Your Cytoskeleton in animal and plant cells images are available. Cytoskeleton in animal and plant cells are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Cytoskeleton in animal and plant cells files here. Get all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re looking for cytoskeleton in animal and plant cells images information connected with to the cytoskeleton in animal and plant cells interest, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our website frequently gives you hints for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
Cytoskeleton In Animal And Plant Cells. The plant cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic and versatile intracellular scaffold composed of microtubules and actin microfilaments and plays an important role in many aspects of plant cell growth and development, including such fundamental processes as cell division, cell expansion, and intracellular organization and. Plant cells have a cell wall to support and protect them. The actin cytoskeleton in plant cells is mostly found within more central regions of the cytoplasm, notably within cytoplasmic strands that cross the vacuole and connect to the nucleus (28). Actin is powered by atp to assemble its filamentous form, which serves as a track for the movement of a motor protein called myosin.
 Animal Cell Project Cytoskeleton, HD Png Download vhv From vhv.rs
Animal Cell Project Cytoskeleton, HD Png Download vhv From vhv.rs
The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules that extends throughout a cell, through the cytoplasm, which is all of the material within a cell except for the nucleus. Keeping this in view, do plant cells have a cytoskeleton? We studied that in the cell wall video for plant cells. Animal cells only have the cytoskeleton since they do not have a cell wall. Yes, but it is in a plant cell more often than an animal cell. The mechanical function of cytoskeleton is particularly useful in animal cells, where no cell wall gives consistency to the cell.
Cytoskeleton in animal cell project , transparent cartoon from www.netclipart.com in eukaryotes, it is composed of three main components, microfilaments, intermediate filaments.
This enables actin to engage in cellular events requiring motion, such as cell division in animal cells and cytoplasmic streaming, which is the circular movement of the cell cytoplasm in plant cells. The diagram shows an idealized cell. Animal cells only have the cytoskeleton since they do not have a cell wall. Microfilaments , intermediate filaments and microtubules. A plant cell diagram is. Plants, animals, fungi, and protists have eukaryotic cells.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Email me at this address if a comment is added after. Your comment on this answer: Keeping this in view, do plant cells have a cytoskeleton? In addition, plant cells lack centrosomes, which leads to diffuse mt nucleation within the cell (si appendix, fig. Cytoskeleton in a plant cell diagram.
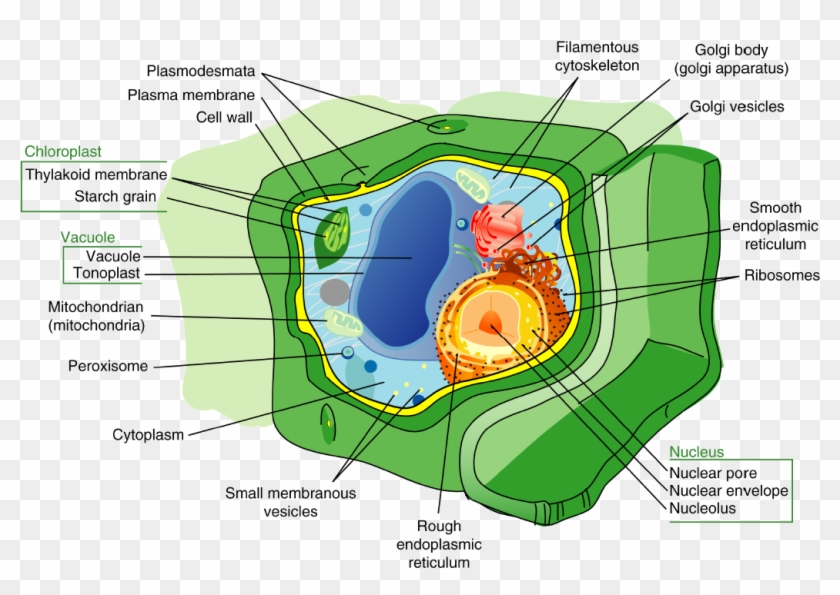 Source: pikpng.com
Source: pikpng.com
The cytoskeleton of eukaryotes is a static structure most resembling scaffolding used at construction sites. It is found in all cells, though the proteins that it is made of vary between organisms The cytoskeleton of prokaryotic cells was originally. The 3 parts of an plant cell are. The cytoskeleton is a complex network of fibers that supports the interior of a cell.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This enables actin to engage in cellular events requiring motion, such as cell division in animal cells and cytoplasmic streaming, which is the circular movement of the cell cytoplasm in plant cells. Without a cytoskeleton, animal cells will break because plasma membrane is just a sheet of fat. The animal cell is going to have a plasma membrane and the plant cell is going to have a plasma membrane and they actually can both have tunnels from neighboring cells, or tunnels between neighboring cells. They also have a cytoskeleton. Animal and plant cells have some of the same cell components in common including a nucleus, golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton, and cell (plasma) membrane.
 Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
The cytoskeleton is a complex network of fibers that supports the interior of a cell. Is the cytoskeleton of eukaryotes static? Plants, animals, fungi, and protists have eukaryotic cells. The cell which lacks cytoskeleton is (a) prokaryotic bacterial cells (b) eukaryotic plant cell (c) both (a) and (b) (d) prokaryotic a The mechanical function of cytoskeleton is particularly useful in animal cells, where no cell wall gives consistency to the cell.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Your name to display (optional): Without a cytoskeleton, animal cells will break because plasma membrane is just a sheet of fat. Yes, but it is in a plant cell more often than an animal cell. Plants, animals, fungi, and protists have eukaryotic cells. Your name to display (optional):
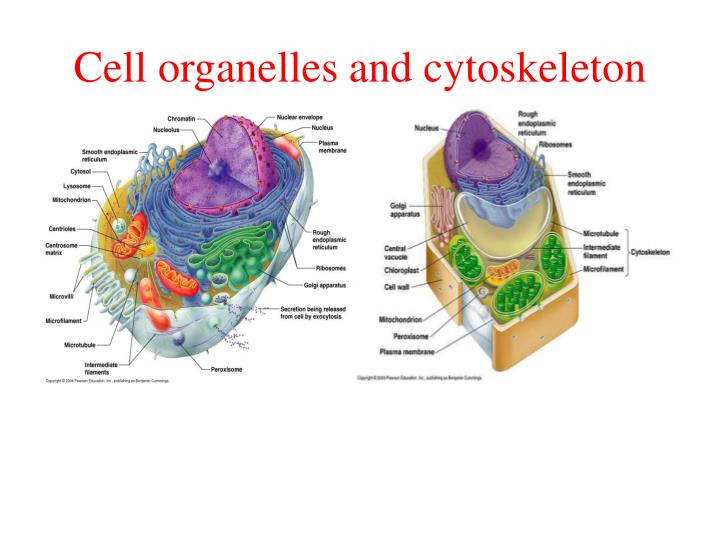 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The plant cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic and versatile intracellular scaffold composed of microtubules and actin microfilaments and plays an important role in many aspects of plant cell growth and development, including such fundamental processes as cell division, cell expansion, and intracellular organization and. Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, plasmodesmata, and plastids used for storage, and a large central vacuole, whereas animal cells do not. A cell is the microscopic functional and structural unit of all living organisms. A plant cell diagram is. Structurally, plant and animal cells are very similar because they are both eukaryotic cells.
