Your Cortex function in plants images are available. Cortex function in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Cortex function in plants files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re searching for cortex function in plants pictures information connected with to the cortex function in plants keyword, you have come to the ideal site. Our site frequently provides you with suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Cortex Function In Plants. The term cortex refers to the outermost layer of cells on a plant’s stem or root. Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which store and transport nutrients throughout the plant. The cortical cells can store starch. The cortex/endodermis initial cell (cei) generates the two ground tissues, cortex and endodermis, via sequential asymmetric divisions.
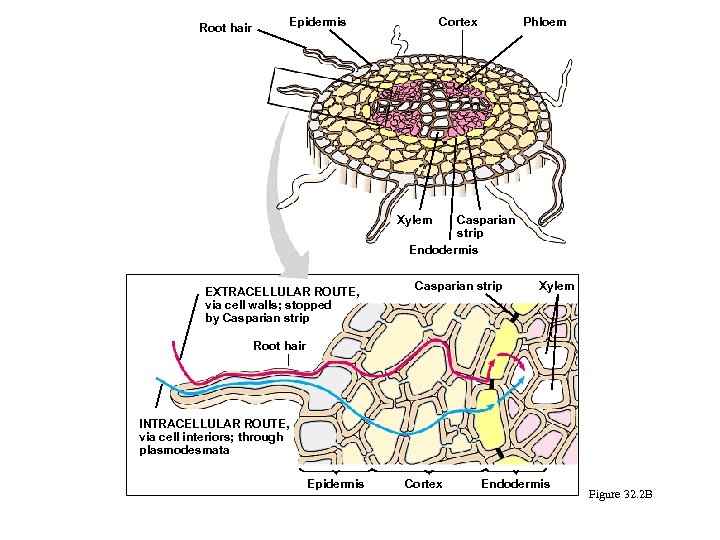 Structure and Function in Land plants ORGANS of From present5.com
Structure and Function in Land plants ORGANS of From present5.com
In addition to being supportive and protective, the cortex functions in the synthesis and localization of many chemical substances; In monocots, dicots and gymnosperms, the sub epidermal cells or cortical cells differentiate into protective tissue known as. In aquatic plants cortical cells are aerenchymatous enclosing air cavities. Cortical cells in herbaceous stems, young woody stems, and stems of succulents (cacti and other fleshy plants) contain chloroplasts and can therefore convert carbon dioxide and water to simple carbohydrates (carbon fixation) using photosynthesis. The cortex has the ability to transport nutrients into the core of the root. The frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes.
The plant cortex is the tissue located between the vascular bundles and epidermis.
The cells of the cortex play a crucial role in the plant’s life. Starch, tannins and crystals are the common inclusions. A cortex is an outer layer of a stem or root in a plant, lying below the epidermis but outside of the vascular bundles. The cortical cells can store starch. The temporal lobe is responsible for cortex function related to auditory perception, language, and memory. It also stores nutrients in the form of starch.
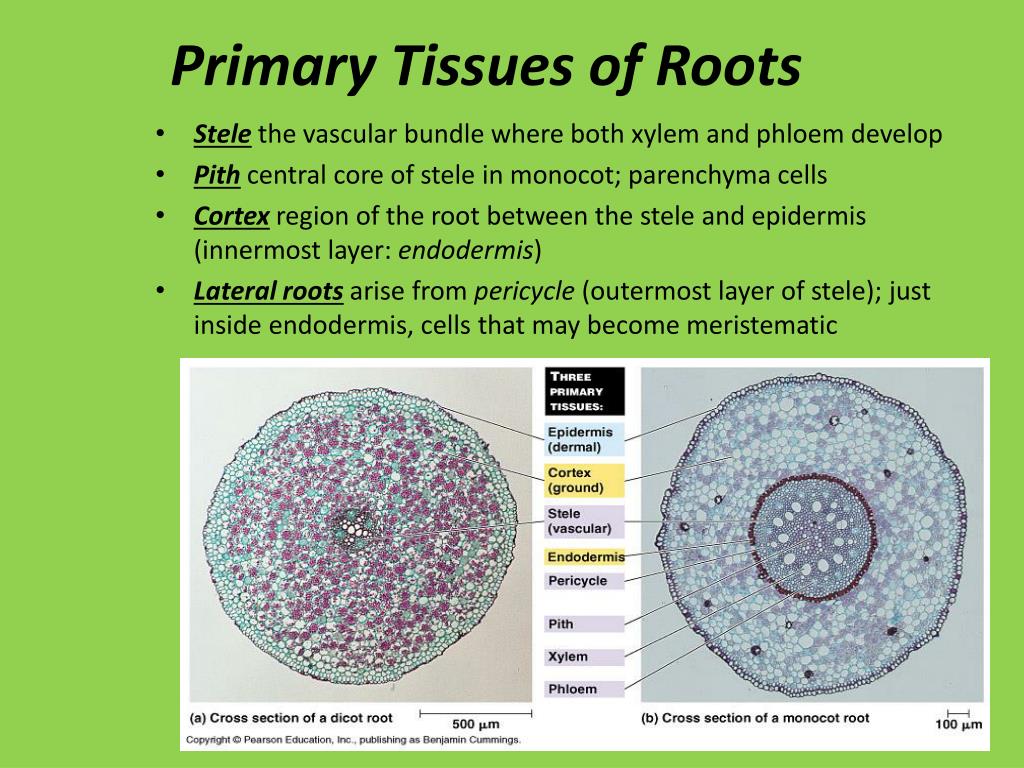 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
In most plants, pith and cortex cells function to support the plant. Woody plants have an extra layer of protection on top of the epidermis known as bark. The temporal lobe is responsible for cortex function related to auditory perception, language, and memory. Certain aerial climbers possess chlorophyll cells to perform photosynthesis. The specific function of the cortex is dependent on the type of cells present.
