Your Cortex in plants images are available. Cortex in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Cortex in plants files here. Find and Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for cortex in plants pictures information connected with to the cortex in plants topic, you have come to the right blog. Our website frequently gives you hints for seeking the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Cortex In Plants. In recent studies, we found that cortex proliferation can be induced by oxidative They never associate with xylem elements. The content above is only an excerpt. Some of the outer cortical cells may contain chloroplasts.
 Young Woody Stem Pith, Xylem, Phloem, Vascular Cambium From pinterest.co.uk
Young Woody Stem Pith, Xylem, Phloem, Vascular Cambium From pinterest.co.uk
It anchors the plant in the soil. The exact function depends on the type of cells present. Some of the outer cortical cells may contain chloroplasts. Cortex, in botany, term generally applied to the outer soft tissues of the leaves, stems, and roots of plants. The cortex can have numerous functions in plants, including food storage, mechanical support and photosynthesis. The cortex is comprised mostly of parenchyma cells, but can also contain sclerenchyma, or collenchyma cells.
It is responsible for the transportation of materials into the central cylinder of the root through diffusion and may.
Cortex expansion by shr reconfiguration. It is the outermost layer of cells in the plant cortex, lying immediately beneath the epidermis. A cortex is an outer layer of a stem or root in a plant, lying below the epidermis but outside of the vascular bundles. On woody stem plants, trees, and roots, the cortex produces a protective, waterproof layer which is often referred to as bark. The thick cortex of the cypripedium root would serve as a buffer against external changes [42], such as those in nutrient types [43] or soil temperature [44],. Cortex, in plants, tissue of unspecialized cells lying between the epidermis (surface cells) and the vascular, or conducting, tissues of stems and roots.
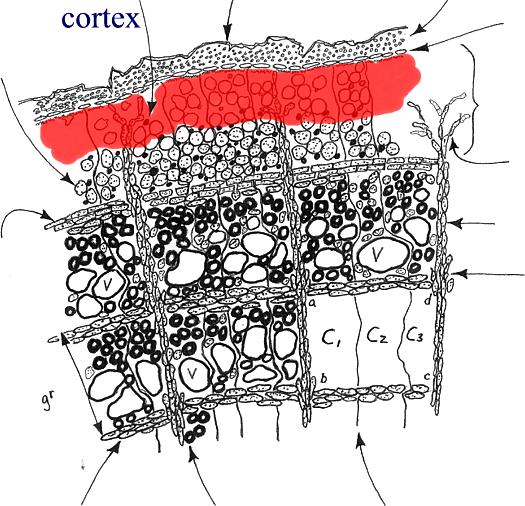 Source: hort.ifas.ufl.edu
Source: hort.ifas.ufl.edu
Cortex is regarded as the least differentiated cell type in the root, but little is known about its role in plant growth and physiology. The cortex is comprised mostly of parenchyma cells, but can also contain sclerenchyma, or collenchyma cells. The hypodermis is the outmost cell layer of the cortex of plants. Cortex, in botany, term generally applied to the outer soft tissues of the leaves, stems, and roots of plants. In roots the cortex almost always consists of parenchyma and is bounded, more or less distinctly, by the hypodermis (exodermis) on the periphery and by the endodermis on the inside.
