Your Contamination control in plant tissue culture images are ready in this website. Contamination control in plant tissue culture are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Contamination control in plant tissue culture files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for contamination control in plant tissue culture images information connected with to the contamination control in plant tissue culture topic, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website frequently provides you with suggestions for refferencing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Contamination Control In Plant Tissue Culture. Get any books you like and read everywhere you want. Contamination in tissue culture covers the sources, prevention, detection, and elimination of contamination in tissue culture. Prior to introduction into sterile murashige and skoog (ms) media, nodal explants obtained from potted plants of solanecio biafrae grown in the screenhouse were given various surface sterilization treatments. The main areas of quality control that are of concern for tissue culture are:
 Different types of contaminants in plant tissue culture From labassociates.com
Different types of contaminants in plant tissue culture From labassociates.com
These steps encompass handling of stock plants, type and handling of explants. Disease indexing) of the stock plants with disease and endophyte elimination where detected; Microbial contamination of plant affect adversely in plant tissue culture. Bacterial contaminants are often difficult to Every step of the plant tissue culture process should be considered in order to prevent contamination. Most microbial contaminants are expressed (i.e.
In the intervening years there have been considerable advances in both plant disease diagnostics and in the development of structured approaches to.
Indexing to avoid tissue multiplication w/ contamination cassells. Bacterial contamination is very common in fungal cultures. Quality is important in all aspects of tissue culture. Ptc3 (plant tissue culture contamination control) is a broad spectrum biostat/fungistat that can be added to plant tissue culture media to reduce microbial and fungal contamination. Bacteria, mold, and mycoplasma are common contaminants that most lab personnel are familiar with throughout their work with tissue culture media. In particular, prompt removal of contaminated cultures is needed to protect neighboring cultures, as well as the sterile tissue culture environment including culture incubators, baths, and the biosafety cabinet.
 Source: pinterest.com.au
Source: pinterest.com.au
Additionally, specific testing for bacteria and fungi should be used as part of a routine and regular quality control screening procedure. Some microorganisms are biomarkers for system failures. Recent advances in plant tissue culture, iv: The best way to get rid of contamination is to sterilize the explants. These steps encompass handling of stock plants, type and handling of explants.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Bacteria, mold, and mycoplasma are common contaminants that most lab personnel are familiar with throughout their work with tissue culture media. The best strategy to control tissue culture contamination is to establish aseptic cultures and to maintain good laboratory practice, including routine testing for contamination by cultivable micro. Disease indexing) of the stock plants with disease and endophyte elimination where detected; Losing your tissue culture to everyday contamination. (2011) in plant tissue culture, development and biotechnology ed:
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Using isothiazolone biocides to control microbial and fungal contaminants in plant tissue cultures. The best strategy to control tissue culture contamination is to establish aseptic cultures and to maintain good laboratory practice, including routine testing for contamination by cultivable micro. Detection, and at least partial identification, is a prerequisite for the control and elimination of laboratory contamination. In the intervening years there have been considerable advances in both plant disease diagnostics and in the development of structured approaches to. How is contamination removed from plant tissue culture?
 Source: flickr.com
Source: flickr.com
Bacterial contamination in tissue culture is well documented, and the failure of surface sterilization procedures to produce aseptic cultures is a major problem with woody plants. The main areas of quality control that are of concern for tissue culture are: Currently, the commonly used approach for inhibiting bacteria is antibiotic treatment; Ptc3 (plant tissue culture contamination control) is a broad spectrum biostat/fungistat that can be added to plant tissue culture media to reduce microbial and fungal contamination. (2011) in plant tissue culture, development and biotechnology ed:
 Source: plantcelltechnology.com
Source: plantcelltechnology.com
Detection, and at least partial identification, is a prerequisite for the control and elimination of laboratory contamination. Some microorganisms are biomarkers for system failures. Currently, the commonly used approach for inhibiting bacteria is antibiotic treatment; The best strategy to control tissue culture contamination is to establish aseptic cultures and to maintain good laboratory practice, including routine testing for contamination by cultivable micro. These steps encompass handling of stock plants, type and handling of explants.
 Source: labassociates.com
Source: labassociates.com
Surface sterilization of plant materials is a very problematic step in establishing plant tissue culture protocol. Important contaminants in micropropagated plant cultures. Detection, and at least partial identification, is a prerequisite for the control and elimination of laboratory contamination. Quality is important in all aspects of tissue culture. In particular, prompt removal of contaminated cultures is needed to protect neighboring cultures, as well as the sterile tissue culture environment including culture incubators, baths, and the biosafety cabinet.
