Your Circadian rhythm in plants images are available in this site. Circadian rhythm in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Circadian rhythm in plants files here. Get all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for circadian rhythm in plants pictures information linked to the circadian rhythm in plants keyword, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website always gives you hints for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Circadian Rhythm In Plants. In order to discuss the circadian (or other types) rhythms in plants, it is necessary first to get acquainted with common terms usually encountered in bio. The scientific literature on circadian rhythms began in 1729 when the french astronomer de mairan reported that the daily leaf movements of the sensitive heliotrope plant (probably mimosa pudica) persisted in constant darkness, demonstrating their endogenous origin (de mairan, 1729). Although plants have provided many examples of rhythmic outputs and our understanding of photoreceptors of circadian input pathways is well advanced, studies with plants have lagged in the identification of components of the central circadian oscillator. It has become clear that plants are richly rhythmic, and many aspects of plant biology, including photosynthetic light harvesting and carbon assimilation, resistance to abiotic stresses, pathogens, and pests, photoperiodic flower induction, petal movement, and floral.
 Thermal adaptation and plasticity of the plant circadian From nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Thermal adaptation and plasticity of the plant circadian From nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
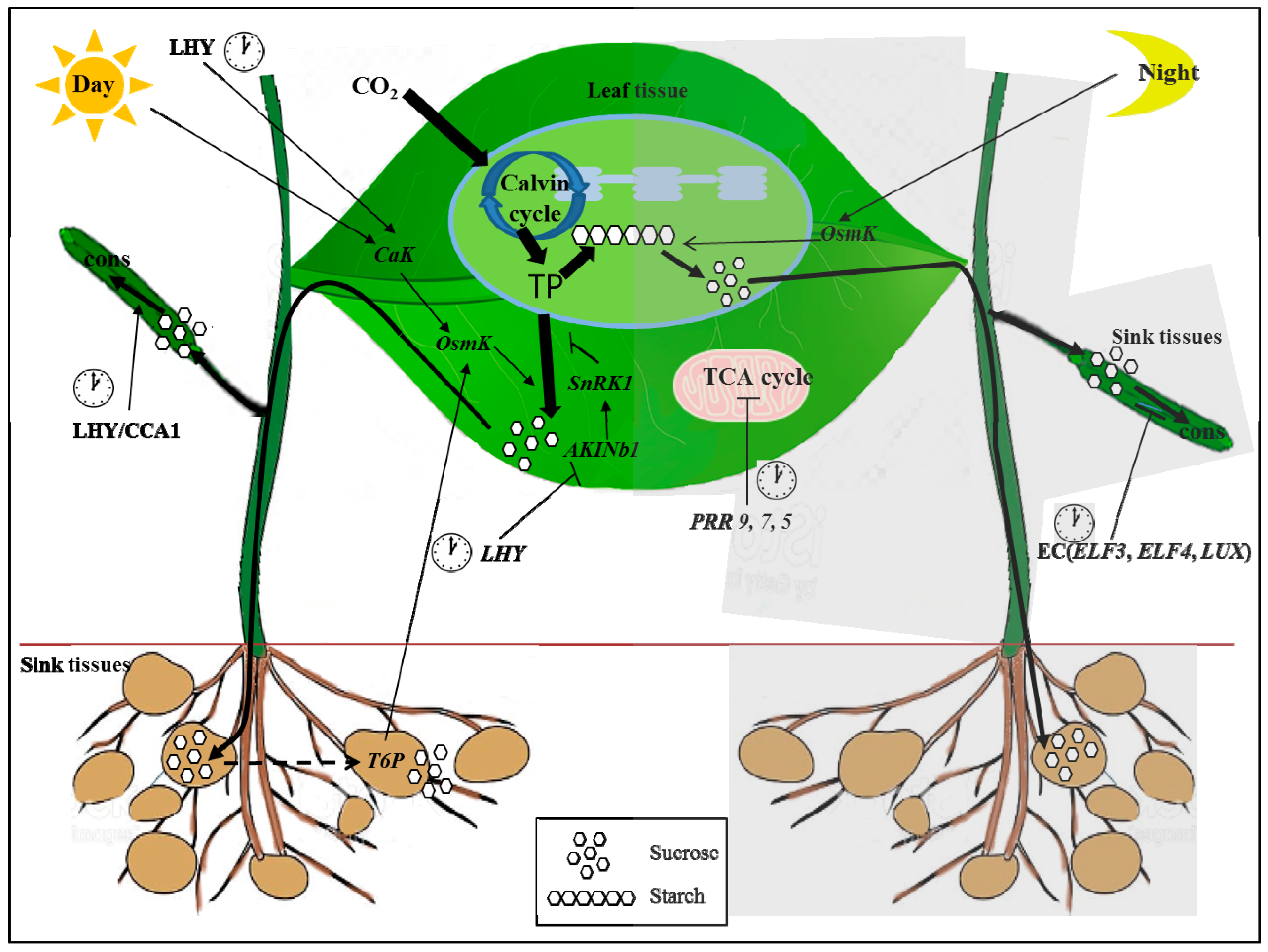