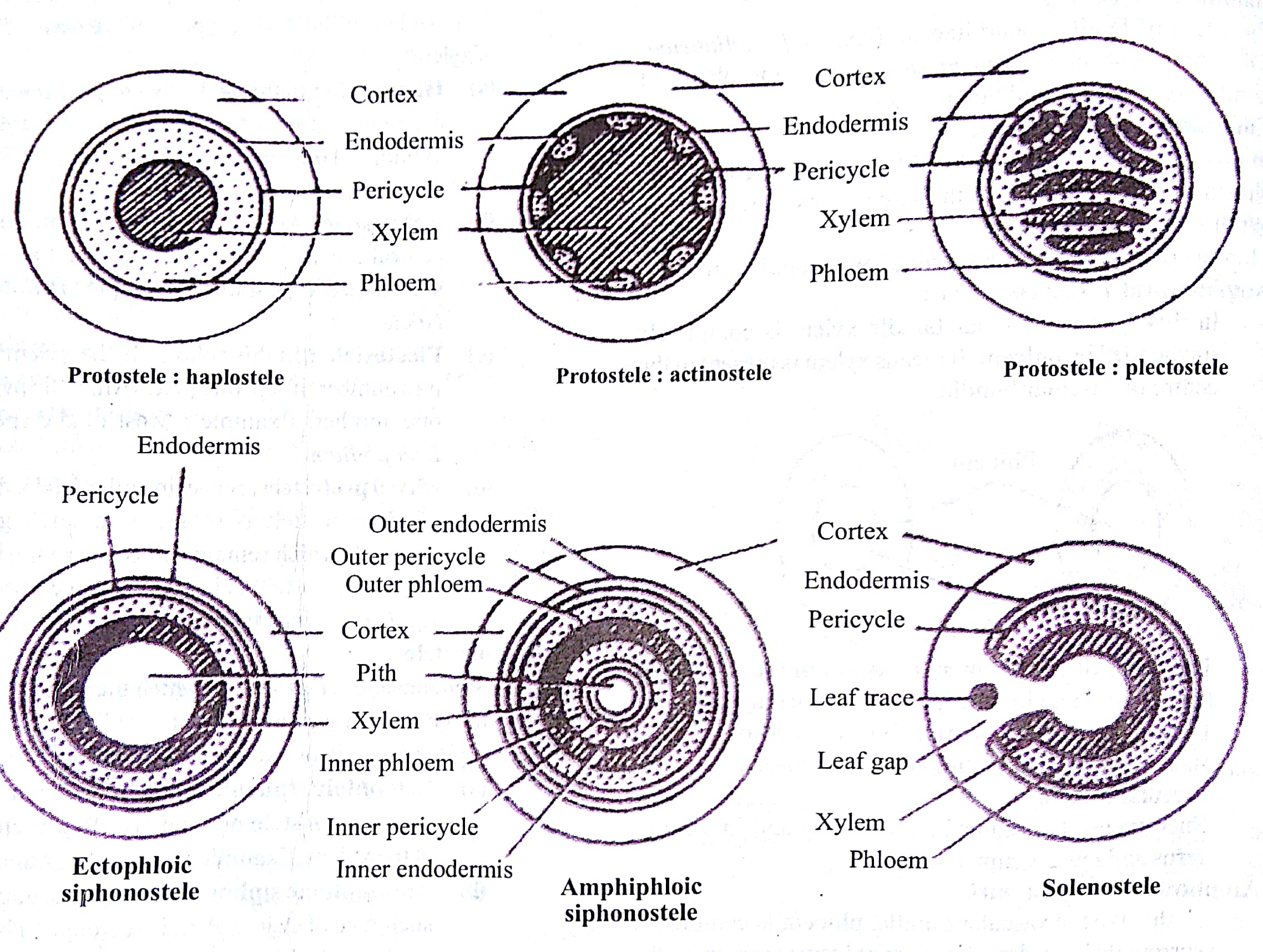 Source: learn.careers360.com
Source: learn.careers360.com
The content above is only an excerpt. The cortex can have numerous functions in plants, including food storage, mechanical support and photosynthesis. Where in the plant does ground tissue occur? It is the outermost layer of cells in the plant cortex, lying immediately beneath the epidermis. Cortex is composed of following types of tissues:
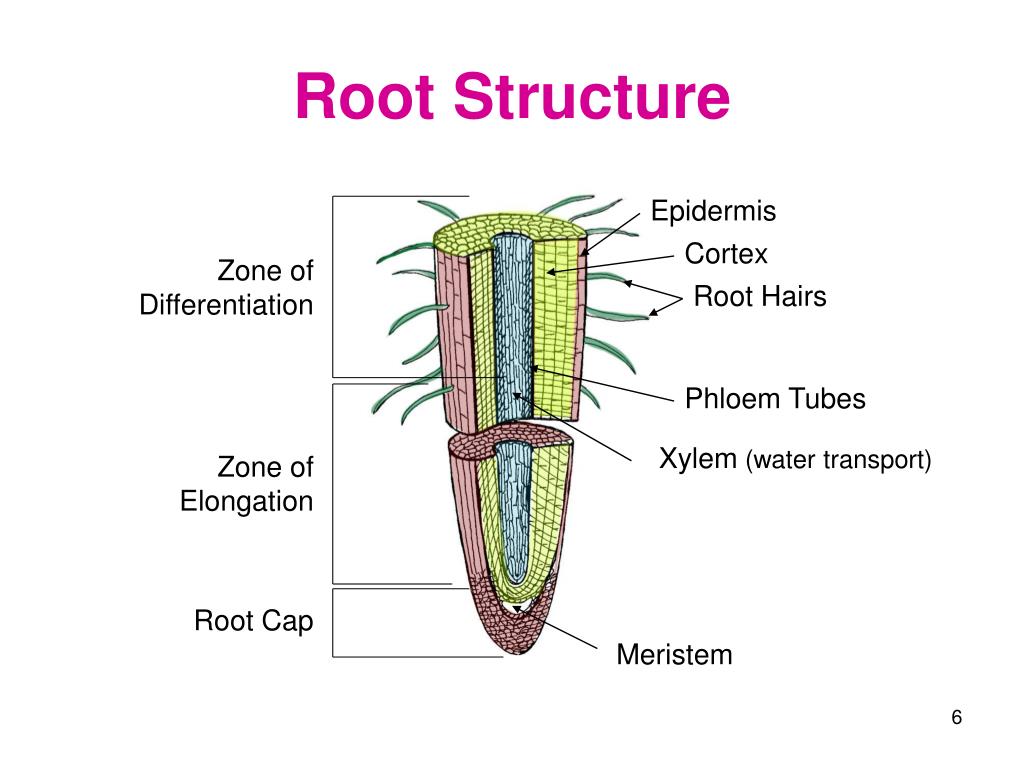 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Often as a plant ages, the cortex becomes thicker and more impenetrable. They never associate with xylem elements. The cells of the cortex play a crucial role in the plant’s life. It is composed of parenchyma cells and shows little or no structural differentiation. In recent studies, we found that cortex proliferation can be induced by oxidative
 Source: botit.botany.wisc.edu
Cortical cells of the leaves and outer layers of nonwoody stems contain chloroplasts, and are modified for food storage (usually in the form of starch) in. The thick cortex of the cypripedium root would serve as a buffer against external changes [42], such