Your Cytoskeleton in plant cell images are available. Cytoskeleton in plant cell are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Cytoskeleton in plant cell files here. Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for cytoskeleton in plant cell images information related to the cytoskeleton in plant cell interest, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our site always gives you hints for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
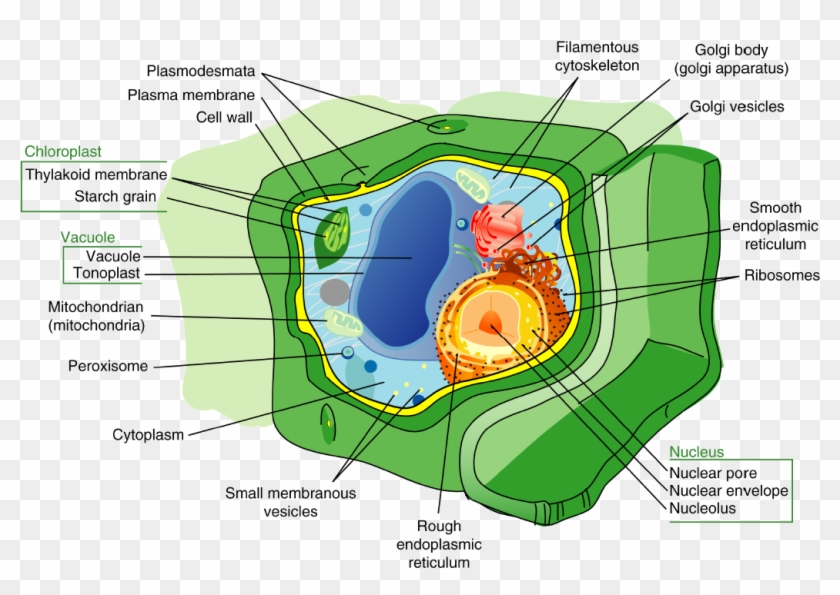
Cytoskeleton In Plant Cell. The cytoskeleton is a complex network of fibers that supports the interior of a cell. The plant cytoskeleton is the network of protein filaments, microtubules, and interconnecting filamentous bridges that give shape, structure and organization to the cytoplasm of the plant cell. It extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. Prokaryotic cells are less complex, with no true nuclei or.
 Do Plants Have A Cytoskeleton Plants BP From ninithesociopath.blogspot.com
Do Plants Have A Cytoskeleton Plants BP From ninithesociopath.blogspot.com
It is important to distinguish between cell graviperception and cell gravisensing. Plant cytoskeleton the plant cytoskeleton is the network of protein filaments, microtubules, and interconnecting filamentous bridges that give shape, structure and organization to the cytoplasm of. It is a complex network of interlinking. 13 how does cytoskeleton help cells move? The plant cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic and versatile intracellular scaffold composed of microtubules and actin microfilaments and plays an important role in many aspects of plant cell growth and development, including such fundamental processes as cell division, cell expansion, and intracellular organization and. Virtually all eukaryotic cells, including plant cells, have a cytoskeleton.
It holds different cell organelles in place.
It assists in cell signalling. It supports intracellular movements like the migration of cell organelles, transportation of vesicles in and out of the cell, etc. 11 do animal cells have cytoskeleton? There are considerable data that the plant cytoskeleton is reorganised in response to pcd, with remodelling of both microtubules and microfilaments taking place. 12 are cytoskeleton in plant and animal cells? The cytoskeleton supports the cell, shapes the organelles, organizes and teters them, and plays a role in molecule transport, cell division and cell signaling.
 Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
Source: plantcellbiology.masters.grkraj.org
In eukaryotic cells the cytoskeleton. In eukaryotes, it is composed of three main components, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and. The plant cell wall is an extracellular matrix that envelopes cells, gives them structure and shape, constitutes the interface with symbionts, and defends plants against external biotic and abiotic stress factors. The cytoskeleton is a complex network of fibers that supports the interior of a cell. It is found in all cells, though the proteins that it is made of vary between organisms.