Plants produce sugar via photosynthesis; The circadian clock helps plants to anticipate diurnal changes. Although plants have provided many examples of rhythmic outputs and our understanding of photoreceptors of circadian input pathways is well advanced, studies with plants have lagged in the identification of components of the central circadian oscillator. The genetic identity of some of the components of the core circadian oscillator has recently become known. Behaviors showing rhythms include leaf movement, growth, germination, stomatal/gas exchange, enzyme activity, photosynthetic activity, and. The timing of the rhythms depends on the interaction between the external signal of the surrounding and internal systems of the organism.
Some of the examples of circadian rhythms in plants are given in table 22.1.
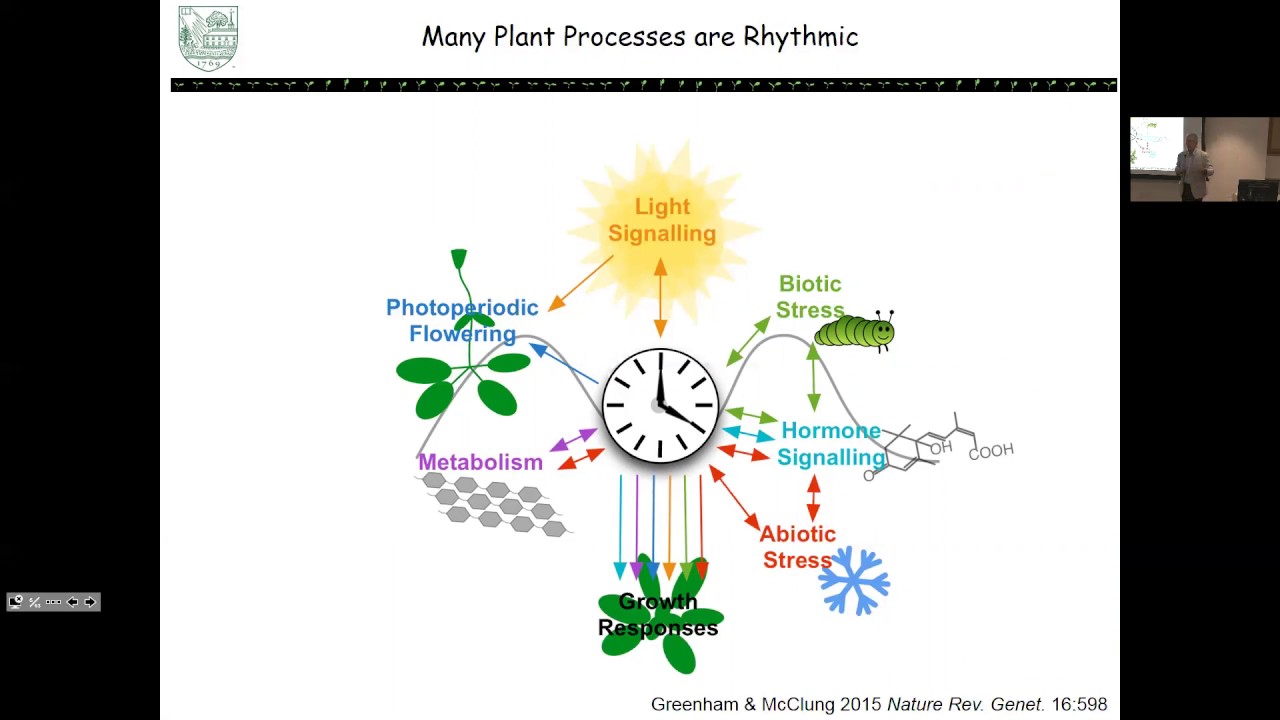
Circadian rhythms are also known to play a key role in water and carbon utilization, plants’ response towards both biotic and abiotic stresses, gas exchange and other important metabolic processes related to growth [9,26,30,31]. The circadian oscillator is a complex network of interconnected feedback loops that regulates a wide range of physiological processes. It is their way of converting the sun�s energy into a usable chemical form needed for growth and function. Similarly, the photoperception and phototransduction pathways that entrain the oscillator to the It has become clear that plants are richly rhythmic, and many aspects of plant biology, including photosynthetic light harvesting and carbon assimilation, resistance to abiotic stresses, pathogens, and pests, photoperiodic flower induction, petal movement, and floral. The circadian biological clock is controlled by a part of the brain called the.