as those in nutrient types [43] or soil temperature [44],. A ground tissue is a plant tissue other than those of the dermal tissues and the vascular tissues. The outer part of the cortex contains collenchyma cells. Parenchyma in plants is the types of simple permanent tissue that possesses some ideal properties that discriminate it from the other cells.
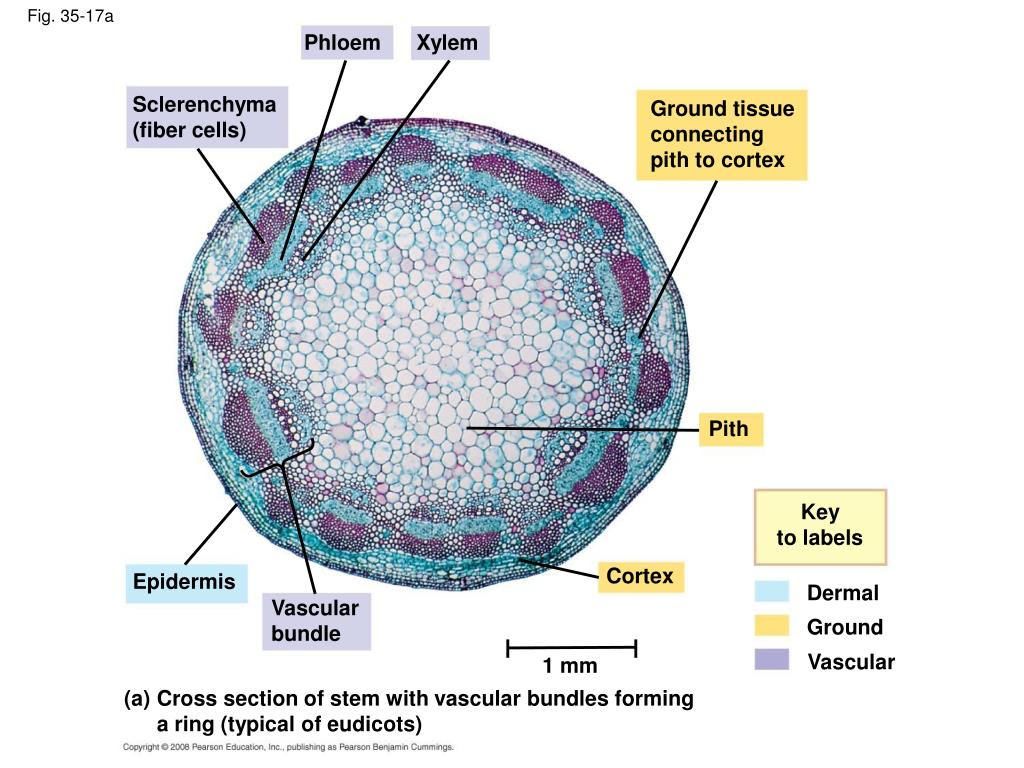 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The cells of the cortex play a crucial role in the plant’s life. The root is underground part of the plant. The cortex, composed primarily of parenchyma cells, is the largest part of the primary root, but in most dicots (eudicots) and in gymnosperms that undergo extensive secondary growth, it is soon crushed, and its storage function assumed by other tissues. On woody stem plants, trees, and roots, the cortex produces a protective, waterproof layer which is often referred to as bark. The outer part of the cortex contains collenchyma cells.
 Source: plantphysiol.org
Source: plantphysiol.org