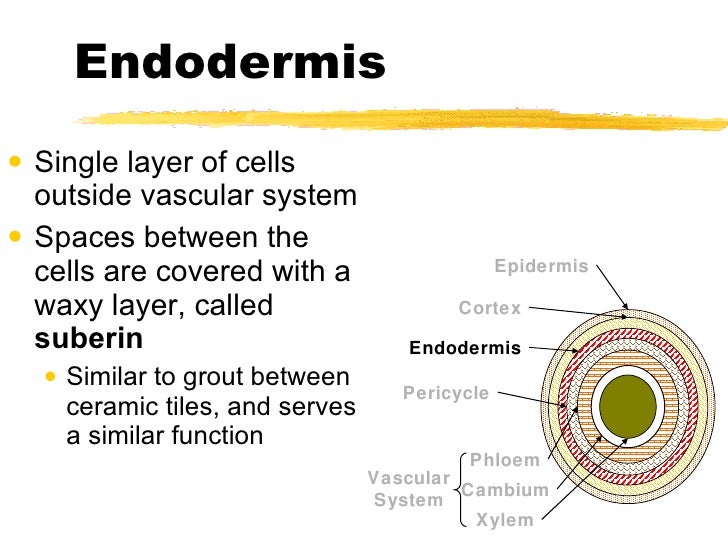 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Cortical cells in herbaceous stems, young woody stems, and stems of succulents (cacti and other fleshy plants) contain chloroplasts and can therefore convert carbon dioxide and water to simple carbohydrates (carbon fixation) using photosynthesis. In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem. Woody plants have an extra layer of protection on top of the epidermis known as bark. The cortex is the outermost layer of the stem or root of a plant. It includes the whole area from beneath the epiblema up to above pericycle.
 Source: present5.com
Source: present5.com
The plant cortex is the tissue located between the vascular bundles and epidermis. In most plants, pith and cortex cells function to support the plant. The cortex can have numerous functions in plants, including food storage, mechanical support and photosynthesis. On woody stem plants, trees, and roots, the cortex produces a protective, waterproof layer which is often referred to as bark. The cells of the cortex play a crucial role in the plant’s life.
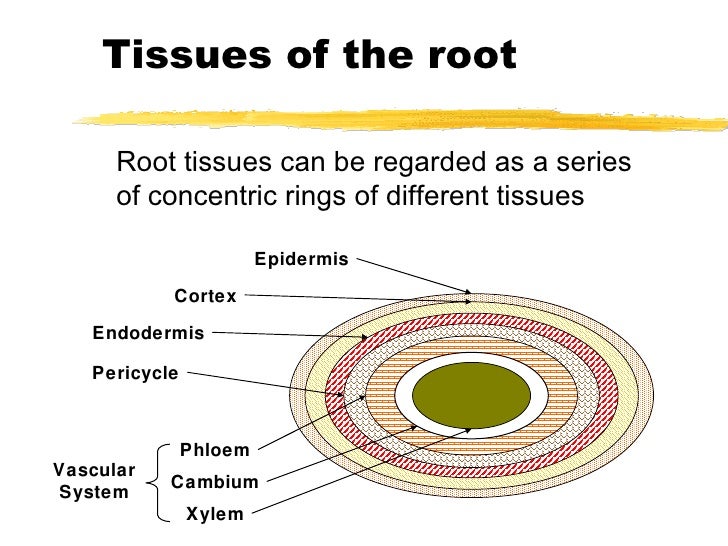 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The region that lies next to the epidermis is the cortex. They convert the carbon dioxide and water that the plant absorbs into simple carbohydrates which the plant then uses for photosynthesis. What is the function of pith in plants? Starch, tannins and crystals are the common inclusions. It transports materials into the central cylinder of the root through diffusion and stores food in the form of starch.