 Source: labroots.com
Source: labroots.com
Circadian rhythms are also known to play a key role in water and carbon utilization, plants’ response towards both biotic and abiotic stresses, gas exchange and other important metabolic processes related to growth [9,26,30,31]. Circadian rhythms regulate many aspects of plant physiology including leaf, organ and stomatal movements, growth and signalling. Various species ranging from bacteria to vertebrates have circadian clocks. Similarly, the photoperception and phototransduction pathways that entrain the oscillator to the It has become clear that plants are richly rhythmic, and many aspects of plant biology, including photosynthetic light harvesting and carbon assimilation, resistance to abiotic stresses, pathogens, and pests, photoperiodic flower induction, petal movement, and floral.
 Source: journal.frontiersin.org
Source: journal.frontiersin.org
Circadian rhythms regulate many aspects of plant physiology including leaf, organ and stomatal movements, growth and signalling. Some of the examples of circadian rhythms in plants are given in table 22.1. Indeed, variation in clock genes has been implicated in an array of plant environmental adaptations, including growth regulation, photoperiodic control of flowering, and responses to abiotic and biotic stress. Behaviors showing rhythms include leaf movement, growth, germination, stomatal/gas exchange, enzyme activity, photosynthetic activity, and. Role of circadian rhythm in plant system:
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The timing of the rhythms depends on the interaction between the external signal of the surrounding and internal systems of the organism. Similarly, the photoperception and phototransduction pathways that entrain the oscillator to the The genetic identity of some of the components of the core circadian oscillator has recently become known. Some of the examples of circadian rhythms in plants are given in table 22.1. Circadian rhythms regulate many aspects of plant physiology including leaf, organ and stomatal movements, growth and signalling.
 Source: apbiowiki.com
Source: apbiowiki.com
Circadian rhythms in plants circadian rhythms in plants abstract the circadian oscillator is a complex network of interconnected feedback loops that regulates a. Using mathematical modeling and experimental approaches, workers in the field have developed a. However, it is emerging that the circadian clock has. Plants have internal timekeeper known as a circadian clock that anticipates environmental cues such as light, temperature and regulates photoperiodic rhythmicity for the proper growth and fitness of the plants. Leaf movement, germination, stomatal/gas exchange, development, photosynthetic activity, fragrance emission and enzyme activity are just a few of the behaviours that display rhythms.
 Source: en.getmoona.com
Source: en.getmoona.com
16 rows circadian rhythm prepares the plants for upcoming challenges by anticipating daily. Srivastava, d., shamim, m., kumar, m., mishra, a., maurya, r., sharma, d.,. Presciently, de mairan suggested that these rhythms were related to the sleep rhythms of. Most of our knowledge of the molecular aspects of circadian regulation in plants is derived from laboratory experiments that are performed under controlled conditions. Circadian rhythm in plants plant circadian rhythms notify each plant what season it is and when it is supposed to bloom to maximise pollinator attraction.
 Source: visual.ly
Source: visual.ly
The circadian biological clock is controlled by a part of the brain called the. The circadian clock helps plants to anticipate diurnal changes. Circadian rhythms regulate many aspects of plant physiology including leaf, organ and stomatal movements, growth and signalling. The genetic identity of some of the components of the core circadian oscillator has recently become known. Indeed, variation in clock genes has been implicated in an array of plant environmental adaptations, including growth regulation, photoperiodic control of flowering, and responses to abiotic and biotic stress.
