Your Cytokinins in plants images are available in this site. Cytokinins in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Cytokinins in plants files here. Get all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for cytokinins in plants images information connected with to the cytokinins in plants topic, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our site always gives you suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
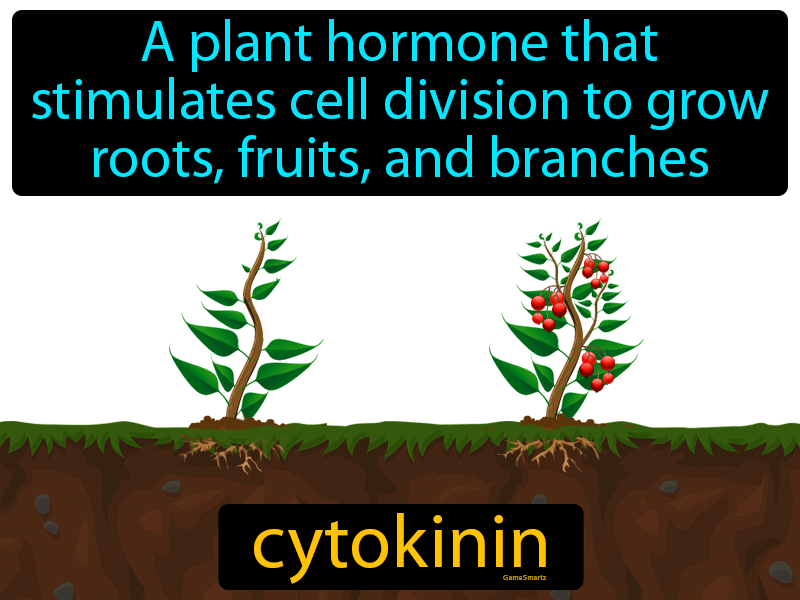
Cytokinins In Plants. More recently, functions of cks in plant stress defense including salt have been increasingly characterized. Today there are more than 200 natural and synthetic cytokinins combined. Cytokinins are a class of plant hormones that promote cell division in plant roots and shoots. Thank you so much for the encouragement.
 Should I fight or should I grow? Cytokinins in defence From botany.one
Should I fight or should I grow? Cytokinins in defence From botany.one
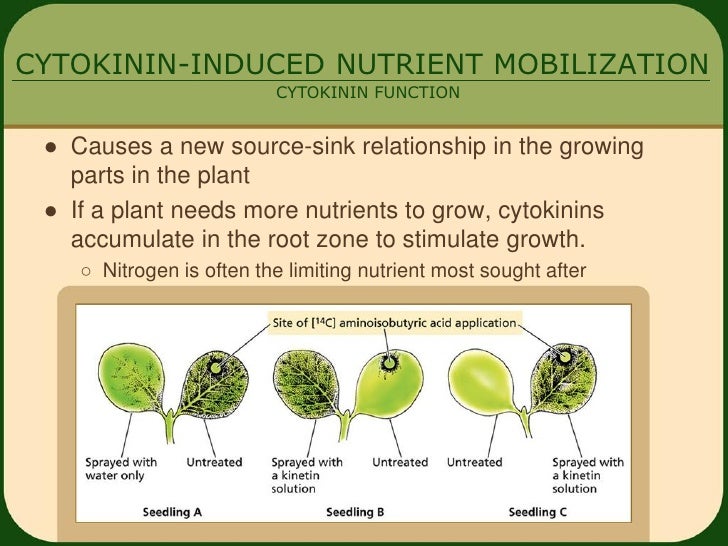
Functional activity of cytokinins occurs in the presence of. Cytokinins comprise a family of signaling molecules essential for regulating the growth and development of plants, acting both locally and at a distance. This hormone helps in promoting the cell’s growth, development, differentiation, affecting apical dominance and delay in leaf senescence. The uptake of minerals in the root the movement of nutrients into the leaves. Although much is known about their biosynthesis and transport, important open questions remain. Cytokinins are a group of plant growth regulators which are primarily involved in performing cell division in plant roots, shoot system.
They move upward in the xylem (woody tissue) and pass into the leaves and fruits, where they are required for normal growth and cell differentiation.