 Source: instructables.com
Source: instructables.com
Animal cells have centrioles, centrosomes (discussed under the cytoskeleton), and lysosomes, whereas plant cells do not. The cytoskeleton is actually a collective term for three separate structures inside an animal cell. Eukaryotic cells are complex cells that have a nucleus and organelles. Some animal cells do have cytoskeletons though. The cell which lacks cytoskeleton is (a) prokaryotic bacterial cells (b) eukaryotic plant cell (c) both (a) and (b) (d) prokaryotic a
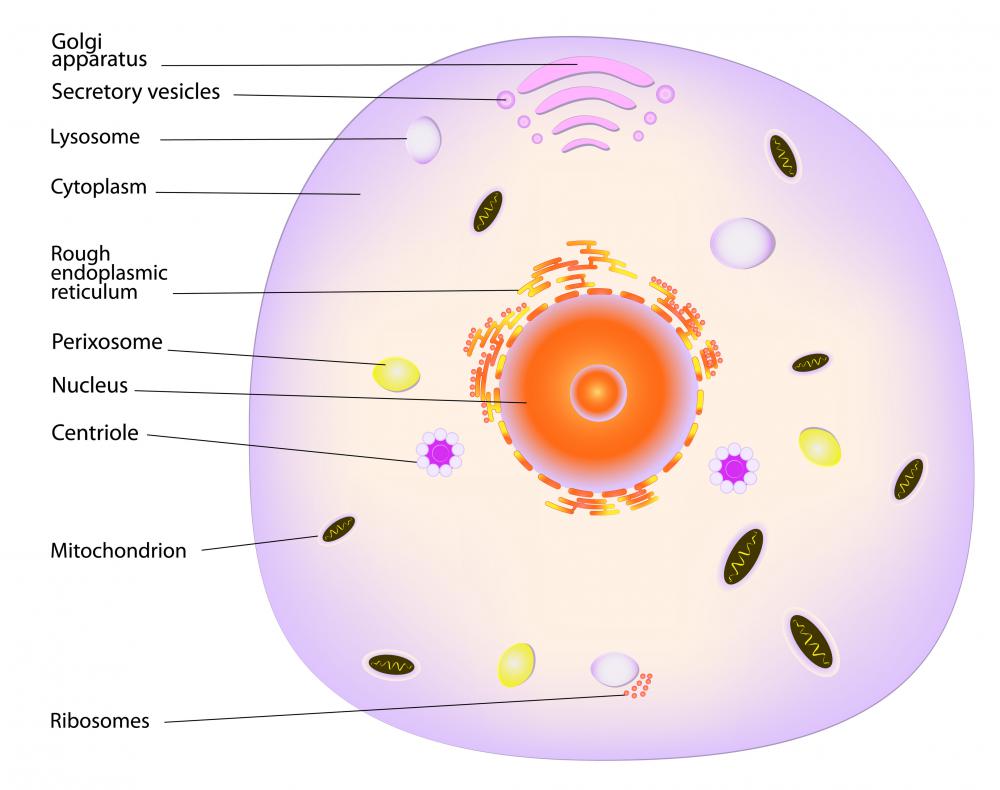 Source: wisegeek.com
Source: wisegeek.com
The plant cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic and versatile intracellular scaffold composed of microtubules and actin microfilaments and plays an important role in many aspects of plant cell growth and development, including such fundamental processes as cell division, cell expansion, and intracellular organization and. Is the cytoskeleton in plant and animal cells? The cell which lacks cytoskeleton is (a) prokaryotic bacterial cells (b) eukaryotic plant cell (c) both (a) and (b) (d) prokaryotic a Animal and plant cells have some of the same cell components in common including a nucleus, golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton, and cell (plasma) membrane. Yes, but it is in a plant cell more often than an animal cell.
 Source: animalsname.neocities.org
Source: animalsname.neocities.org
The plant cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic and versatile intracellular scaffold composed of microtubules and actin microfilaments and plays an important role in many aspects of plant cell growth and development, including such fundamental processes as cell division, cell expansion, and intracellular organization and. The cytoskeleton of prokaryotic cells was originally. It is found in all cells, though the proteins that it is made of vary between organisms Several of the cell components of animal and plant cells are also found in plant cells as well, including a nucleus, golgi complex, reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, oreoskeleton, and cell (plasma) membrane. Plant cells have a cell wall to support and protect them.
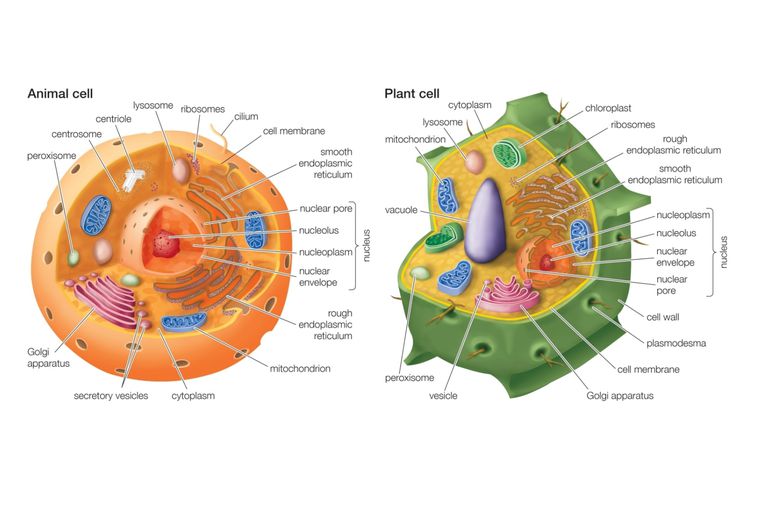 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
Several of the cell components of animal and plant cells are also found in plant cells as well, including a nucleus, golgi complex, reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, oreoskeleton, and cell (plasma) membrane. Several of the cell components of animal and plant cells are also found in plant cells as well, including a nucleus, golgi complex, reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, oreoskeleton, and cell (plasma) membrane. Cytoskeletons occur instead, making up a network of proteins arranged in an arranged manner. The cytoskeleton supports the cell gives it shape organizes and suspends the organelles within the cytoplasm and has roles in molecule transport cell division cell signaling and cell movement. The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules that extends throughout a cell, through the cytoplasm, which is all of the material within a cell except for the nucleus.