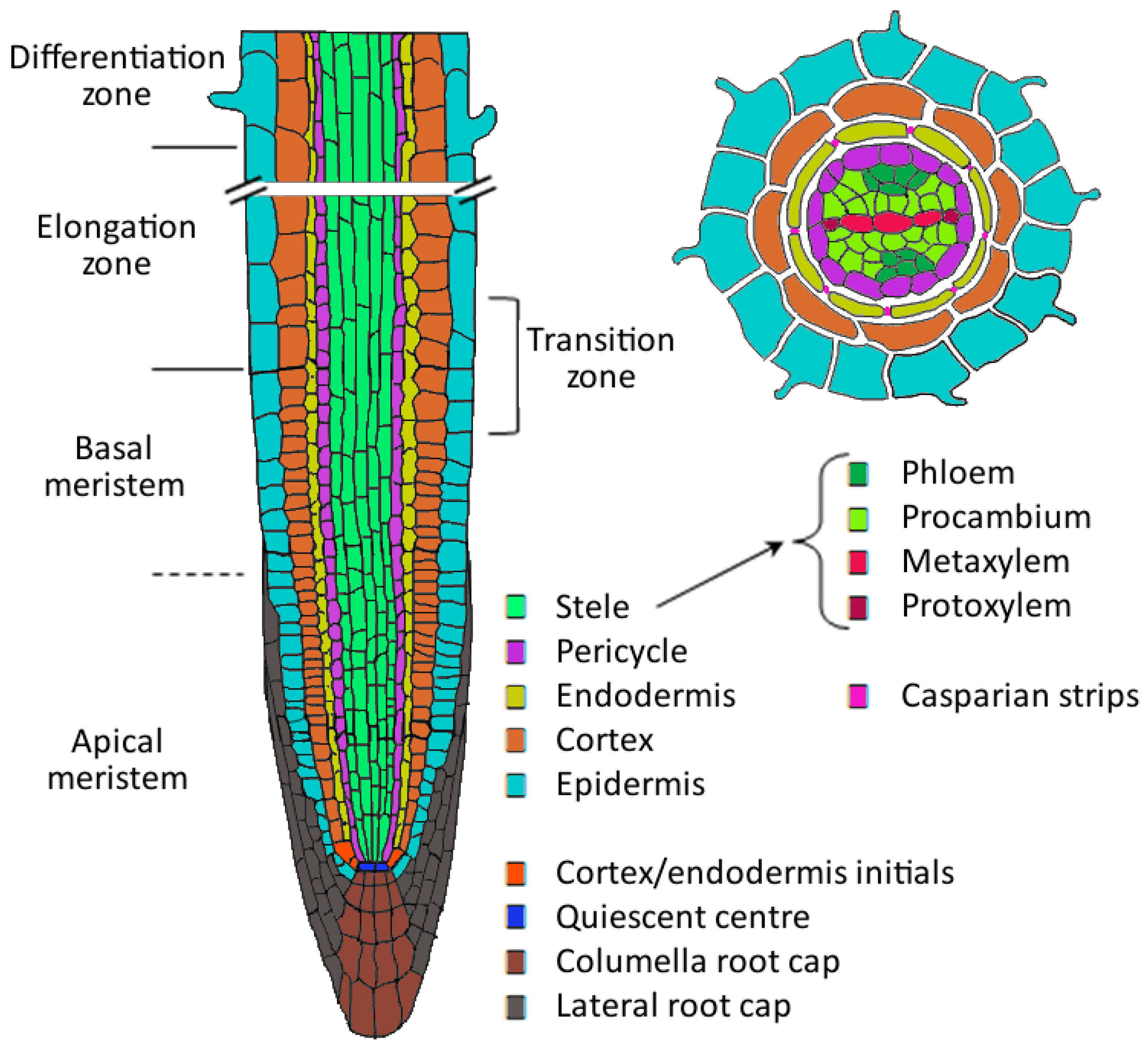 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
The region that lies next to the epidermis is the cortex. Cortical cells in herbaceous stems, young woody stems, and stems of succulents (cacti and other fleshy plants) contain chloroplasts and can therefore convert carbon dioxide and water to simple carbohydrates (carbon fixation) using photosynthesis. Cortex functions as a storage organ in many woody plants sugars and proteins deposited in the cells of the cortex during the fall provide food reserves to support. Starch, tannins and crystals are the common inclusions. It serves mainly for restricting the rate of transpiration;
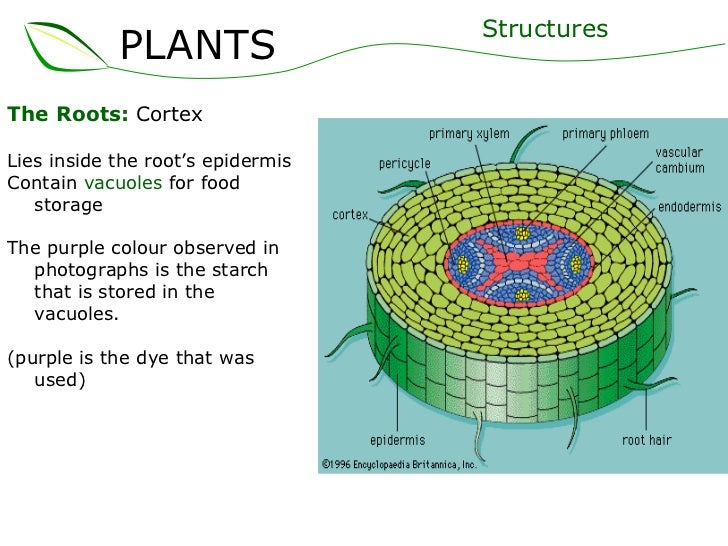 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem. On woody stem plants, trees, and roots, the cortex produces a protective, waterproof layer which is often referred to as bark. It may be located between the vascular tissues and the epidermis in certain plants. The cortex is the outermost layer of the stem or root of a plant. Cortical cells in herbaceous stems, young woody stems, and stems of succulents (cacti and other fleshy plants) contain chloroplasts and can therefore convert carbon dioxide and water to simple carbohydrates (carbon fixation) using photosynthesis.
