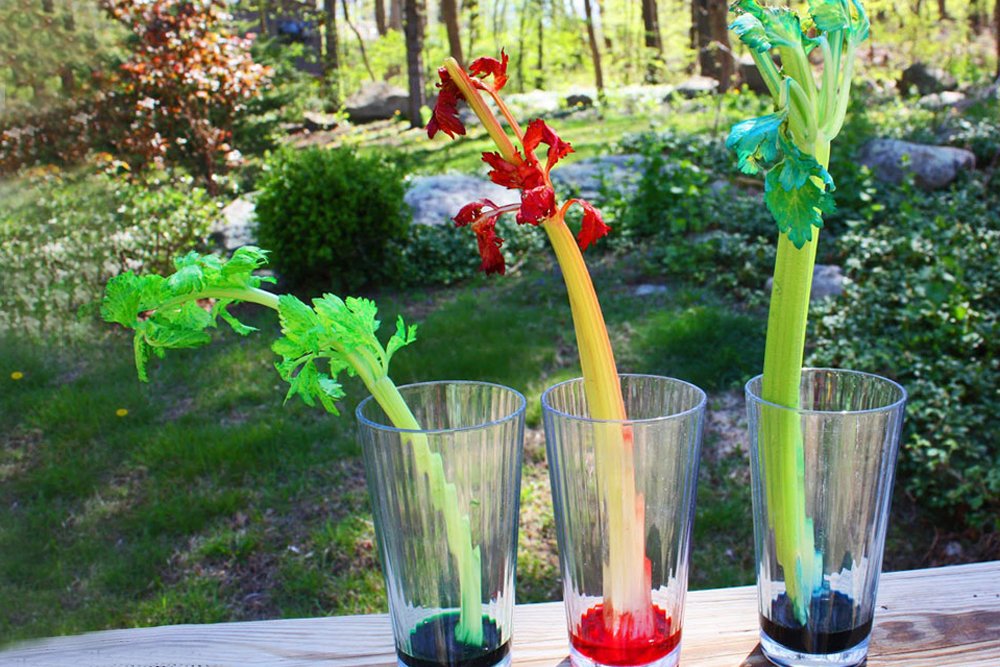
Capillary action serves as a useful phenomenon in vascular plants. It is a process through which liquids move up through a solid like a hollow tube. Have you ever thought of how plants absorb water? Capillary action serves as a useful phenomenon in vascular plants. Watch coloured water flow up a celery stalk, showing just how water moves from the roots of plants to their leaves. All plants need water to survive.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Staining science capillary action of dyed water in plants plant science fair projects plant science science for toddlers. Using a cotton clothesline rope, a bucket of water and the magic of capillary action, the plants water themselves while you are gone. It is defined as the movement of water within the spaces of a porous. But what will captivate your students is the. The capillary action is a clever trick plants use to transport water from the roots, up the stem and through to the rest of the plant.
 Source: bioscvilla-sya.blogspot.com
Source: bioscvilla-sya.blogspot.com
All plants need water to survive. Fresher flowers work better than older ones • knife • camera (optional) preparation • measure a half cup of water and pour. This video is a demonstration of capillary action in plants. Capillary action can be found in numerous examples throughout the world, but it is most significant for its utilization by plants to distribute water to every inch of. It is defined as the movement of water within the spaces of a porous.
 Source: awo.aws.org
Source: awo.aws.org
Plants couldn�t survive without capillary action. All plants need water to survive. The difference between the concentration of water and nutrients between the roots of the plant and the soil. Using capillary action, the dry soil will take the moisture from the bottle. Water starts climbing up through the plant through tiny tubes in the stems and leaves.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
It is defined as the movement of water within the spaces of a porous. Capillary action is responsible for moving water through the xylem of a vascular plant. In the example of a tree and the water in the ground, the liquid is drawn to the cellulose fibers in the tree trunk, which form small capillaries known as xylem. The startling rise of a liquid in a narrow tube is called capillary action or simply, capillarity. In order to transport the water the plant first has to overcome gravity by creating forces that pull the water upwards and through the plant.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Capillary action, properties of water, logging qualitative observations, sc.g.1.3 introduction: All plants need water to survive. Using capillary action, the dry soil will take the moisture from the bottle. The roots of plants draw water via capillary action from the soil, and thus, supply it to various parts of the plant including the stems, branches, and leaves. Watering from the bottom up is better.