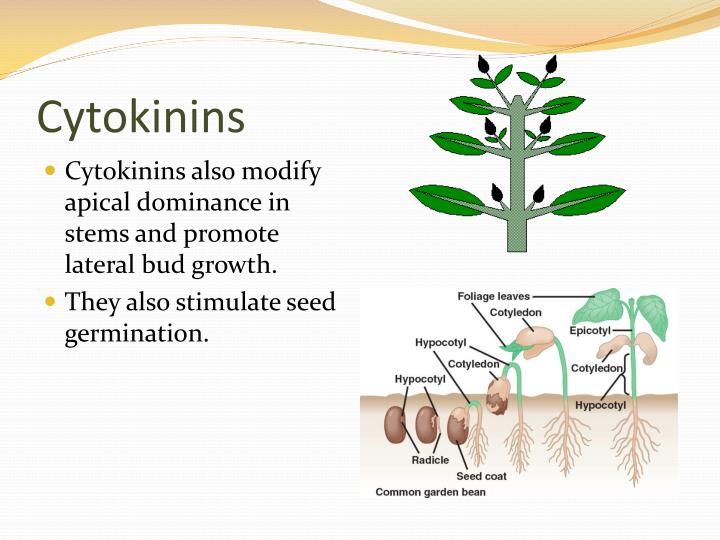
Cytokinin levels in plants are regulated by biosynthesis and inactivation pathways. Cytokinins were originally discovered following the search for a compound that. Cytokinins induce formation of new leaves, chloroplasts in leaves, lateral shoot formation and adventitious shoot formation. Cytokinins are derivatives of adenine. Cytokinins comprise a family of signaling molecules essential for regulating the growth and development of plants, acting both locally and at a distance. This hormone helps in promoting the cell’s growth, development, differentiation, affecting apical dominance and delay in leaf senescence.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
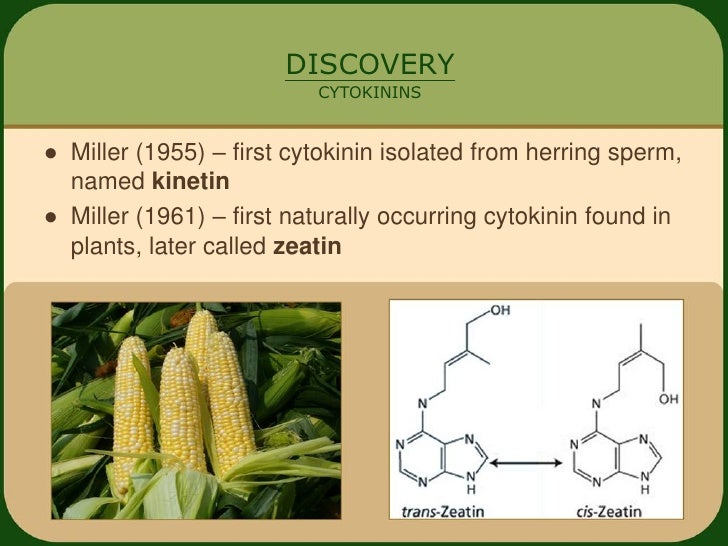
This search resulted in the identification of the synthetic cytokinin kinetin ( miller et al., 1956 , 1955 ), and subsequent studies identified the cytokinin zeatin as an endogenous plant. The most common class of cytokinins have. These hormones have been found in all complex plants as well as mosses, fungi, and. Cytokinins are derivatives of adenine. They are involved primarily in cell growth and differentiation, but also affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and leaf senescence.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Cytokinins comprise a family of signaling molecules essential for regulating the growth and development of plants, acting both locally and at a distance. Cytokinins are a class of phytohormone that participate in the regulation of plant growth, physiological activities, and yield. Cytokinins are adenine derivatives with distinct substitutions attached to the n6position of the adenine ring (figure 1). As was the case for ethylene, the cytokinin receptors were found to be histidine kinase sensors. Cytokinins induce formation of new leaves, chloroplasts in leaves, lateral shoot formation and adventitious shoot formation.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
More recently, functions of cks in plant stress defense including salt have been increasingly characterized. The most common class of cytokinins have. Although much is known about their biosynthesis and transport, important open questions remain. This hormone helps in promoting the cell’s growth, development, differentiation, affecting apical dominance and delay in leaf senescence. Cytokinins are a class of phytohormone that participate in the regulation of plant growth, physiological activities, and yield.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