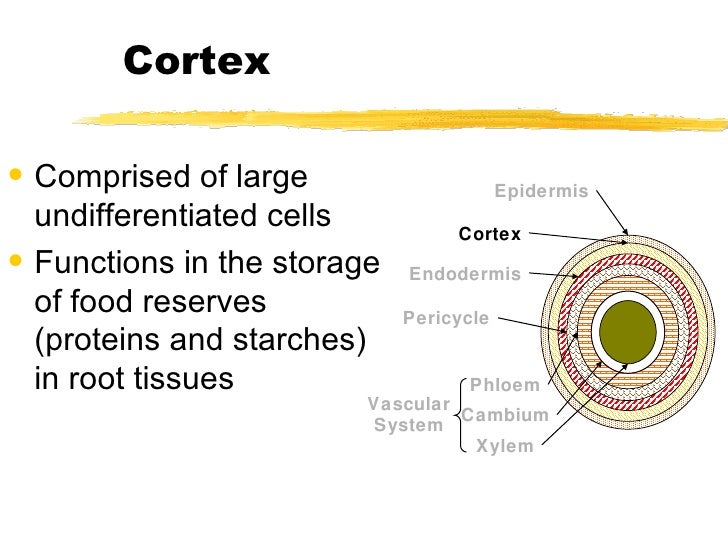 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
What is the function of the cortex in a plant? Thin waxy layer on the epidermis: Because the living protoplasts of the cortex are so highly specialized, patterns and. Cortex functions as a storage organ in many woody plants sugars and proteins deposited in the cells of the cortex during the fall provide food reserves to support. The cortex can have numerous functions in plants, including food storage, mechanical support and photosynthesis.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Both the cortex and pith are composed mainly of parenchyma cells. In botany, the cortex pertains to the tissue of the stem and the root that lies outward to the vascular tissues. The plant cortex is the tissue located between the vascular bundles and epidermis. The cortex acts as a protective covering on plant and is often waterproof. Though cortex is often composed of various types of cells, naturally with different functions, but it is primarily a protective layer.