 Source: scienceabc.com
Source: scienceabc.com
For capillary action to work, the adhesion force between the water and plant tissues must be stronger than the cohesion between water molecules. In this activity, students see capillary action. In the process of capillary action, three forces are involved, such as: For capillary action to work, the adhesion force between the water and plant tissues must be stronger than the cohesion between water molecules. This movement does not require the force of gravity to occur.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The capillary action is a clever trick plants use to transport water from the roots, up the stem and through to the rest of the plant. Along with root pressure, capillary action contributes in the absorption of water from the soil by the root system up in the xylem vessels from where it is transposed to the other parts of. Watering from the bottom up is better. Plants grow roots into the moist soil and roots absorb water into the plant. Capillary action is important for moving water (and all things dissolved in it) around.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
But capillary action can only pull water up a short distance, In the process of capillary action, three forces are involved, such as: Capillarity plays a crucial role in many natural and engineered systems, ranging from nutrient delivery in plants to functional textiles for wear comfort or thermal heat pipes for heat dissipation. Capillary action is sometimes called capillary motion, capillarity, or. The difference between the concentration of water and nutrients between the roots of the plant and the soil.
 Source: 123homeschool4me.com
Source: 123homeschool4me.com
It is defined as the movement of water within the spaces of a porous. Using capillary action, the dry soil will take the moisture from the bottle. Capillary action can be found in numerous examples throughout the world, but it is most significant for its utilization by plants to distribute water to every inch of. Roots will absorb water from the ground and share it to other parts of the plant like stem, leaves etc. Plants couldn�t survive without capillary action.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
In the example of a tree and the water in the ground, the liquid is drawn to the cellulose fibers in the tree trunk, which form small capillaries known as xylem. Fresher flowers work better than older ones • knife • camera (optional) preparation • measure a half cup of water and pour. The second factor is adhesion, the tendency of some substances to be drawn to unlike substances. Capillary action can be found in numerous examples throughout the world, but it is most significant for its utilization by plants to distribute water to every inch of. The movement of water from the root to other parts of the plant is known as capillary action in plants.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Plants grow roots into the moist soil and roots absorb water into the plant. Capillary action s the movement of a liquid through a narrow space as a result of cohesion, surface tension and adhesion. It is a process through which liquids move up through a solid like a hollow tube. In fact, it often acts in opposition to gravity. Once the nutrients and water enter inside.
 Source: mamaslittlemuse.blogspot.com
Source: mamaslittlemuse.blogspot.com
Capillary action has fascinated people so deeply, in fact, that einstein’s first paper didn’t explore his esoteric theory of cause and effect or gravity, nor did it demonstrate the particle nature of light. Amaze your toddlers, preschoolers, kindegartners, and grade 1 students with this magical blooming flowers capillary action experiment for kids!this super simple experiment only needs our flower template, markers, and water to make a walking water science experiment. Roots will absorb water from the ground and share it to other parts of the plant like stem, leaves etc. In the process of capillary action, three forces are involved, such as: University of florida chemistry outreach program capillary action in plants estimated time:
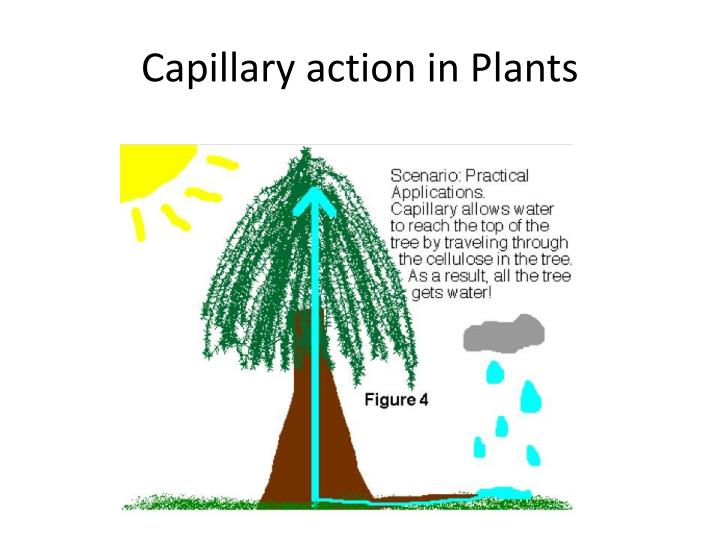 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Capillary action can be found in numerous examples throughout the world, but it is most significant for its utilization by plants to distribute water to every inch of. Capillary action can be found in numerous examples throughout the world, but it is most significant for its utilization by plants to distribute water to every inch of. Capillary action is defined as the spontaneous flow of a liquid into a narrow tube or porous material. The startling rise of a liquid in a narrow tube is called capillary action or simply, capillarity. Watch coloured water flow up a celery stalk, showing just how water moves from the roots of plants to their leaves.
 Source: homeschoolden.com
Source: homeschoolden.com
In the process of capillary action, three forces are involved, such as: Using a cotton clothesline rope, a bucket of water and the magic of capillary action, the plants water themselves while you are gone. This movement does not require the force of gravity to occur. University of florida chemistry outreach program capillary action in plants estimated time: Capillary action has fascinated people so deeply, in fact, that einstein’s first paper didn’t explore his esoteric theory of cause and effect or gravity, nor did it demonstrate the particle nature of light.
