Your Causes of polyploidy in plants images are available. Causes of polyploidy in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Causes of polyploidy in plants files here. Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for causes of polyploidy in plants pictures information linked to the causes of polyploidy in plants interest, you have come to the ideal site. Our site frequently provides you with suggestions for viewing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
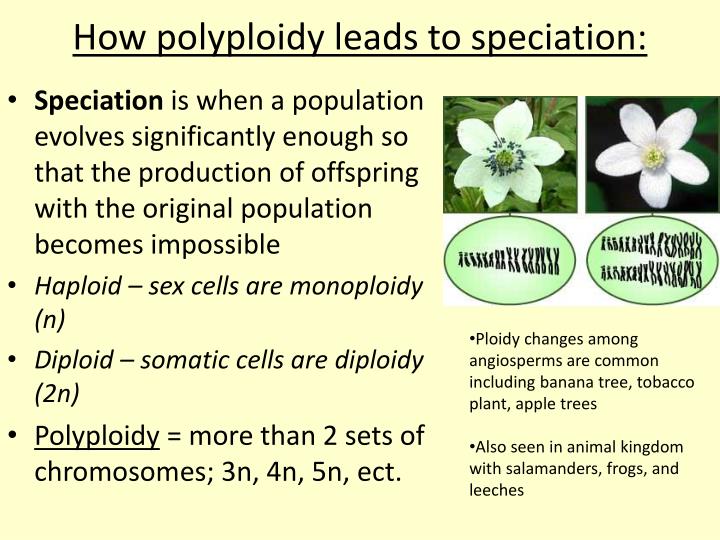
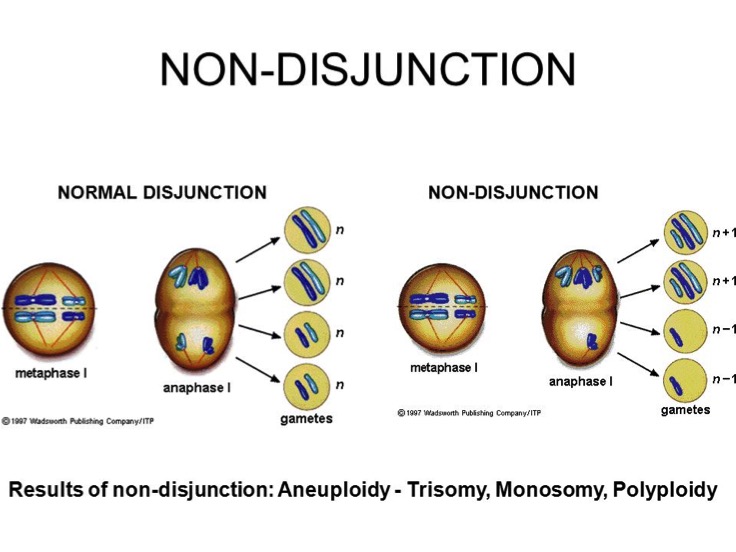
Causes Of Polyploidy In Plants. 6 what are the advantages of polyploidy in plant improvement? This occurs mostly during the meiotic cell divisions. 7 how are somatic polyploid cells formed? Polyploidy arises as the result of total nondisjunction of chromosomes during mitosis or meiosis.
 PPT 15.2 Species and Speciation Overview PowerPoint From slideserve.com
PPT 15.2 Species and Speciation Overview PowerPoint From slideserve.com
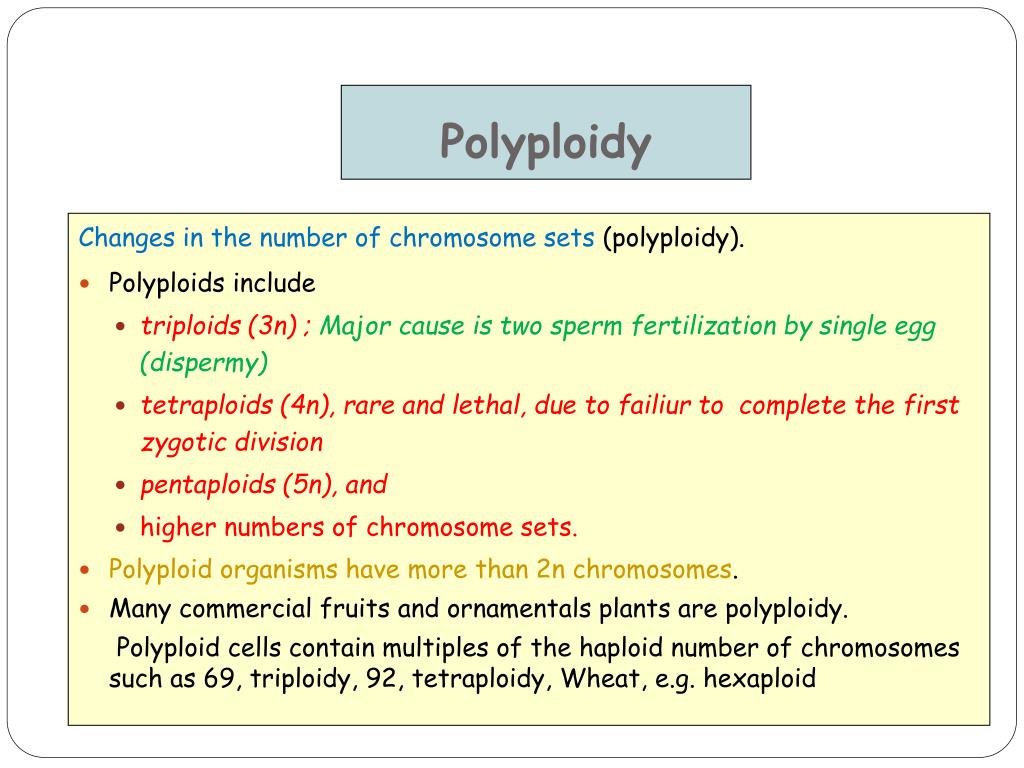
Distribution of polyploidy in the plant kingdom polyploidy is known to a greater or lesser degree in all groups of plants. Polyploidy arises as the result of total nondisjunction of chromosomes during mitosis or meiosis. 7 why is polyploidy common among plants but not animals? In natural plant populations polyploidy usually results from a mutation during cell division, which can be spontaneous mutations or or due to damage from bacteria or other external factors. Polyploidy mostly can be seen in plants, and it mostly finds in the angiosperms. Many plants, however, have more than two copies of each chromosome.