The cortex can have numerous functions in plants, including food storage, mechanical support and photosynthesis. The cortex, composed primarily of parenchyma cells, is the largest part of the primary root, but in most dicots (eudicots) and in gymnosperms that undergo extensive secondary growth, it is soon crushed, and its storage function assumed by other tissues. The root is underground part of the plant. These may be intercellular, where hyphae grow in the intercellular spaces of the root cortex, or intracellular involving arbuscules, hyphal coils or arbusculate coils.the structure and composition of these interfaces vary in the details of. The cortex is responsible for the storage of photosynthetic products and the uptake of water and minerals.
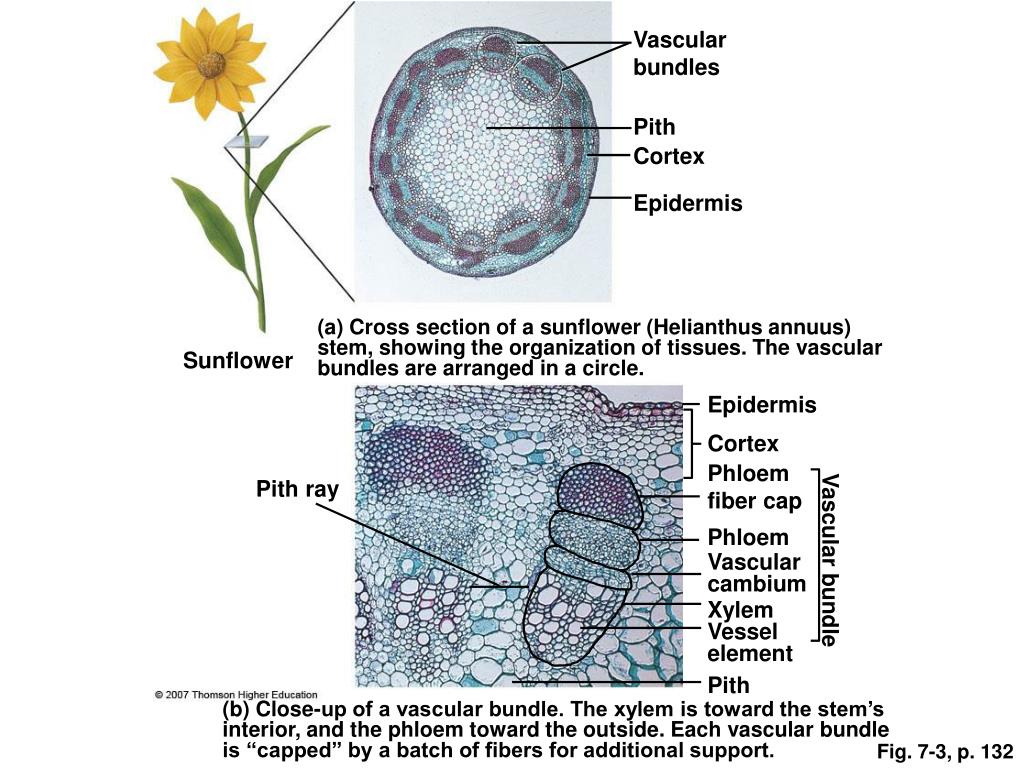 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The cortex can have numerous functions in plants, including food storage, mechanical support and photosynthesis. These cells often contain ctiloroplasts, especially in the young herbaceous plants. Structurally and physically, parenchyma is a kind of unspecialised tissue. The epidermis, cortex, and the primary vascular tissues are developed during the primary growth. It may form an uninterrupted cylinder on the ground tissue.