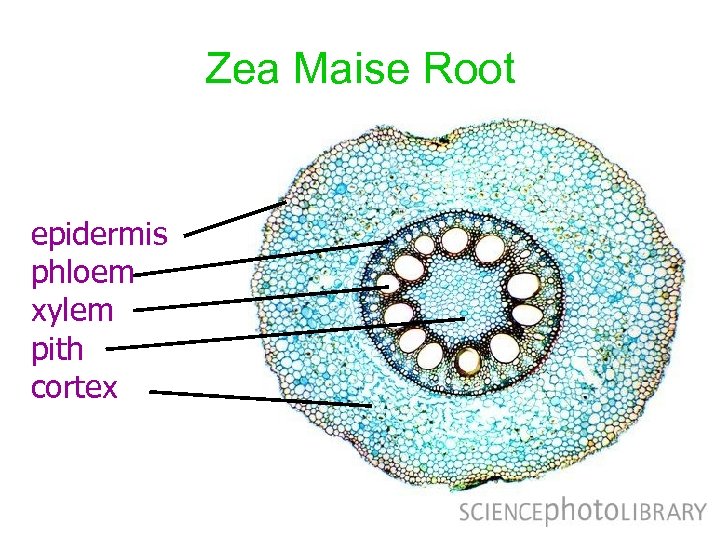 Source: present5.com
Source: present5.com
The cells of the pith readily fill up with nutrients and water and swell. Woody plants have an extra layer of protection on top of the epidermis known as bark. In most plants, pith and cortex cells function to support the plant. They convert the carbon dioxide and water that the plant absorbs into simple carbohydrates which the plant then uses for photosynthesis. Cortical cells in herbaceous stems, young woody stems, and stems of succulents (cacti and other fleshy plants) contain chloroplasts and can therefore convert carbon dioxide and water to simple carbohydrates (carbon fixation) using photosynthesis.
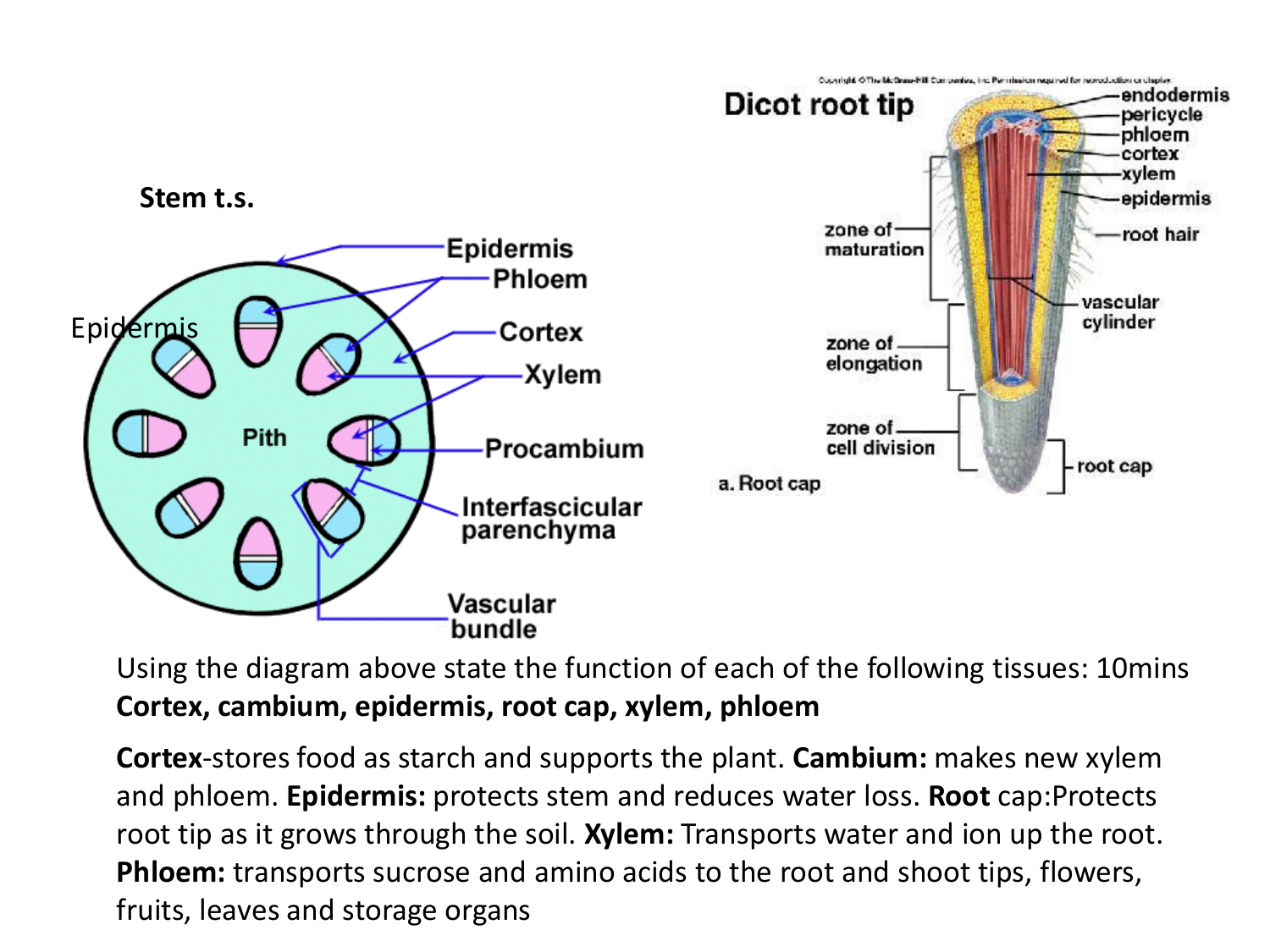 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
Pith, or medulla, is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants. In monocots, dicots and gymnosperms, the sub epidermal cells or cortical cells differentiate into protective tissue known as. They convert the carbon dioxide and water that the plant absorbs into simple carbohydrates which the plant then uses for photosynthesis. The cells of the pith readily fill up with nutrients and water and swell. Cortex functions as a storage organ in many woody plants sugars and proteins deposited in the cells of the cortex during the fall provide food reserves to support plant growth in the spring.