What is polyploidy in plant breeding?
Obligate apomicts are the most desired of hybrids but little gain has been realized towards their development. These mutations in apical meristems results in doubling of growth in plants. 9 how is polyploidy induced in plants? Most apomictic plants are polyploid but most polyploid plants are not apomictic (otto and whitton, 2000). 7 how are somatic polyploid cells formed? In this sense, elucidating the causes and consequences of polyploidy appears fundamental to the study of eukaryotic life forms.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
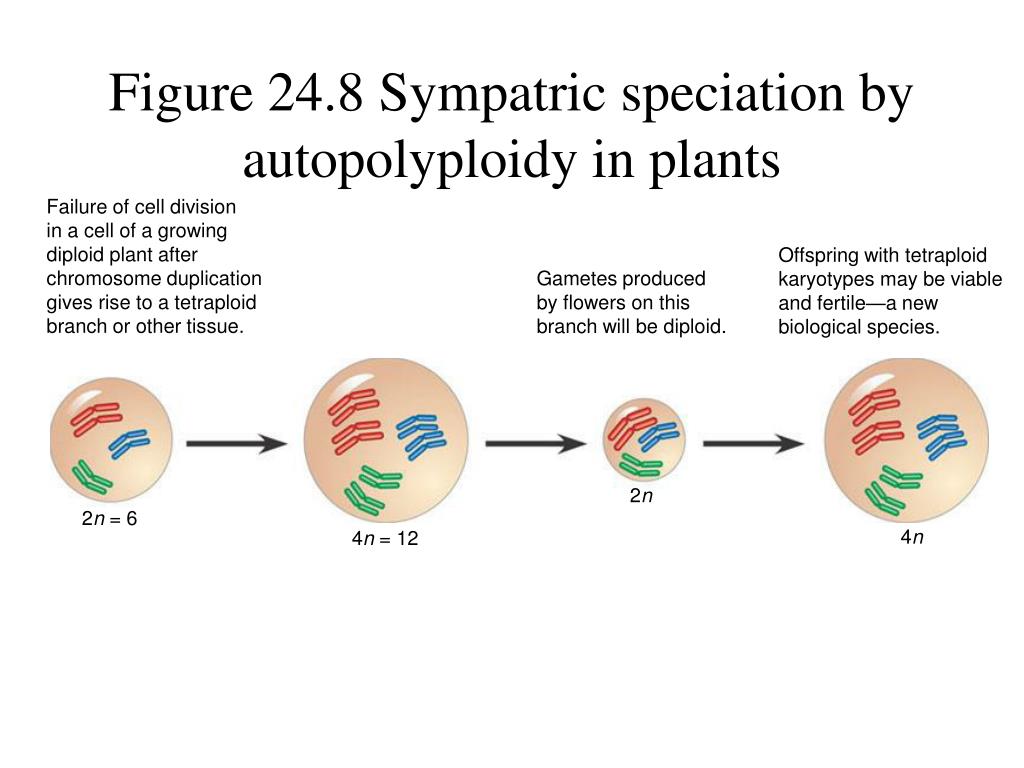
Because chromosome sets are duplicated in polyploids, heterozygosity may be fixed, and random mutation or factors modulating gene expression may be buffered (unlike a diploid), so new genes and gene functions may evolve, leaving the original function in the other chromosome set. Polyploidy arises as the result of total nondisjunction of chromosomes during mitosis or meiosis. Most apomictic plants are polyploid but most polyploid plants are not apomictic (otto and whitton, 2000). Polyploidy can be the result of a spontaneous multiplication of a plants genetic material or through hybridization, and is extremely common in domesticated crops. Polyploidy mostly can be seen in plants, and it mostly finds in the angiosperms.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Schinkel et al., 2016 ). Ehrendorfer, 1980 ), and this has recently been confirmed with more precise data (e.g. In this sense, elucidating the causes and consequences of polyploidy appears fundamental to the study of eukaryotic life forms. Polyploidy can be the result of a spontaneous multiplication of a plants genetic material or through hybridization, and is extremely common in domesticated crops. The causes and molecular consequences of polyploidy in flowering plants.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Obligate apomicts are the most desired of hybrids but little gain has been realized towards their development. 12 what are the causes of aneuploidy and. Lower temperatures), a correlation known for decades (e.g. In this sense, elucidating the causes and consequences of polyploidy appears fundamental to the study of eukaryotic life forms. Most apomictic plants are polyploid but most polyploid plants are not apomictic (otto and whitton, 2000).