 Source: blogs.berkshirecc.edu
Source: blogs.berkshirecc.edu
These fibres occur in the cortex, pith and in association with phloem as phloem or bast fibre. In roots the cortex almost always consists of parenchyma and is bounded, more or less distinctly, by the hypodermis (exodermis) on the periphery and by the endodermis on the inside. On woody stem plants, trees, and roots, the cortex produces a protective, waterproof layer which is often referred to as bark. The cortex, composed primarily of parenchyma cells, is the largest part of the primary root, but in most dicots (eudicots) and in gymnosperms that undergo extensive secondary growth, it is soon crushed, and its storage function assumed by other tissues. The epidermis, cortex, and the primary vascular tissues are developed during the primary growth.
 Source: schools.aglasem.com
Source: schools.aglasem.com
It is composed of a few layers parenchymatous cells. They comprises a large vacuole. These cells often contain ctiloroplasts, especially in the young herbaceous plants. It may form an uninterrupted cylinder on the ground tissue. Sometimes the cortex is referred to as the plant�s skin, but this is an oversimplification.
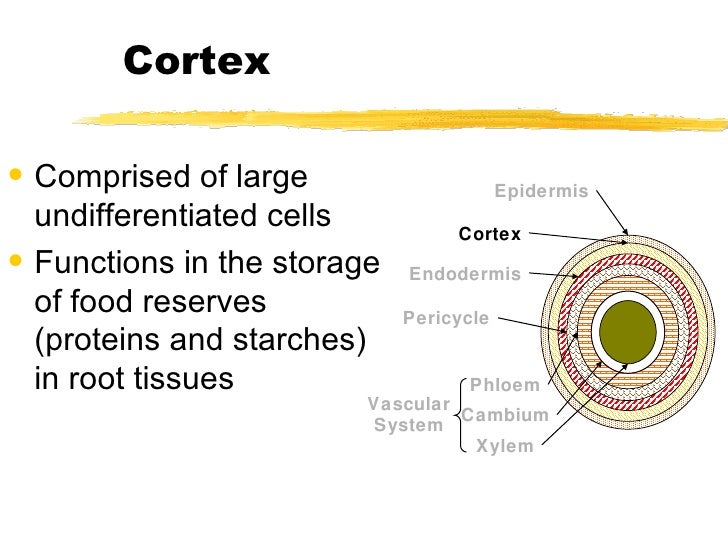 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
It is composed of parenchyma cells and shows little or no structural differentiation. Transfer of hexoses from plant to fungus, as well as mineral nutrient transfer in the opposite direction, occurs across symbiotic interfaces. Root structure consists of epidermis ,cortex , vascular tissues and rot cap. Cortex, in plants, tissue of unspecialized cells lying between the epidermis (surface cells) and the vascular, or conducting, tissues of stems and roots. It is also used to absorb water and minerals from the soil.