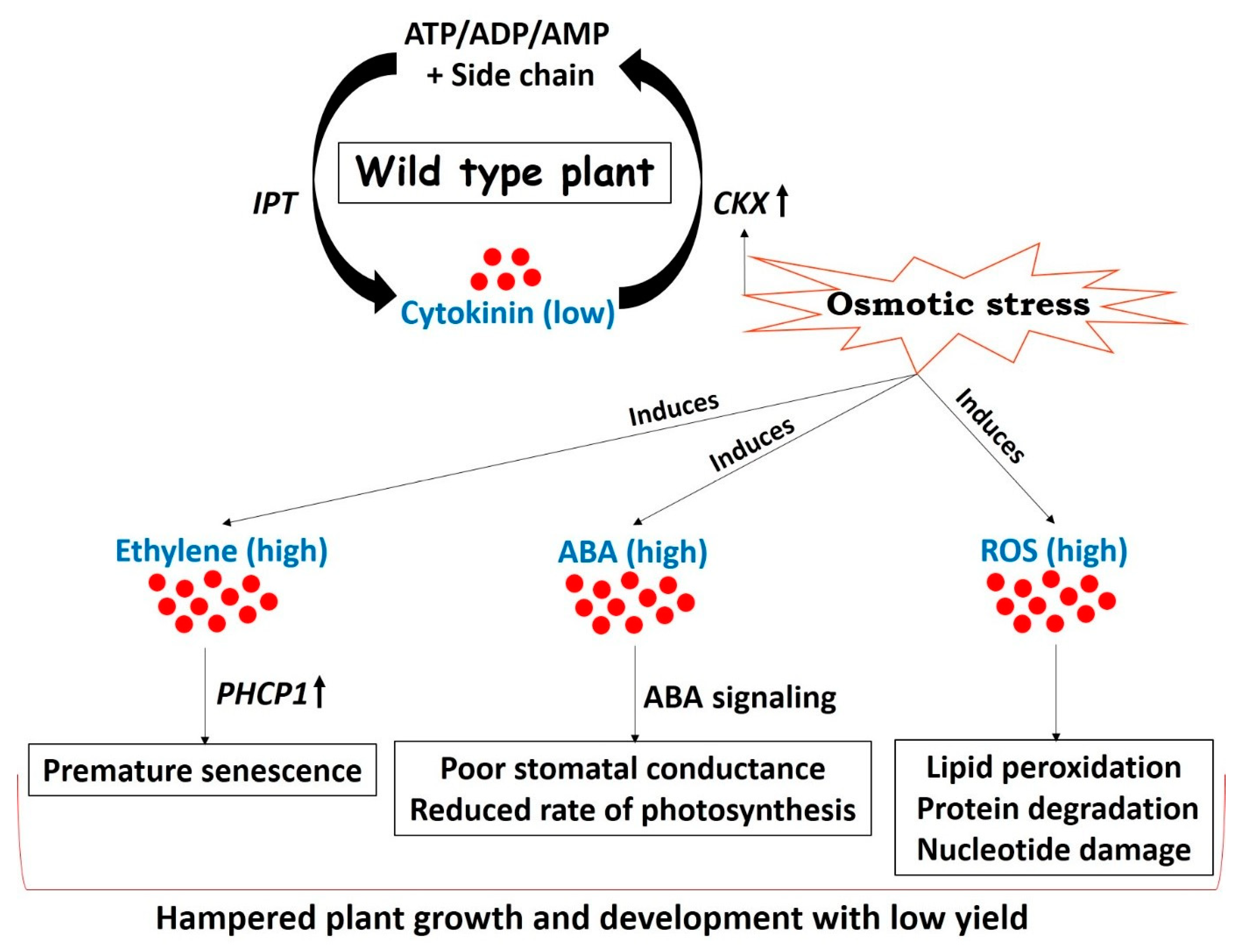
Although much is known about their biosynthesis and transport, important open questions remain. Cytokinins also play a key role in response to abiotic stresses, such as drought, salt and high or low temperature. They are involved primarily in cell growth and differentiation, but also affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and leaf senescence. Although much is known about their biosynthesis and transport, important open questions remain. 2institut fu¨r botanik, technische universita¨t.
 Source: botany.one
Source: botany.one
Cytokinins are synthesized in the roots and are usually derived from adenine. The delay of senescence (plant aging and die off). Today there are more than 200 natural and synthetic cytokinins combined. Although this cytokinin was known earlier but it was obtained in pure crystalline form in 1963 by letham from immature corn grains and named as zeatin. The most common class of cytokinins have.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
Cytokinins are a class of plant growth hormones (phytohormones) that promote cell division and cell differentiation. Cytokinins were the second plant hormone (after ethylene) for which receptors were discovered. What do cytokinins do in plants? Cytokinins were originally discovered following the search for a compound that. I think that this study will make an important contribution to the understanding of cytokinins metabolic genes in plants, especially in phalaenopsis plant.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
The most common form of naturally occurring cytokinin in plants today is called zeatin which was isolated from corn (zea mays). As was the case for ethylene, the cytokinin receptors were found to be histidine kinase sensors. Cytokinins are a group of plant growth regulators which are primarily involved in performing cell division in plant roots, shoot system. 2institut fu¨r botanik, technische universita¨t. This hormone helps in promoting the cell’s growth, development, differentiation, affecting apical dominance and delay in leaf senescence.
 Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
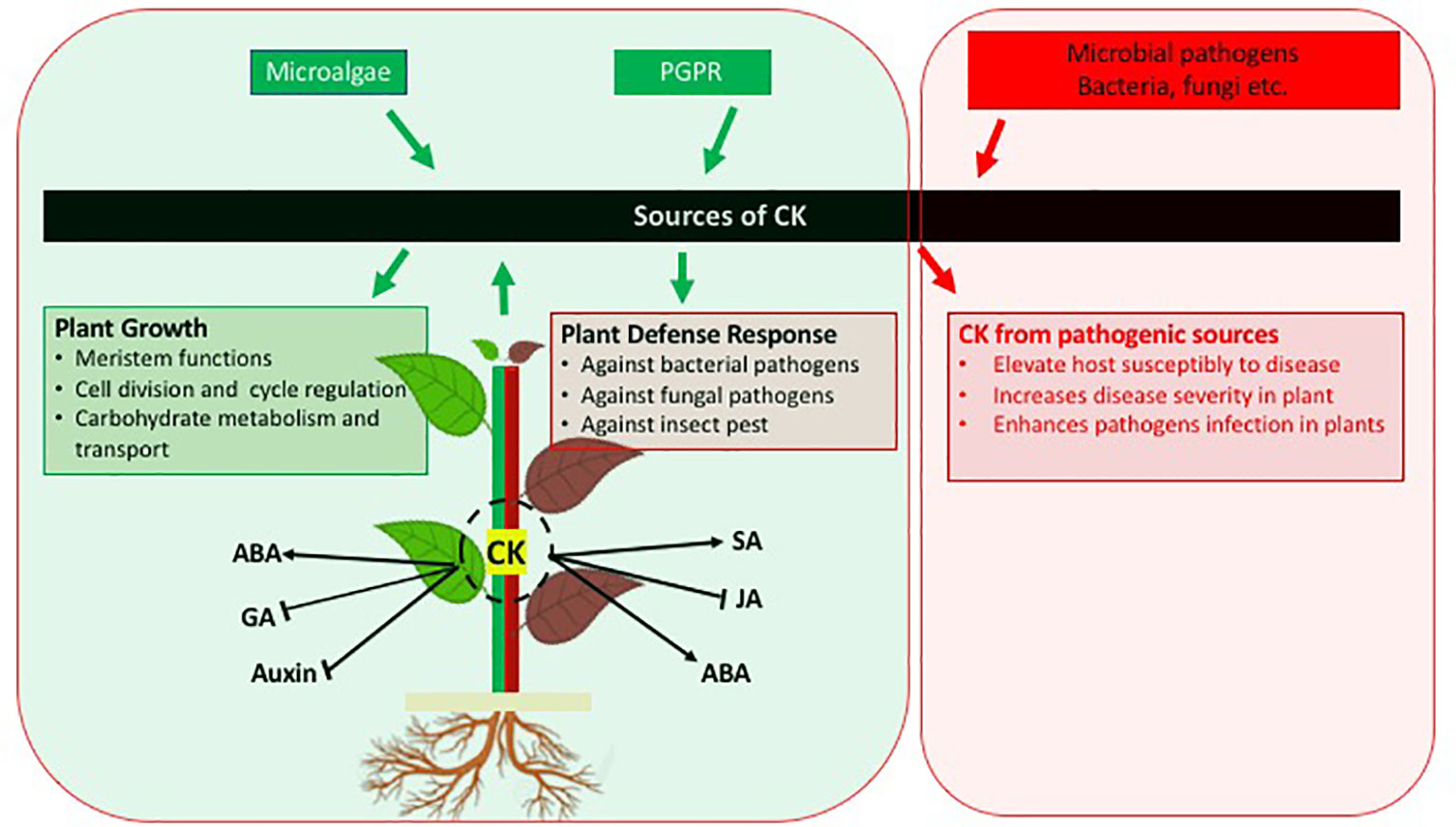
Among the plant growth regulators used in tissue culture, cytokinins (cks) are key regulators in cell division and differentiation in plants [4,5]. The phytohormone cytokinin plays diverse roles in plant development, influencing many agriculturally important processes, including growth, nutrient responses and the response to biotic and abiotic stresses. The delay of senescence (plant aging and die off). This hormone helps in promoting the cell’s growth, development, differentiation, affecting apical dominance and delay in leaf senescence. Cytokinins have been found in almost all higher plants as well as mosses, fungi, bacteria, and also in trna of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Cytokinins are derivatives of adenine. Functional activity of cytokinins occurs in the presence of. As was the case for ethylene, the cytokinin receptors were found to be histidine kinase sensors. They are involved primarily in cell growth and differentiation, but also affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and leaf senescence. I think that this study will make an important contribution to the understanding of cytokinins metabolic genes in plants, especially in phalaenopsis plant.
 Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
Among the plant growth regulators used in tissue culture, cytokinins (cks) are key regulators in cell division and differentiation in plants [4,5]. They are involved primarily in cell growth and differentiation, but also affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and leaf senescence. Cytokinins have been found in almost all higher plants as well as mosses, fungi, bacteria, and also in trna of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 2institut fu¨r botanik, technische universita¨t. Cytokinins are a group of hormones that promote cell division in plant roots and shoots and the growth of buds.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Cytokinins were discovered in a search for factors that promote cell proliferation in cultured plant cells in concert with a second phytohormone, auxin. More recently, functions of cks in plant stress defense including salt have been increasingly characterized. Today there are more than 200 natural and synthetic cytokinins combined. Cytokinins also play a key role in response to abiotic stresses, such as drought, salt and high or low temperature. Cytokinins were discovered in a search for factors that promote cell proliferation in cultured plant cells in concert with a second phytohormone, auxin.
 Source: gamesmartz.com
Source: gamesmartz.com
Cytokinins induce formation of new leaves, chloroplasts in leaves, lateral shoot formation and adventitious shoot formation. The uptake of minerals in the root the movement of nutrients into the leaves. Cks are isoprenoid substituted adenines molecule. Cytokinins comprise a family of signaling molecules essential for regulating the growth and development of plants, acting both locally and at a distance. Today there are more than 200 natural and synthetic cytokinins combined.
 Source: plantcell.org
Source: plantcell.org
Although much is known about their biosynthesis and transport, important open questions remain. Cytokinins are a class of phytohormone that participate in the regulation of plant growth, physiological activities, and yield. Cytokinins are a group of plant growth regulators which are primarily involved in performing cell division in plant roots, shoot system. They mainly affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and leaf vigor. Zeatin is the most abundant and widely distributed natural cytokinin in higher plants and in some bacteria.
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Cell division, shoot growth, regulating seed germination, new bud formation, leaf expansion reproductive development. They move upward in the xylem (woody tissue) and pass into the leaves and fruits, where they are required for normal growth and cell differentiation. Cell division, shoot growth, regulating seed germination, new bud formation, leaf expansion reproductive development. Because of the lack of biosynthetic and signaling mutants, the regulatory roles of cytokinins are not well understood. The most common class of cytokinins have.
 Source: besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Cytokinins are synthesized in the roots, they will move upward and enter the leaves and fruits of the plants, to maintain normal growth and cell differentiation of them. The plant hormone cytokinins (cks) were generally considered associated with plant development. Cytokinins were originally discovered following the search for a compound that. They are involved primarily in cell growth and differentiation, but also affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and leaf senescence. Thank you so much for the encouragement.
Source: researchgate.net
Cytokinins are a class of plant growth hormones (phytohormones) that promote cell division and cell differentiation. Cks are isoprenoid substituted adenines molecule. Cell division, shoot growth, regulating seed germination, new bud formation, leaf expansion reproductive development. More recently, functions of cks in plant stress defense including salt have been increasingly characterized. The phytohormone cytokinin plays diverse roles in plant development, influencing many agriculturally important processes, including growth, nutrient responses and the response to biotic and abiotic stresses.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Cytokinins are synthesized in the roots, they will move upward and enter the leaves and fruits of the plants, to maintain normal growth and cell differentiation of them. The most common class of cytokinins have. Cytokinins (cks) are key phytohormones that not only regulate plant growth and development but also mediate plant tolerance to drought stress. Cytokinins have been found in almost all higher plants as well as mosses, fungi, bacteria, and also in trna of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Cytokinins are synthesized in the roots and are usually derived from adenine.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The most common form of naturally occurring cytokinin in plants today is called zeatin which was isolated from corn (zea mays). Today there are more than 200 natural and synthetic cytokinins combined. Internally, cks play significant roles in plant cell division, nutrient allocation, and photosynthetic performance, and they are also detection and signaling agents for plant read more. Thank you so much for the encouragement. More recently, functions of cks in plant stress defense including salt have been increasingly characterized.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title cytokinins in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.