 Source: cannabisindustryjournal.com
Source: cannabisindustryjournal.com
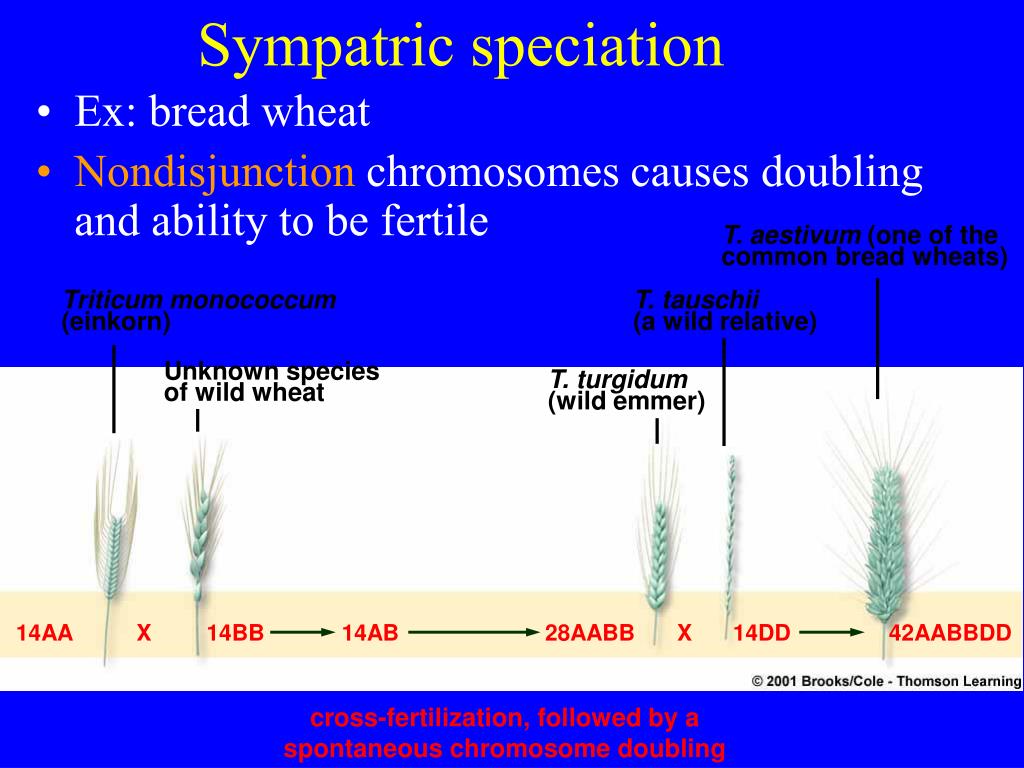
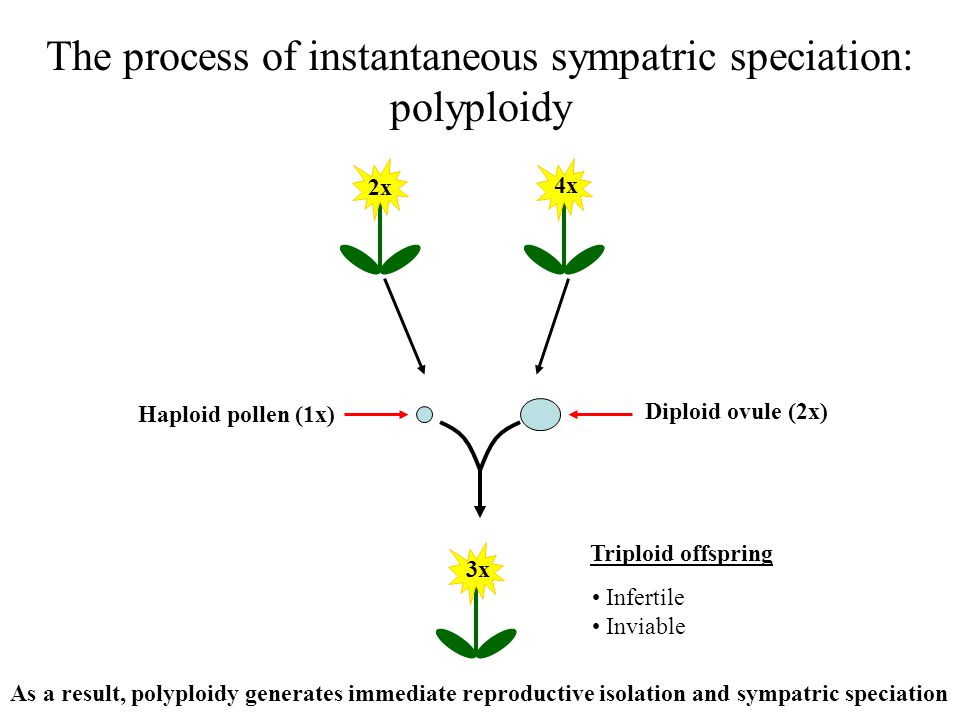
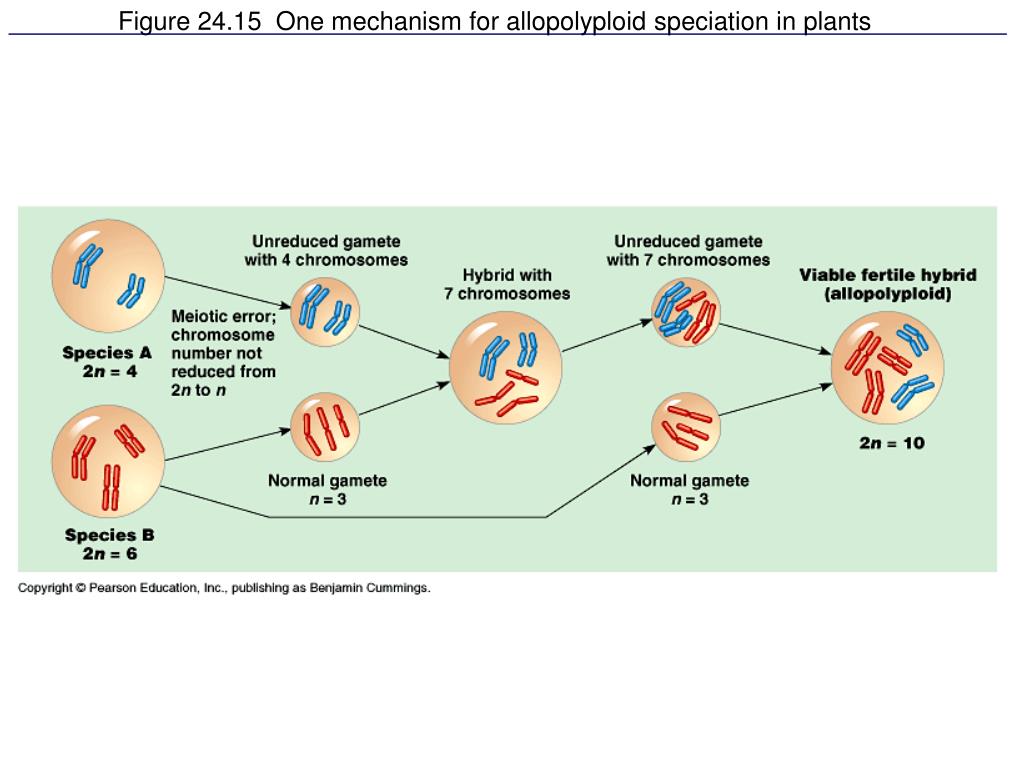
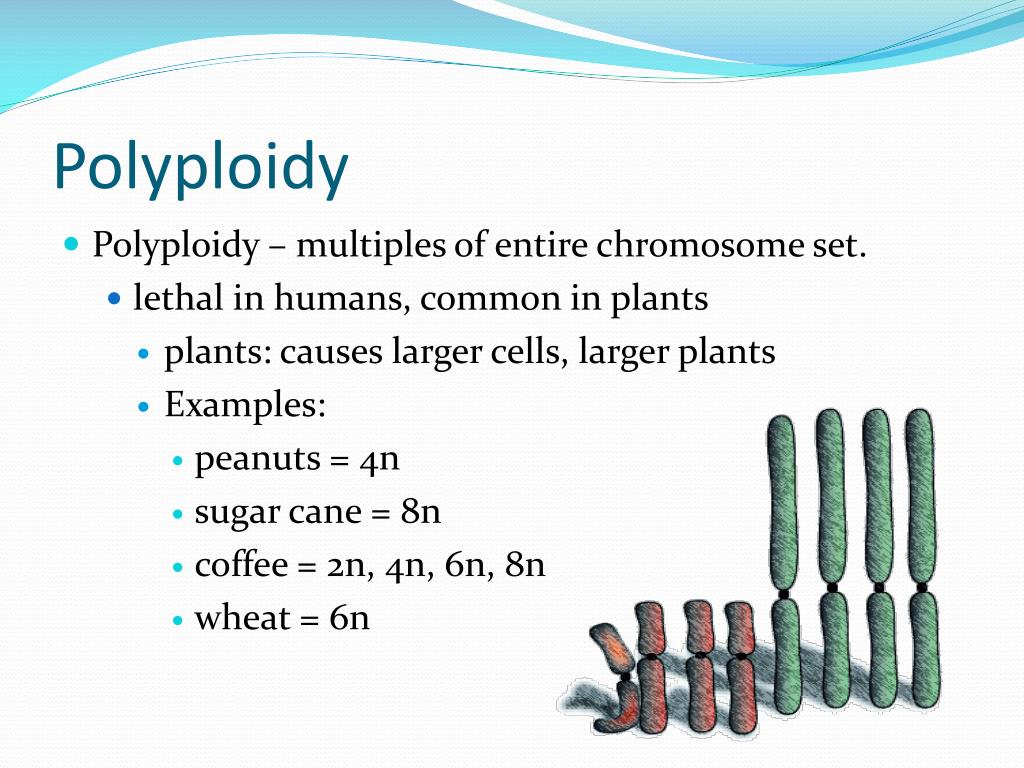
All flowering plants are descendants of an ancestral polyploid species, and up to 70% of extant vascular plant species are believed to be recent polyploids. One mutation occurs as an interruption of meiosis when the plant cells are dividing and making egg cells or pollen (gametes). Some of the most important consequences of polyploidy for plant breeding are the increment in plant organs (“gigas” effect), buffering of deleterious mutations, increased heterozygosity, and. Most apomictic plants are polyploid but most polyploid plants are not apomictic (otto and whitton, 2000). That makes you a diploid organism.