 Source: plantcelltechnology.com
Source: plantcelltechnology.com
Different experimental procedures including chemical sterilization and antibiotics have been used at various levels of success to minimize or eliminate such. Additionally, specific testing for bacteria and fungi should be used as part of a routine and regular quality control screening procedure. Microbial contamination of plant tissue cultures., mohegan lake, n.y. (2011) in plant tissue culture, development and biotechnology ed: In the intervening years there have been considerable advances in both plant disease diagnostics and in the development of structured approaches to.
Source: researchgate.net
Surface sterilization of plant materials is a very problematic step in establishing plant tissue culture protocol. In the intervening years there have been considerable advances in both plant disease diagnostics and in the development of structured approaches to. Bacterial contamination is very common in fungal cultures. Grow) on plant tissue culture media but some may be latent (i.e. Evaluation of microbial extracts for contamination control in plant tissue culture systems.
 Source: plantcelltechnology.com
Source: plantcelltechnology.com
Currently, the commonly used approach for inhibiting bacteria is antibiotic treatment; Plant tissue culture can be used widely in plant science or horticulture, primarily for the commercial production of plants in the absence of seeds or necessary pollinators. However, there are drawbacks to using antibiotics, including incomplete removal, limited antibacterial spectra,. In the intervening years there have been considerable advances in both plant disease diagnostics and in the development of structured approaches to. The best way to get rid of contamination is to sterilize the explants.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
However, there are drawbacks to using antibiotics, including incomplete removal, limited antibacterial spectra,. The quality of the reagents and materials Important contaminants in micropropagated plant cultures. Losing your tissue culture to everyday contamination. These steps encompass handling of stock plants, type and handling of explants.
 Source: bukalapak.com
Source: bukalapak.com
Most microbial contaminants are expressed (i.e. Using isothiazolone biocides to control microbial and fungal contaminants in plant tissue cultures. Ptc3 (plant tissue culture contamination control) is a broad spectrum biostat/fungistat that can be added to plant tissue culture media to reduce microbial and fungal contamination. Contamination may arise from the operator and the laboratory environment, from other cells used in the laboratory, and from reagents. Composed of 12 chapters, the book describes the frequency of occurrence of contamination and the many different effects of contamination on cultured cells.
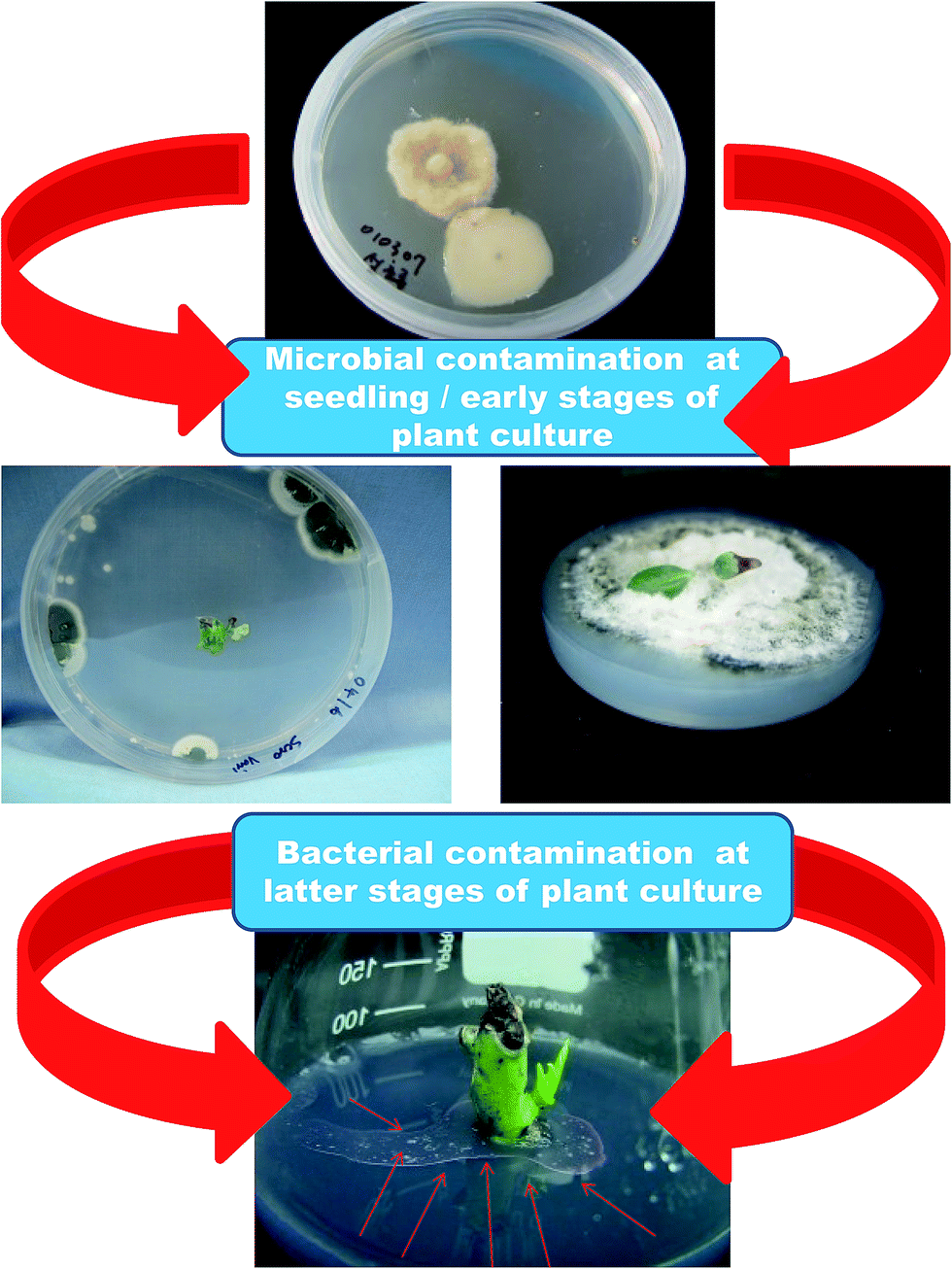 Source: pubs.rsc.org
Source: pubs.rsc.org
Grow) on plant tissue culture media but some may be latent (i.e. The main areas of quality control that are of concern for tissue culture are: Currently, the commonly used approach for inhibiting bacteria is antibiotic treatment; In the intervening years there have been considerable advances in both plant disease diagnostics and in the development of structured approaches to. Plants growing in the external environments contaminated with microorganisms.
 Source: bukalapak.com
Source: bukalapak.com