 Source: plantae.org
Source: plantae.org
The genetic identity of some of the components of the core circadian oscillator has recently become known. Various species ranging from bacteria to vertebrates have circadian clocks. Plants produce sugar via photosynthesis; The scientific literature on circadian rhythms began in 1729 when the french astronomer de mairan reported that the daily leaf movements of the sensitive heliotrope plant (probably mimosa pudica) persisted in constant darkness, demonstrating their endogenous origin ( de mairan, 1729 ). And their complex patterns were being noted by albertus magnus in the thirteenth century.
 Source: phys.org
Source: phys.org
Most of our knowledge of the molecular aspects of circadian regulation in plants is derived from laboratory experiments that are performed under controlled conditions. Molecular identification of clock components, primarily in arabidopsis, has led to recent rapid progress in our understanding of the clock mechanism in higher plants. In plants, proper entrainment of the. It is their way of converting the sun�s energy into a usable chemical form needed for growth and function. However, it is emerging that the circadian clock has.
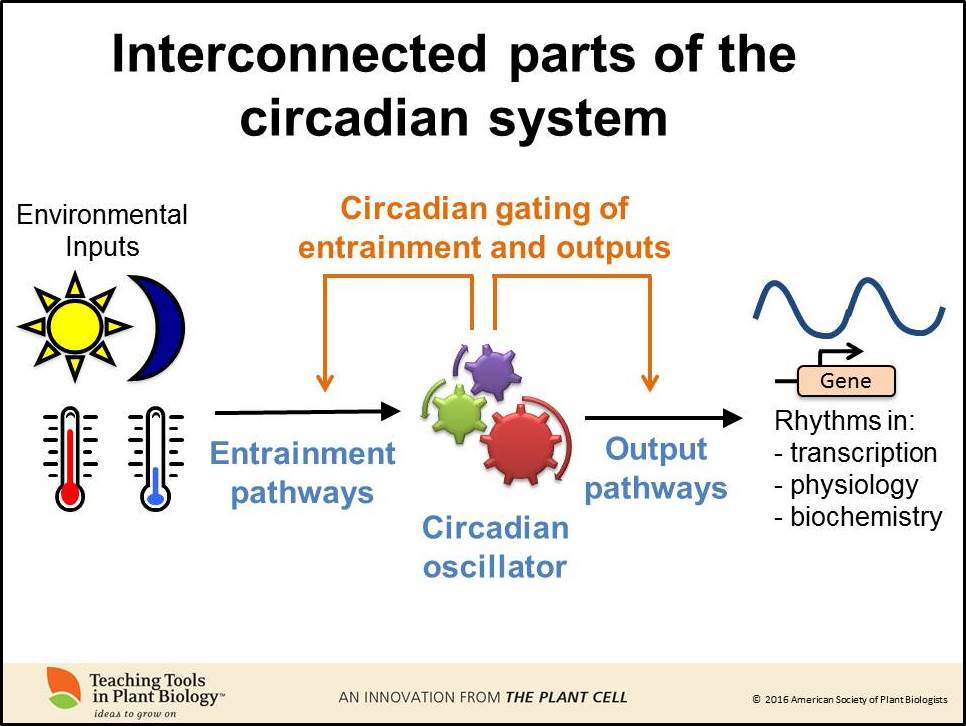 Source: blog.aspb.org
Source: blog.aspb.org
Circadian rhythms in plants definition. In plants, circadian regulation forms an essential adaptation to the fluctuating environment. Many physiological processes in plants like stress acclimatization, hormone signaling, photo morphogenesis, carbon metabolism and defense signaling are currently being explored for their cross linking with the circadian clock. Leaf movement, germination, stomatal/gas exchange, development, photosynthetic activity, fragrance emission and enzyme activity are just a few of the behaviours that display rhythms. The scientific literature on circadian rhythms began in 1729 when the french astronomer de mairan reported that the daily leaf movements of the sensitive heliotrope plant (probably mimosa pudica) persisted in constant darkness, demonstrating their endogenous origin ( de mairan, 1729 ).