 Source: biodiversity.institute.ufl.edu
Source: biodiversity.institute.ufl.edu
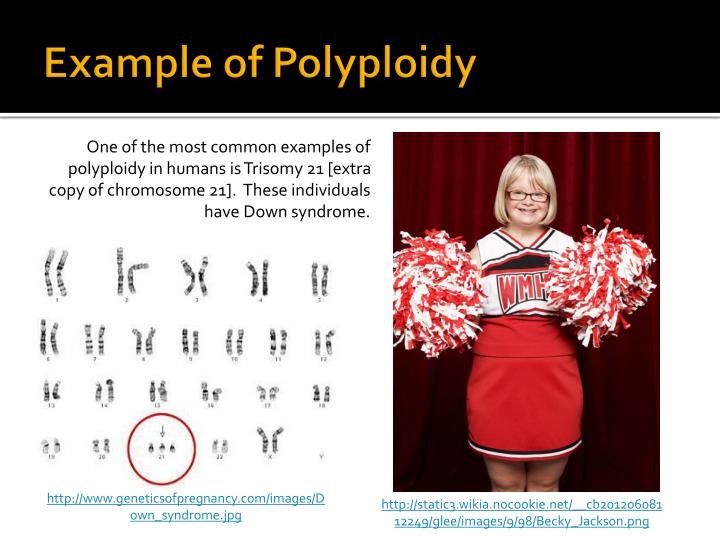
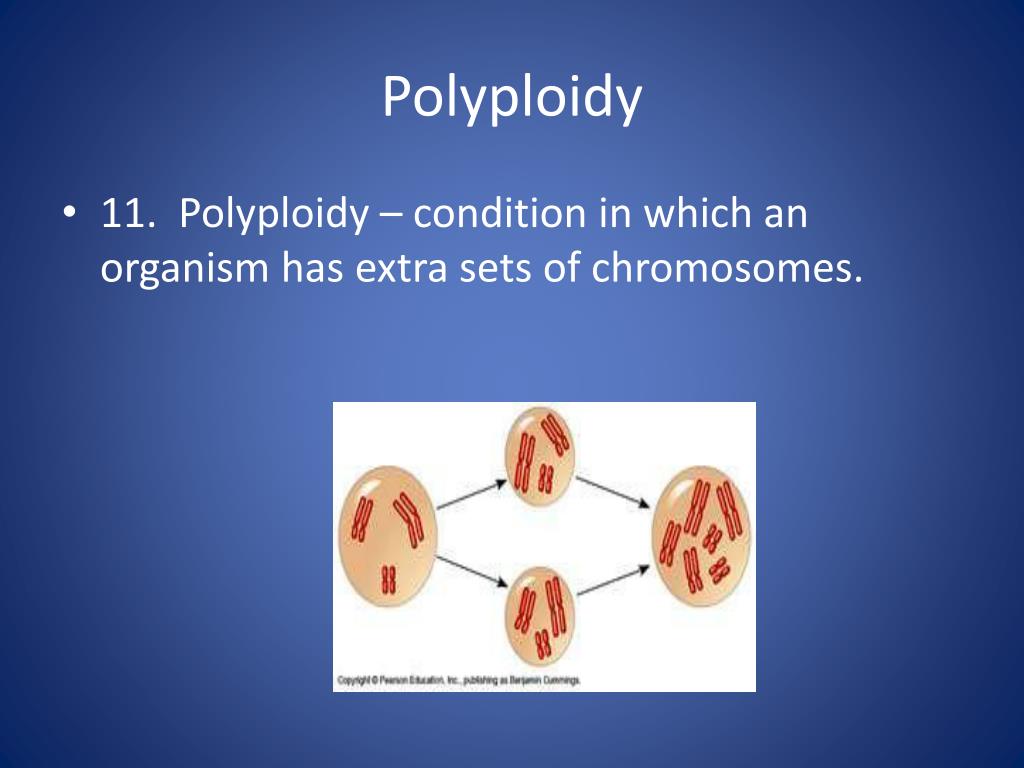
That makes you a diploid organism. This occurs mostly during the meiotic cell divisions. Polyploidy, the condition in which a normally diploid cell or organism acquires one or more additional sets of chromosomes. Polyploidy is a major force in the evolution of both wild and cultivated plants. Polyploidy arises as the result of total nondisjunction of chromosomes during mitosis or meiosis.