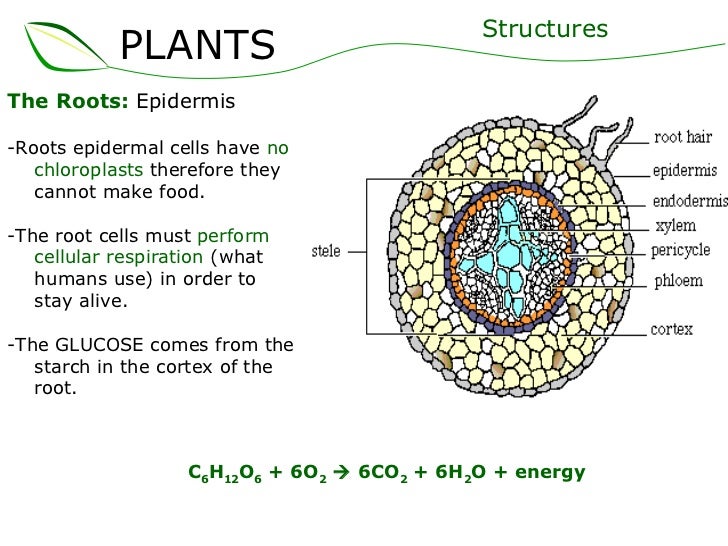 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Root structure consists of epidermis ,cortex , vascular tissues and rot cap. The cells of the cortex play a crucial role in the plant’s life. The cortex can have numerous functions in plants, including food storage, mechanical support and photosynthesis. Often as a plant ages, the cortex becomes thicker and more impenetrable. Where in the plant does ground tissue occur?
 Source: dev.biologists.org
Source: dev.biologists.org
In roots the cortex almost always consists of parenchyma and is bounded, more or less distinctly, by the hypodermis (exodermis) on the periphery and by the endodermis on the inside. It is also used to absorb water and minerals from the soil. Parenchyma in plants is the types of simple permanent tissue that possesses some ideal properties that discriminate it from the other cells. Transfer of hexoses from plant to fungus, as well as mineral nutrient transfer in the opposite direction, occurs across symbiotic interfaces. Cortex is regarded as the least differentiated cell type in the root, but little is known about its role in plant growth and physiology.
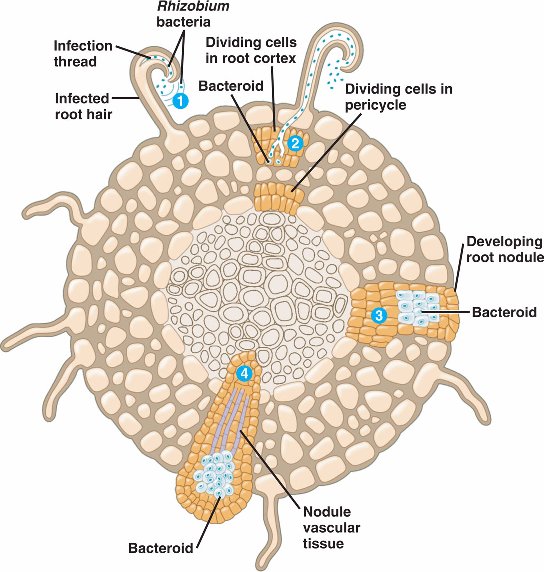 Source: bio1152.nicerweb.com
Source: bio1152.nicerweb.com
In plants, the cortex is a relatively undifferentiated cell type and is part of what is called the ground tissue. These may be intercellular, where hyphae grow in the intercellular spaces of the root cortex, or intracellular involving arbuscules, hyphal coils or arbusculate coils.the structure and composition of these interfaces vary in the details of. Cortex, in botany, term generally applied to the outer soft tissues of the leaves, stems, and roots of plants. Some of the outer cortical cells may contain chloroplasts. The root is underground part of the plant.

The cortex, composed primarily of parenchyma cells, is the largest part of the primary root, but in most dicots (eudicots) and in gymnosperms that undergo extensive secondary growth, it is soon crushed, and its storage function assumed by other tissues. These fibres occur in the cortex, pith and in association with phloem as phloem or bast fibre. Parenchyma in plants is the types of simple permanent tissue that possesses some ideal properties that discriminate it from the other cells. Some of the outer cortical cells may contain chloroplasts. In roots the cortex almost always consists of parenchyma and is bounded, more or less distinctly, by the hypodermis (exodermis) on the periphery and by the endodermis on the inside.