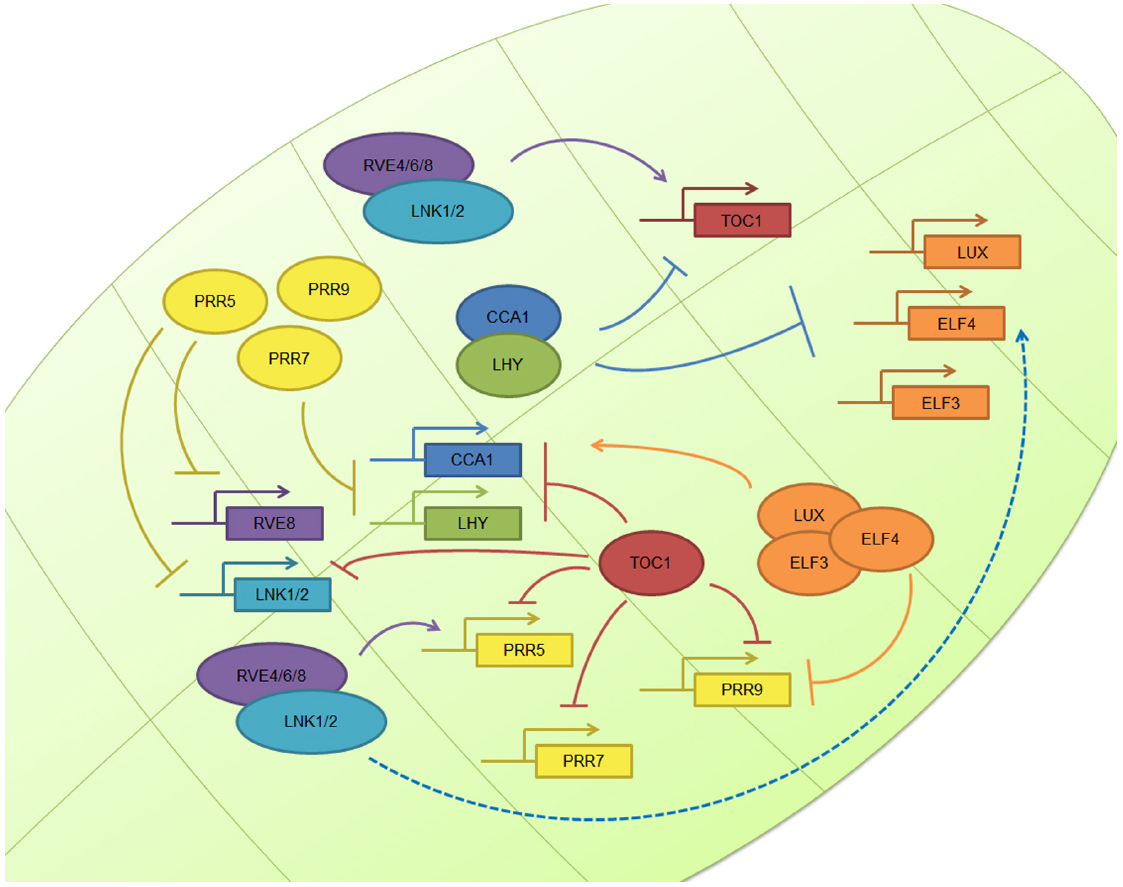 Source: journal.frontiersin.org
Source: journal.frontiersin.org
Circadian rhythms are also known to play a key role in water and carbon utilization, plants’ response towards both biotic and abiotic stresses, gas exchange and other important metabolic processes related to growth [9,26,30,31]. The circadian biological clock is controlled by a part of the brain called the. Role of circadian rhythm in plant system: The timing of the rhythms depends on the interaction between the external signal of the surrounding and internal systems of the organism. Presciently, de mairan suggested that these rhythms were related to the sleep rhythms of.