 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
Polyploidy is an important force shaping plant genomes. That makes you a diploid organism. 7 how are somatic polyploid cells formed? (i) doubling of the chromosomes during early stage of development of the embryo. What is polyploidy in plant breeding?
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
7 how are somatic polyploid cells formed? Polyploidy mostly can be seen in plants, and it mostly finds in the angiosperms. They causes triploid and tetraploid condition which are lethal. 9 how is polyploidy induced in plants? There are several possible explanations for this observation.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
7 how are somatic polyploid cells formed? In other words, the polyploid cell or organism has three or more times the haploid chromosome number. Polyploidy arises as the result of total nondisjunction of chromosomes during mitosis or meiosis. Although it has been studied very little in the thallo phytes, multiple series of chromosome numbers have been re ported in some genera of algae, such as cladophora, chara} and lornentaria (tischler 1931, 1936, 1938. This occurs mostly during the meiotic cell divisions.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
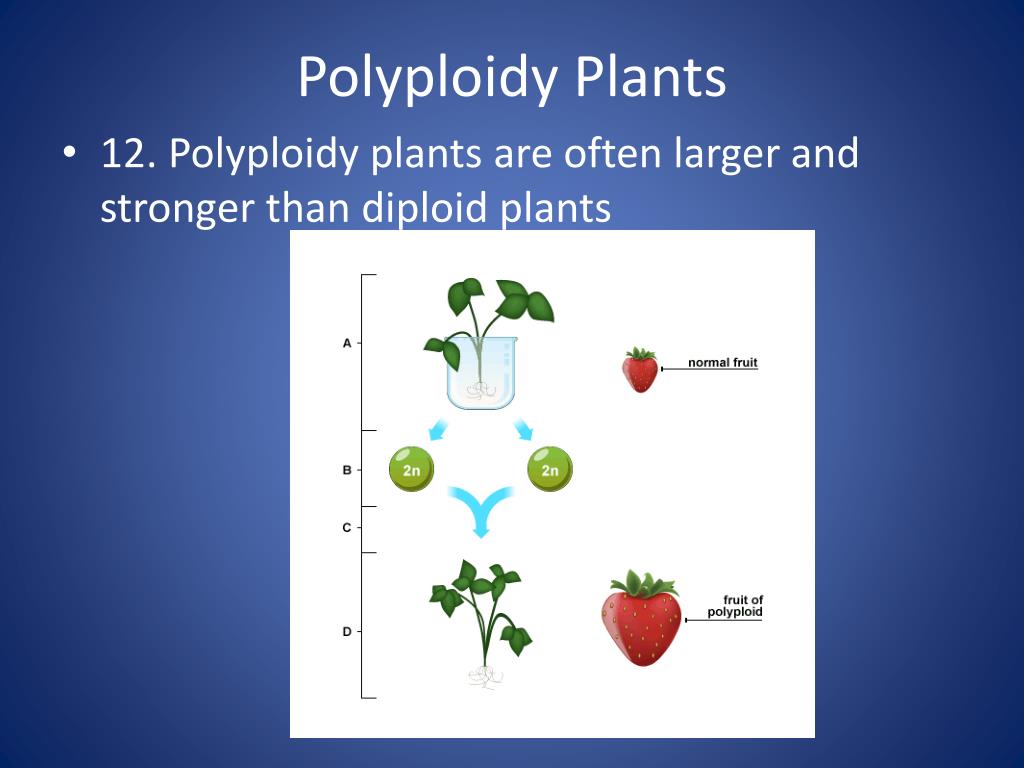
8 how does polyploidy cause reproductive isolation quizlet? Causes or origin of polyploidy: Schinkel et al., 2016 ). Polyploidy is an important force shaping plant genomes. Along with increasing the size of various vegetative and reproductive parts in tetraploid plants, chromosome duplication may also alter the plant growth habits, sexuality patterns, sterility and sometimes, increases the cold hardiness [ 16 ].
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Keeping this in view, what causes polyploidy in plants? Polyploidy is an important force shaping plant genomes. In plants capable of both sexual and asexual reproduction, polyploidy promotes the latter (dhawan and lavania, 1996; What is the cause of polyploidy class 12? 11 what is the significance of polyploidy in evolution?
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Along with increasing the size of various vegetative and reproductive parts in tetraploid plants, chromosome duplication may also alter the plant growth habits, sexuality patterns, sterility and sometimes, increases the cold hardiness [ 16 ]. Polyploids arise when a rare mitotic or meiotic catastrophe, such as nondisjunction, causes the formation of gametes that have a complete set of duplicate chromosomes. The formation of polyploids does correlate with some environmental factors, such as latitude and elevation (i.e. Polyploidy causes intensification of flower color, increasing flower size and alters the plant shape. Polyploidy mostly can be seen in plants, and it mostly finds in the angiosperms.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
2 why ploidy is more in plants? This occurs mostly during the meiotic cell divisions. Although it has been studied very little in the thallo phytes, multiple series of chromosome numbers have been re ported in some genera of algae, such as cladophora, chara} and lornentaria (tischler 1931, 1936, 1938. Lower temperatures), a correlation known for decades (e.g. There are several possible explanations for this observation.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Polyploidy is a major force in the evolution of both wild and cultivated plants. 3 why is polyploidy so much more common in plants than in animals? Autopolyploids results from failure of segregation of chromosomes during game formation. Over the past century, a significant body of knowledge has accumulated regarding the prevalence and ecology of polyploid plants. What is the cause of polyploidy class 12?