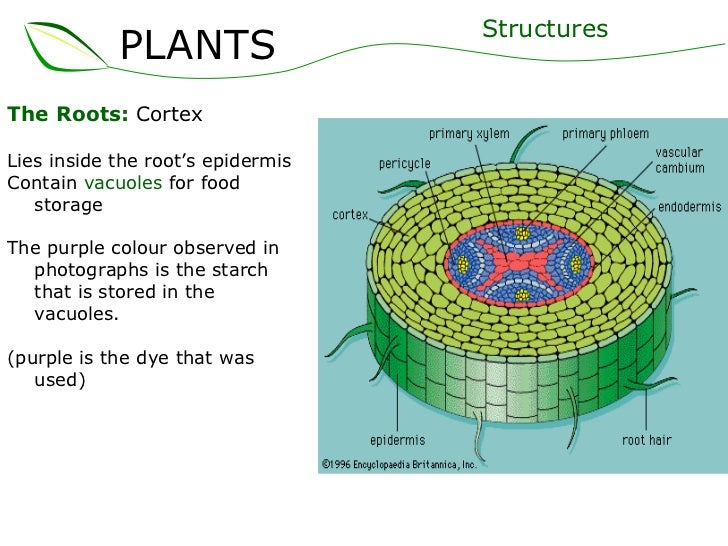 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
In roots and in some herbaceous stems but not usually in woody stems, the innermost layer of cortical cells. The exact function depends on the type of cells present. It arises from the ground meristem. On woody stem plants, trees, and roots, the cortex produces a protective, waterproof layer which is often referred to as bark. Parenchyma in plants is the types of simple permanent tissue that possesses some ideal properties that discriminate it from the other cells.
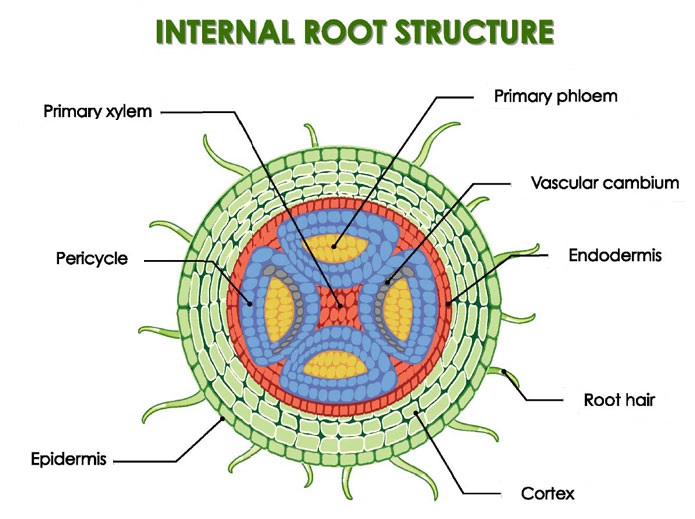 Source: studyread.com
Source: studyread.com
The exact function depends on the type of cells present. In recent studies, we found that cortex proliferation can be induced by oxidative It is composed of a few layers parenchymatous cells. In roots and in some herbaceous stems but not usually in woody stems, the innermost layer of cortical cells. It may form an uninterrupted cylinder on the ground tissue.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Cortical cells of the leaves and outer layers of nonwoody stems contain chloroplasts, and are modified for food storage (usually in the form of starch) in. They comprises a large vacuole. The cells of the cortex play a crucial role in the plant’s life. In botany, the cortex is the outermost layer of the stem or root of a plant, bounded on the outside by the epidermis and on the inside by the endodermis. Cortex is regarded as the least differentiated cell type in the root, but little is known about its role in plant growth and physiology.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
A ground tissue is a plant tissue other than those of the dermal tissues and the vascular tissues. Structurally and physically, parenchyma is a kind of unspecialised tissue. Transfer of hexoses from plant to fungus, as well as mineral nutrient transfer in the opposite direction, occurs across symbiotic interfaces. The main difference between primary and secondary growth is that primary growth increases the length of the plant whereas secondary growth increases the thickness. In plants, the cortex is a relatively undifferentiated cell type and is part of what is called the ground tissue.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title cortex in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