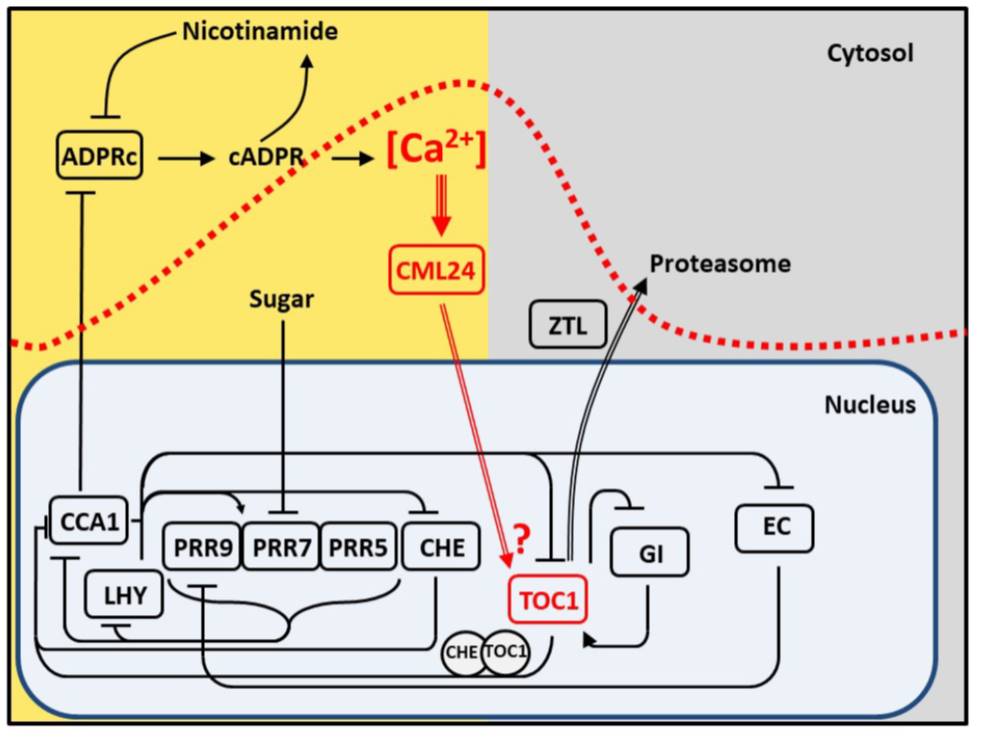 Source: plantae.org
Source: plantae.org
Role of circadian rhythm in plant system: Behaviors showing rhythms include leaf movement, growth, germination, stomatal/gas exchange, enzyme activity, photosynthetic activity, and. In order to discuss the circadian (or other types) rhythms in plants, it is necessary first to get acquainted with common terms usually encountered in bio. The circadian rhythm in plants allows them to time their defenses against invading hosts, anticipate attacks and plan for a defensive response. Most of our knowledge of the molecular aspects of circadian regulation in plants is derived from laboratory experiments that are performed under controlled conditions.
 Source: pdfslide.net
Source: pdfslide.net
Circadian rhythms produce a biological measure of the time of day. In plants, circadian regulation forms an essential adaptation to the fluctuating environment. The circadian biological clock is controlled by a part of the brain called the. The movement of leaves had attracted the attention of pliny in the first century a.d. Circadian rhythms in plants circadian rhythms in plants abstract the circadian oscillator is a complex network of interconnected feedback loops that regulates a.
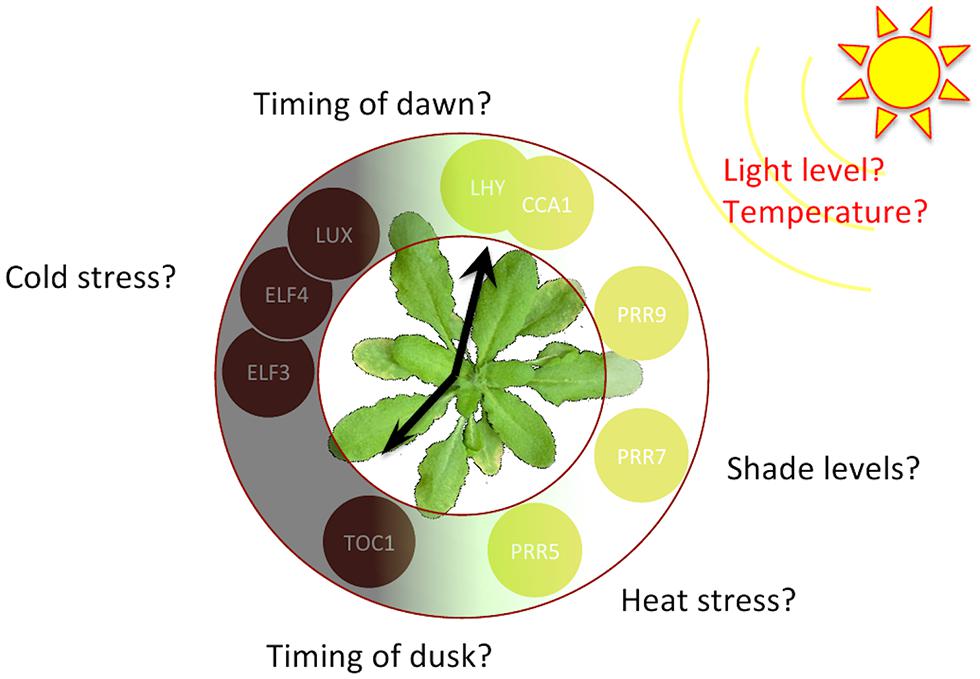 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Presciently, de mairan suggested that these rhythms were related to the sleep rhythms of. Although plants have provided many examples of rhythmic outputs and our understanding of photoreceptors of circadian input pathways is well advanced, studies with plants have lagged in the identification of components of the central circadian oscillator. In order to discuss the circadian (or other types) rhythms in plants, it is necessary first to get acquainted with common terms usually encountered in bio. Plant circadian rhythms include cycles in gene regulation, enzyme activity, leaf movements, flower opening, and stomatal opening.circadian rhythms also interact with photoperiodism in the control of major developmental processes, such as dormancy and the induction of flowering. The circadian clock helps plants to anticipate diurnal changes.
 Source: pdfslide.net
Source: pdfslide.net
Plants have internal timekeeper known as a circadian clock that anticipates environmental cues such as light, temperature and regulates photoperiodic rhythmicity for the proper growth and fitness of the plants. Circadian rhythms in plants circadian rhythms in plants abstract the circadian oscillator is a complex network of interconnected feedback loops that regulates a. Indeed, variation in clock genes has been implicated in an array of plant environmental adaptations, including growth regulation, photoperiodic control of flowering, and responses to abiotic and biotic stress. Abstract circadian rhythms, endogenous rhythms with periods of approximately 24 h, are widespread in nature. Most of our knowledge of the molecular aspects of circadian regulation in plants is derived from laboratory experiments that are performed under controlled conditions.