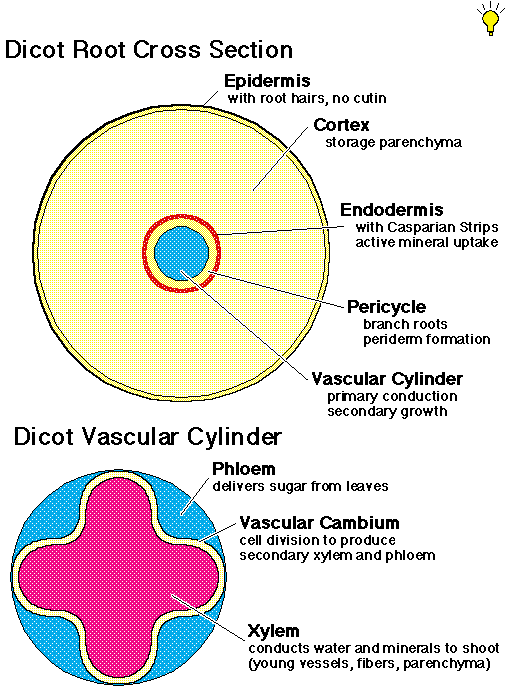 Source: www1.biologie.uni-hamburg.de
Source: www1.biologie.uni-hamburg.de
Parenchyma cells have thin cell walls that can have. Certain aerial climbers possess chlorophyll cells to perform photosynthesis. It may be located between the vascular tissues and the epidermis in certain plants. Prevent microorganisms from entering (barrier to disease) helps keep leaf’s shape: Cortex functions as a storage organ in many woody plants sugars and proteins deposited in the cells of the cortex during the fall provide food reserves to support.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
In woody plants, the cortex is located between the vascular tissue (particularly phloem) and the periderm. The cells inside the cortex may also contain stored carbohydrates or. In botany, the cortex pertains to the tissue of the stem and the root that lies outward to the vascular tissues. What is the main function of the cortex and pith? The cortex can have numerous functions in plants, including food storage, mechanical support and photosynthesis.