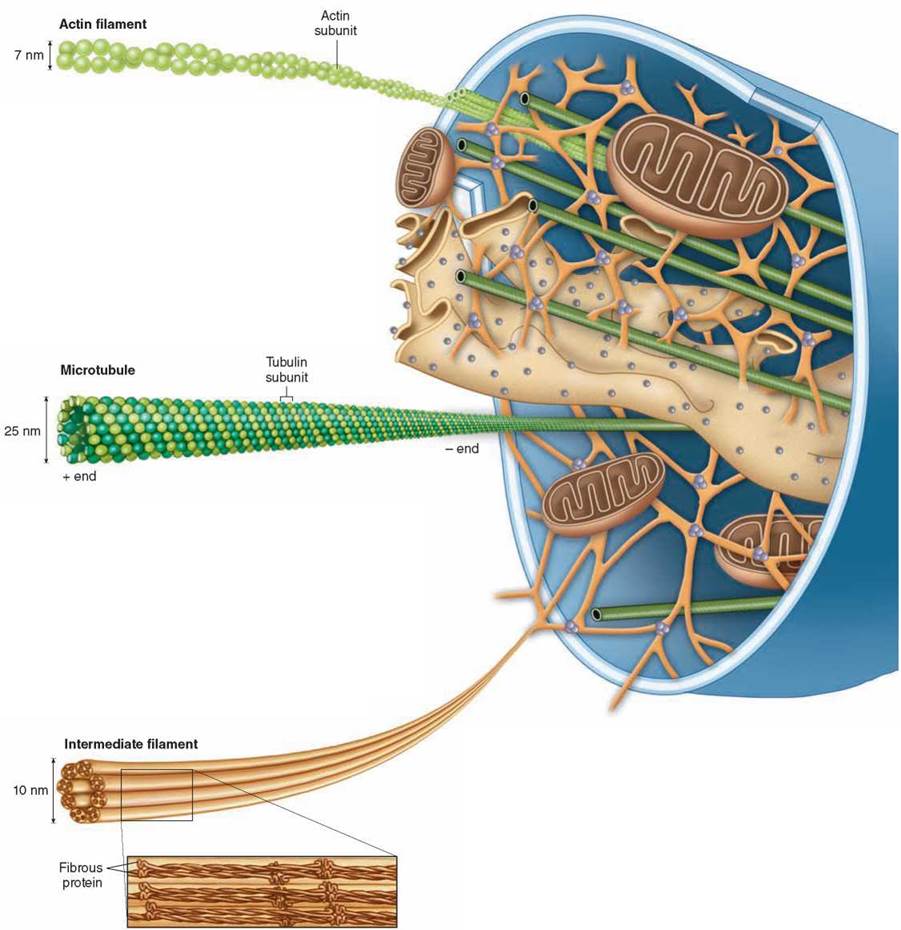 Source: schoolbag.info
Source: schoolbag.info
The 3 parts of an plant cell are. It is found in all cells, though the proteins that it is made of vary between organisms Both also contain similar membranes, cytosol, and cytoskeletal. The cell walls of bacteria, fungi, and plant cells, and the extracellular matrix of animal cells are all external to the plasma membrane. Is the cytoskeleton of eukaryotes static?