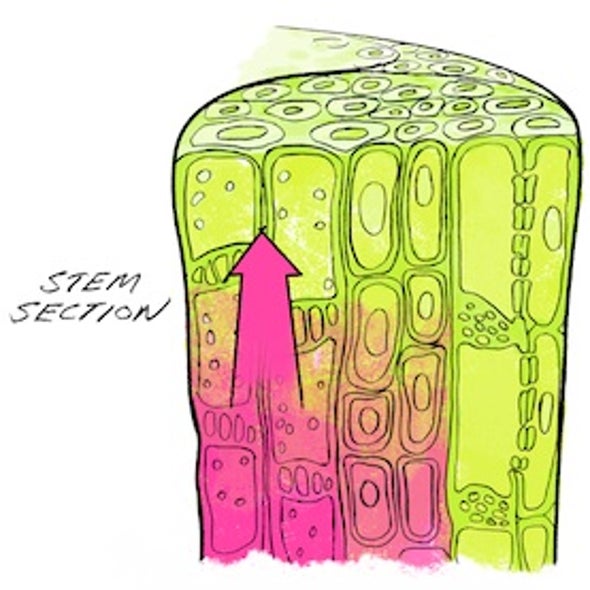 Source: scientificamerican.com
Source: scientificamerican.com
Amaze your toddlers, preschoolers, kindegartners, and grade 1 students with this magical blooming flowers capillary action experiment for kids!this super simple experiment only needs our flower template, markers, and water to make a walking water science experiment. All plants need water to survive. Capillary action is the reason why every plant or tree is still living in the world. Capillary action, properties of water, logging qualitative observations, sc.g.1.3 introduction: Water starts climbing up through the plant through tiny tubes in the stems and leaves.
 Source: single-workingmom.blogspot.com
Source: single-workingmom.blogspot.com
This movement does not require the force of gravity to occur. Using capillary action, the dry soil will take the moisture from the bottle. Capillarity plays a crucial role in many natural and engineered systems, ranging from nutrient delivery in plants to functional textiles for wear comfort or thermal heat pipes for heat dissipation. Capillary action is defined as the spontaneous flow of a liquid into a narrow tube or porous material. University of florida chemistry outreach program capillary action in plants estimated time:
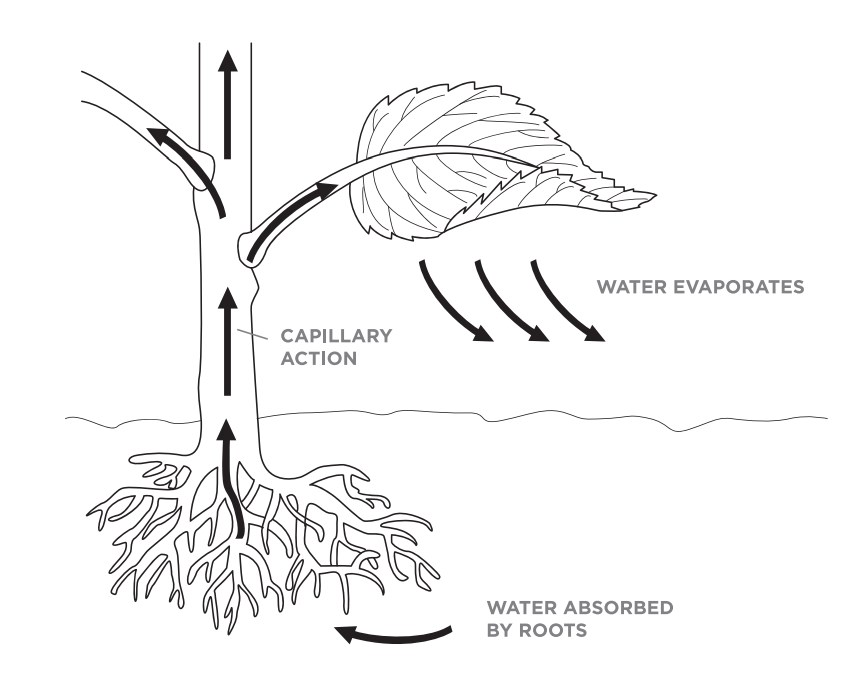 Source: scienceworld.ca
Source: scienceworld.ca
This video is a demonstration of capillary action in plants. Amaze your toddlers, preschoolers, kindegartners, and grade 1 students with this magical blooming flowers capillary action experiment for kids!this super simple experiment only needs our flower template, markers, and water to make a walking water science experiment. All plants need water to survive. The movement of water from the root to other parts of the plant is known as capillary action in plants. Capillary action is the reason why every plant or tree is still living in the world.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Using capillary action, the dry soil will take the moisture from the bottle. In this activity, students see capillary action. In fact, it often acts in opposition to gravity. Along with root pressure, capillary action contributes in the absorption of water from the soil by the root system up in the xylem vessels from where it is transposed to the other parts of. All plants need water to survive.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title capillary action in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