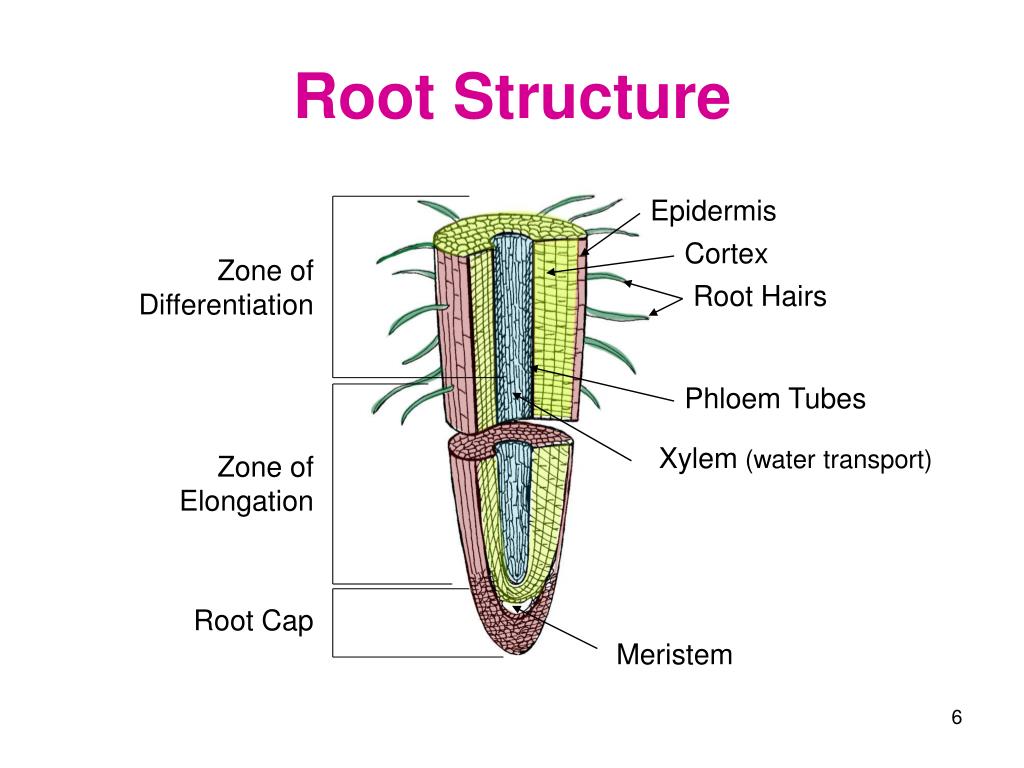 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which store and transport nutrients throughout the plant. Pith, or medulla, is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants. What is the main function of the cortex and pith? The cortex/endodermis initial cell (cei) generates the two ground tissues, cortex and endodermis, via sequential asymmetric divisions. Though cortex is often composed of various types of cells, naturally with different functions, but it is primarily a protective layer.
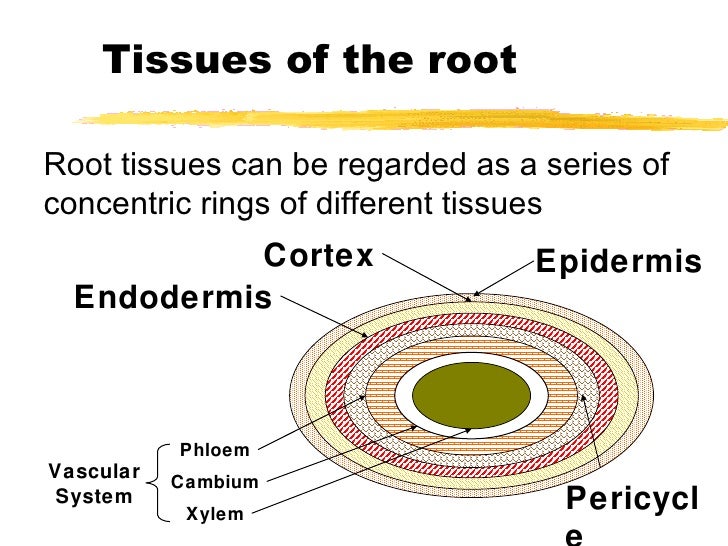 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Allow light to pass through. It uses diffusion to achieve the transport. The cells of the cortex play a crucial role in the plant’s life. In woody plants, the cortex is located between the vascular tissue (particularly phloem) and the periderm. It transports materials into the central cylinder of the root through diffusion and stores food in the form of starch.
 Source: oercommons.org
Source: oercommons.org
The cells of the cortex play a crucial role in the plant’s life. A cortex is an outer layer of a stem or root in a plant, lying below the epidermis but outside of the vascular bundles. The cortical cells can store starch. Starch, tannins and crystals are the common inclusions. The cells of the pith readily fill up with nutrients and water and swell.