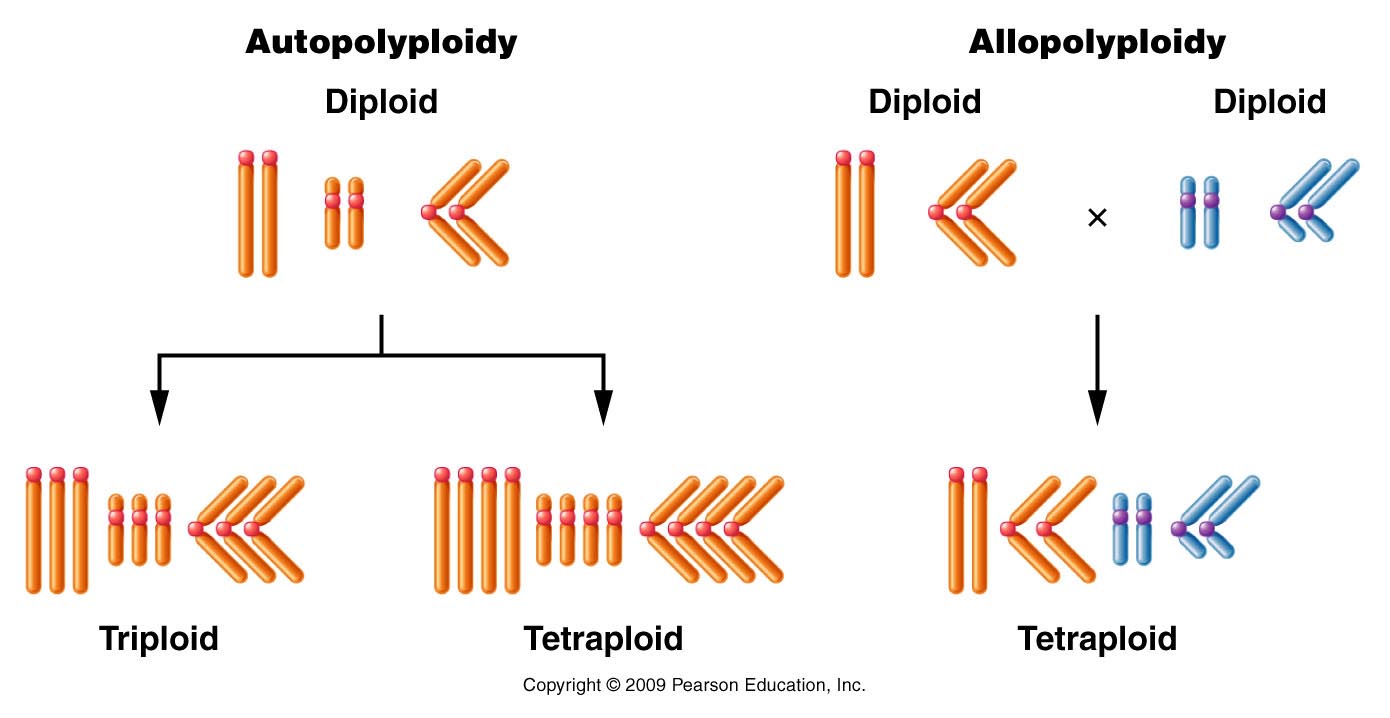 Source: www2.samford.edu
Source: www2.samford.edu
Although it has been studied very little in the thallo phytes, multiple series of chromosome numbers have been re ported in some genera of algae, such as cladophora, chara} and lornentaria (tischler 1931, 1936, 1938. That makes you a diploid organism. They cause chromosomal disorders which are lethal. Along with increasing the size of various vegetative and reproductive parts in tetraploid plants, chromosome duplication may also alter the plant growth habits, sexuality patterns, sterility and sometimes, increases the cold hardiness [ 16 ]. There are several possible explanations for this observation.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
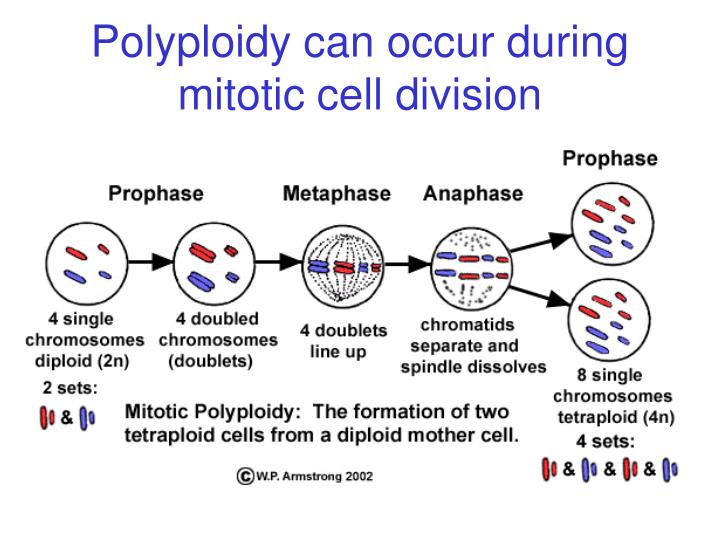
Along with increasing the size of various vegetative and reproductive parts in tetraploid plants, chromosome duplication may also alter the plant growth habits, sexuality patterns, sterility and sometimes, increases the cold hardiness [ 16 ]. Over the past century, a significant body of knowledge has accumulated regarding the prevalence and ecology of polyploid plants. In natural plant populations polyploidy usually results from a mutation during cell division, which can be spontaneous mutations or or due to damage from bacteria or other external factors. All flowering plants are descendants of an ancestral polyploid species, and up to 70% of extant vascular plant. Polyploids arise when a rare mitotic or meiotic catastrophe, such as nondisjunction, causes the formation of gametes that have a complete set of duplicate chromosomes.