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The timing of the rhythms depends on the interaction between the external signal of the surrounding and internal systems of the organism. Abstract circadian rhythms, endogenous rhythms with periods of approximately 24 h, are widespread in nature. Indeed, variation in clock genes has been implicated in an array of plant environmental adaptations, including growth regulation, photoperiodic control of flowering, and responses to abiotic and biotic stress. Circadian rhythms in plants definition. However, it is emerging that the circadian clock has.
 Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
Behaviors showing rhythms include leaf movement, growth, germination, stomatal/gas exchange, enzyme activity, photosynthetic activity, and. Plant circadian rhythms tell the plant what season it is and when to flower for the best chance of attracting pollinators. | powerpoint ppt presentation | free to view Similarly, the photoperception and phototransduction pathways that entrain the oscillator to the The genetic identity of some of the components of the core circadian oscillator has recently become known.
 Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Circadian rhythms regulate many aspects of plant physiology including leaf, organ and stomatal movements, growth and signalling. Molecular identification of clock components, primarily in arabidopsis, has led to recent rapid progress in our understanding of the clock mechanism in higher plants. Using mathematical modeling and experimental approaches, workers in the field have developed a. Circadian rhythms in plants circadian rhythms in plants abstract the circadian oscillator is a complex network of interconnected feedback loops that regulates a. The scientific literature on circadian rhythms began in 1729 when the french astronomer de mairan reported that the daily leaf movements of the sensitive heliotrope plant (probably mimosa pudica) persisted in constant darkness, demonstrating their endogenous origin (de mairan, 1729).
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
It is their way of converting the sun�s energy into a usable chemical form needed for growth and function. Indeed, variation in clock genes has been implicated in an array of plant environmental adaptations, including growth regulation, photoperiodic control of flowering, and responses to abiotic and biotic stress. Using mathematical modeling and experimental approaches, workers in the field have developed a. The existence of circadian rhythms in living organisms was first established during a detailed study of leaf movement in plants more than 200 years ago. The circadian clock regulates diverse aspects of plant growth and development and promotes plant fitness.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title circadian rhythm in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