Incubation, and storage of sterile culture plant tissue culture and biot~nology december 1995 volume; Surface sterilization of plant materials is a very problematic step in establishing plant tissue culture protocol. In order to read online or download evaluation of microbial extracts for contamination control in plant tissue culture systems full ebooks in pdf, epub, tuebl and mobi you need to create a free account. These microbes can compete for nutrients, increase culture mortality and may result in variable growth, tissue necrosis, reduced shoot proliferation and rooting [4]. In the intervening years there have been considerable advances in both plant disease diagnostics and in the development of structured approaches to.
 Source: plantcelltechnology.com
Source: plantcelltechnology.com
Microbial contamination is a major issue in cell culture, but there are a range of procedures which can be adopted to prevent or eliminate contamination. These steps encompass handling of stock plants, type and handling of explants. Contamination control and removal are very important technical aspects of microbiological research. Microbial contamination of plant tissue cultures., mohegan lake, n.y. The management of contamination in tissue culture involves three stages:
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Nijkamp h.j.j., van der plas l.h.w. The quality of materials used (cell lines, media and other reagents) will affect the quality of the cultures and the subsequent scientific data and products derived from them. Using isothiazolone biocides to control microbial and fungal contaminants in plant tissue cultures. Important contaminants in micropropagated plant cultures. In particular, prompt removal of contaminated cultures is needed to protect neighboring cultures, as well as the sterile tissue culture environment including culture incubators, baths, and the biosafety cabinet.
Source: researchgate.net
In the intervening years there have been considerable advances in both plant disease diagnostics and in the development of structured approaches to. Get any books you like and read everywhere you want. The management of contamination in tissue culture involves three stages: Plant tissue culture can be used widely in plant science or horticulture, primarily for the commercial production of plants in the absence of seeds or necessary pollinators. However, there are drawbacks to using antibiotics, including incomplete removal, limited antibacterial spectra,.
 Source: plantcelltechnology.com
Source: plantcelltechnology.com
The best way to get rid of contamination is to sterilize the explants. Contamination may arise from the operator and the laboratory environment, from other cells used in the laboratory, and from reagents. In the intervening years there have been considerable advances in both plant disease diagnostics and in the development of structured approaches to. In the intervening years there have been considerable advances in both plant disease diagnostics and in the development of structured approaches to. Quality is important in all aspects of tissue culture.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The main areas of quality control that are of concern for tissue culture are: The best strategy to control tissue culture contamination is to establish aseptic cultures and to maintain good laboratory practice, including routine testing for contamination by cultivable micro. The best way to get rid of contamination is to sterilize the explants. The quality of the reagents and materials In the intervening years there have been considerable advances in both plant disease diagnostics and in the development of structured approaches to.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title contamination control in plant tissue culture by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