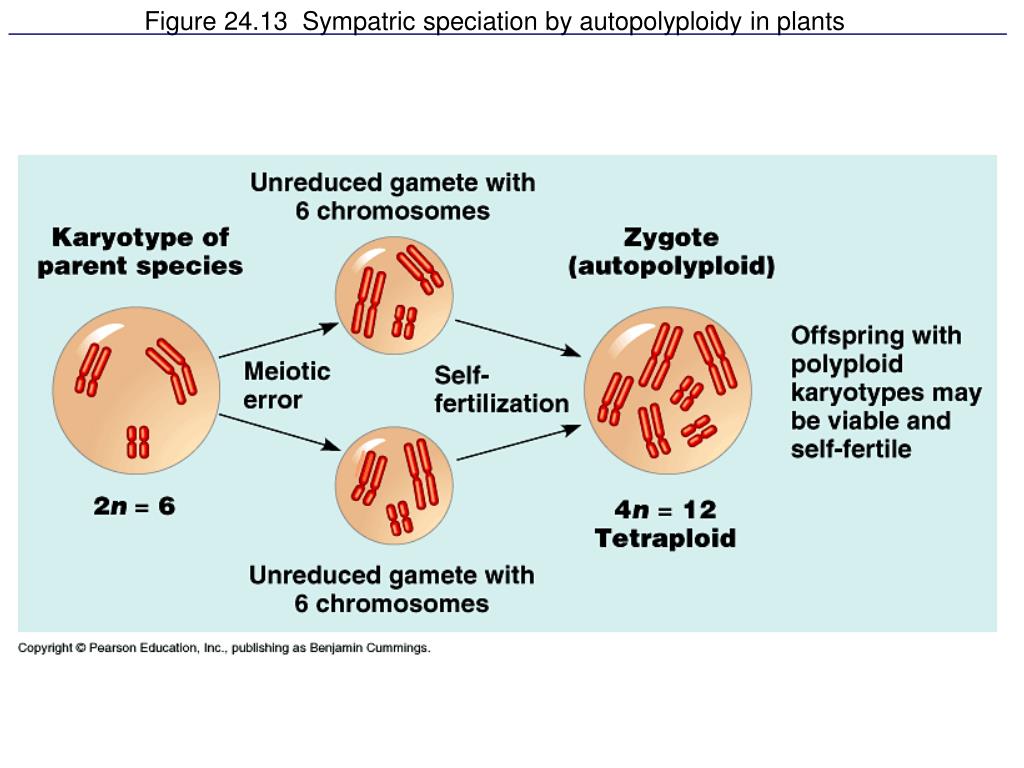 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Polyploids arise when a rare mitotic or meiotic catastrophe, such as nondisjunction, causes the formation of gametes that have a complete set of duplicate chromosomes. Because chromosome sets are duplicated in polyploids, heterozygosity may be fixed, and random mutation or factors modulating gene expression may be buffered (unlike a diploid), so new genes and gene functions may evolve, leaving the original function in the other chromosome set. What is the cause of polyploidy class 12? • polyploidy results in instant speciation as the polyploids will not be able to reproduce with the original population 1 why does polyploidy occur more in plants?
 Source: qspace.library.queensu.ca
Source: qspace.library.queensu.ca
Before undergoing meiosis, the chromosome number is doubled during gamete formation. Before undergoing meiosis, the chromosome number is doubled during gamete formation. 4 is polyploidy more common in plants? In plants capable of both sexual and asexual reproduction, polyploidy promotes the latter (dhawan and lavania, 1996; Autopolyploids results from failure of segregation of chromosomes during game formation.
 Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
1 why does polyploidy occur more in plants? When it occurs due to loss of chromosome it is called hyperploidy and when it occurs due to addition of chromosomes it is called hyper ploidy.complete answer: 8 how does polyploidy cause reproductive isolation quizlet? (i) doubling of the chromosomes during early stage of development of the embryo. 9 how is polyploidy induced in plants?
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title causes of polyploidy in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