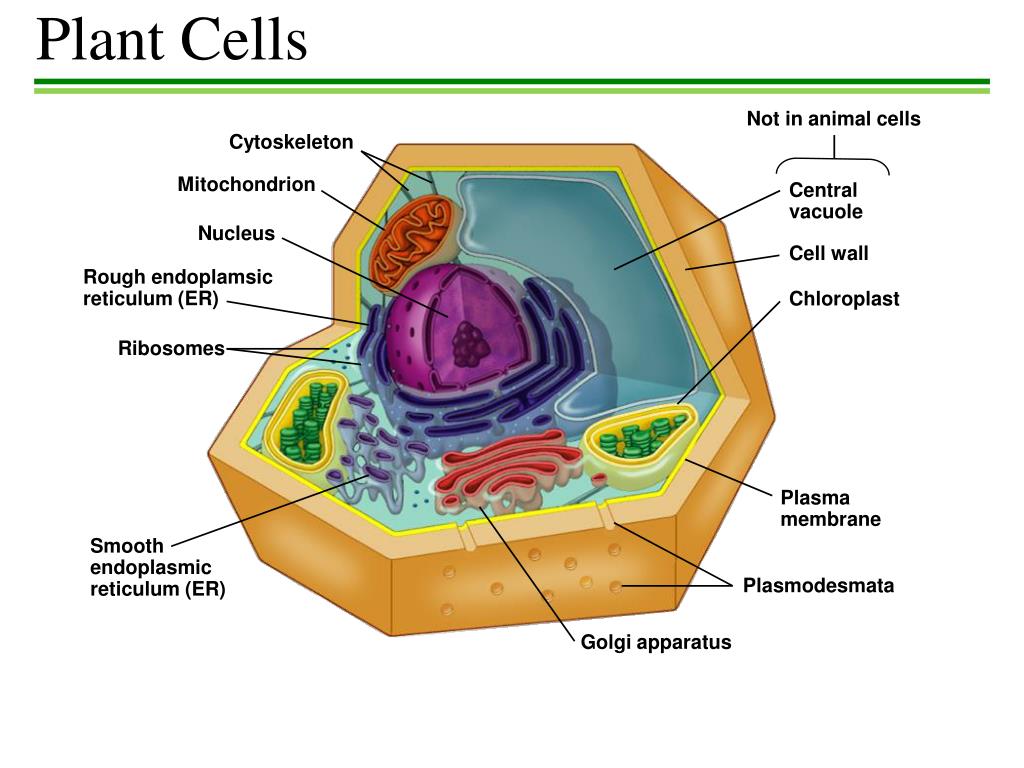 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Cytoskeletons occur instead, making up a network of proteins arranged in an arranged manner. The plant actin cytoskeleton controls the position of the nucleus (see above), around which the ppb is generally formed. The diagram shows an idealized cell. The cytoskeleton is a complex network of fibers that supports the interior of a cell. Structurally, plant and animal cells are very similar because they are both eukaryotic cells.
 Source: netclipart.com
Source: netclipart.com
The actin cytoskeleton in plant cells is mostly found within more central regions of the cytoplasm, notably within cytoplasmic strands that cross the vacuole and connect to the nucleus (28). Some animal cells do have cytoskeletons though. Cytoskeleton in a plant cell diagram. The 3 parts of an plant cell are. The plant cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic and versatile intracellular scaffold composed of microtubules and actin microfilaments and plays an important role in many aspects of plant cell growth and development, including such fundamental processes as cell division, cell expansion, and intracellular organization and.
 Source: aflam-neeeak.blogspot.com
Source: aflam-neeeak.blogspot.com
Animal cells only have the cytoskeleton since they do not have a cell wall. It is found in all cells, though the proteins that it is made of vary between organisms Keeping this in view, do plant cells have a cytoskeleton? The plant cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic and versatile intracellular scaffold composed of microtubules and actin microfilaments and plays an important role in many aspects of plant cell growth and development, including such fundamental processes as cell division, cell expansion, and intracellular organization and. Some animal cells do have cytoskeletons though.
 Source: vhv.rs
Source: vhv.rs
The plant actin cytoskeleton controls the position of the nucleus (see above), around which the ppb is generally formed. In animal cells the cytoskeleton is a network of filaments that gives the cell its shape and forms the support network for cell functions such as cell divisionin addition to giving cells shape and support the cytoskeleton creates particular structures and. The cell walls of bacteria, fungi, and plant cells, and the extracellular matrix of animal cells are all external to the plasma membrane. The mechanical function of cytoskeleton is particularly useful in animal cells, where no cell wall gives consistency to the cell. We saw these things right over here, called plasmodesmata, and we can actually see.