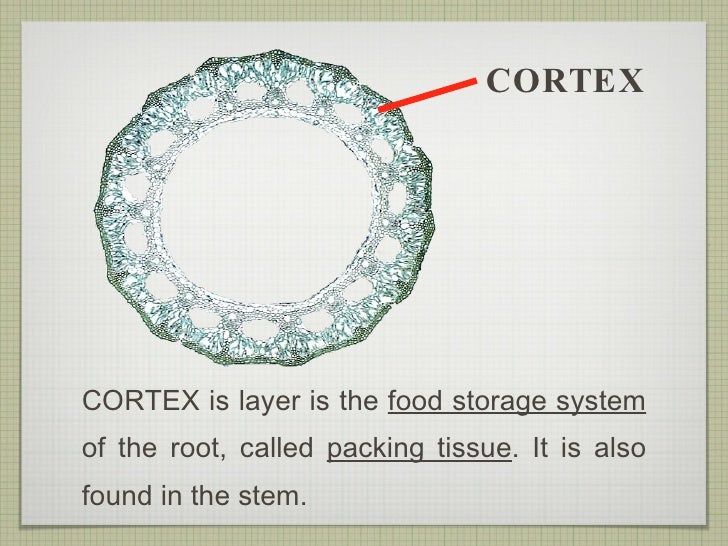 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
You may remember that these parenchymal cells closely resemble generalized plant cells, with large vacuoles. The cortex of root is more homogeneous, as it consists of only parenchyma cells. Cylinder remain undifferentiated, forming the pericycle, a tissue important in the formation of lateral roots. A cortex is an outer layer of a stem or root in a plant, lying below the epidermis but outside of the vascular bundles. The specific function of the cortex is dependent on the type of cells present.
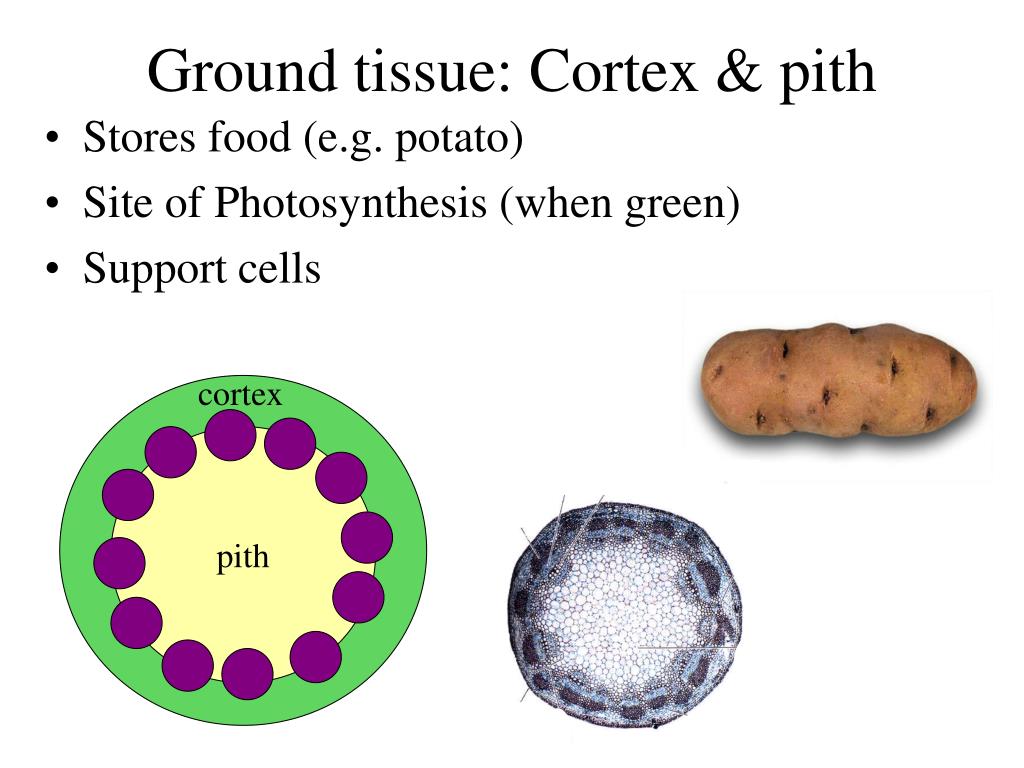 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The cortex acts as a protective covering on plant and is often waterproof. The cells of the pith readily fill up with nutrients and water and swell. In aquatic plants cortical cells are aerenchymatous enclosing air cavities. A cortex is an outer layer of a stem or root in a plant, lying below the epidermis but outside of the vascular bundles. The cortex has the ability to transport nutrients into the core of the root.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The cortex acts as a protective covering on plant and is often waterproof. In monocots, dicots and gymnosperms, the sub epidermal cells or cortical cells differentiate into protective tissue known as. The main function of the cortex is to provide support and perform metabolic processes. The region that lies next to the epidermis is the cortex. The cortical cells can store starch.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title cortex function in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