 Source: blog.udemy.com
Source: blog.udemy.com
In animal cells the cytoskeleton is a network of filaments that gives the cell its shape and forms the support network for cell functions such as cell divisionin addition to giving cells shape and support the cytoskeleton creates particular structures and. The plant actin cytoskeleton controls the position of the nucleus (see above), around which the ppb is generally formed. A cell wall is not necessary for an animal’s cell, for example. It is found in all cells, though the proteins that it is made of vary between organisms The cell walls of bacteria, fungi, and plant cells, and the extracellular matrix of animal cells are all external to the plasma membrane.
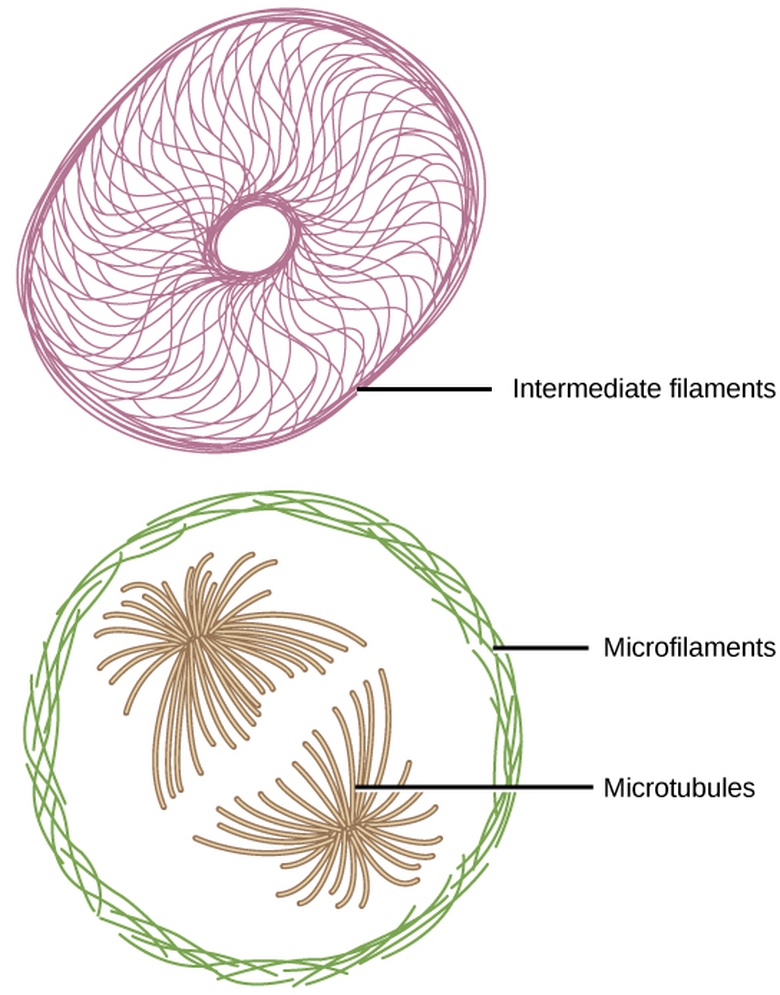 Source: oercommons.org
Source: oercommons.org
Email me at this address if a comment is added after. The plant actin cytoskeleton controls the position of the nucleus (see above), around which the ppb is generally formed. Eukaryotic cells are complex cells that have a nucleus and organelles. Animal and plant cells have some of the same cell components in common including a nucleus, golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton, and cell (plasma) membrane. Likewise, do both animal and plant cells have a cytoskeleton?
 Source: diagram.oyajino.com
Source: diagram.oyajino.com
Microfilaments , intermediate filaments and microtubules. The cytoskeleton is a complex network of fibers that supports the interior of a cell. Animal cells have a basic structure. In animal cells the cytoskeleton is a network of filaments that gives the cell its shape and forms the support network for cell functions such as cell divisionin addition to giving cells shape and support the cytoskeleton creates particular structures and. Likewise, do both animal and plant cells have a cytoskeleton?
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title cytoskeleton in animal and plant cells by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