 Source: eukaryotes.weebly.com
Source: eukaryotes.weebly.com
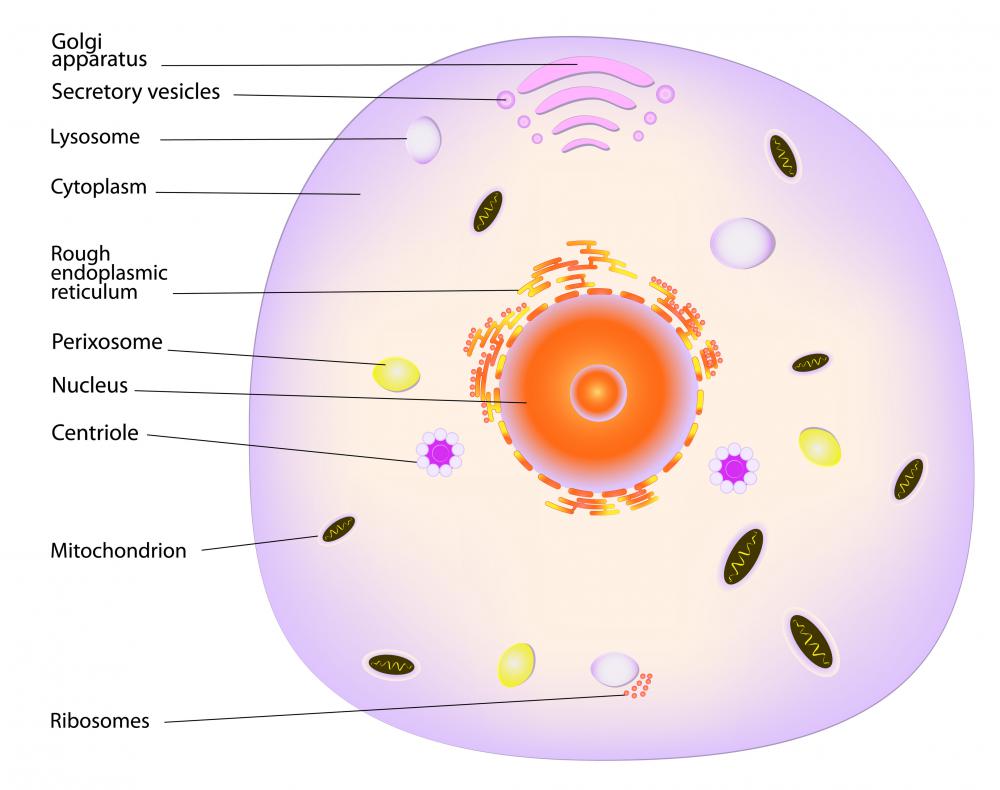
Cytoskeleton in a plant cell diagram. The first descriptive studies of the cytoskeleton in the context of plant defense date back to the early 1990s and were driven by the startling observation of extensive host cell polarization upon pathogen attack (reviewed in ).in challenged plant cells, cytoplasmic aggregation is commonly observed below the attempted microbial entry site. Virtually all eukaryotic cells, including plant cells, have a cytoskeleton. Functions of cytoskeleton in plant cells involve cell support and shape. The important cytoskeleton functions are mentioned below:
 Source: ninithesociopath.blogspot.com
Source: ninithesociopath.blogspot.com
There are considerable data that the plant cytoskeleton is reorganised in response to pcd, with remodelling of both microtubules and microfilaments taking place. It is found in all cells, though the proteins that it is made of vary between organisms. The interactions within the cell wall polymer network and the modification of these interactions provide insight into how the plant cell wall provides its dual function. A cell is the microscopic functional and structural unit of all living organisms. Three different types of linear proteinaceous polymers comprise the cytoskeleton in animal cells:
 Source: pikpng.com
Source: pikpng.com
These functions have been intensively investigated using single cell model systems. The plant cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic and versatile intracellular scaffold composed of microtubules and actin microfilaments and plays an important role in many aspects of plant cell growth and development, including such fundamental processes as cell division, cell expansion, and intracellular organization and. 10 what is the important contribution of cytoskeleton in the entire cell system? Part of the nato science for peace and security series c: The first descriptive studies of the cytoskeleton in the context of plant defense date back to the early 1990s and were driven by the startling observation of extensive host cell polarization upon pathogen attack (reviewed in ).in challenged plant cells, cytoplasmic aggregation is commonly observed below the attempted microbial entry site.
 Source: closerlookatscience.com
Source: closerlookatscience.com
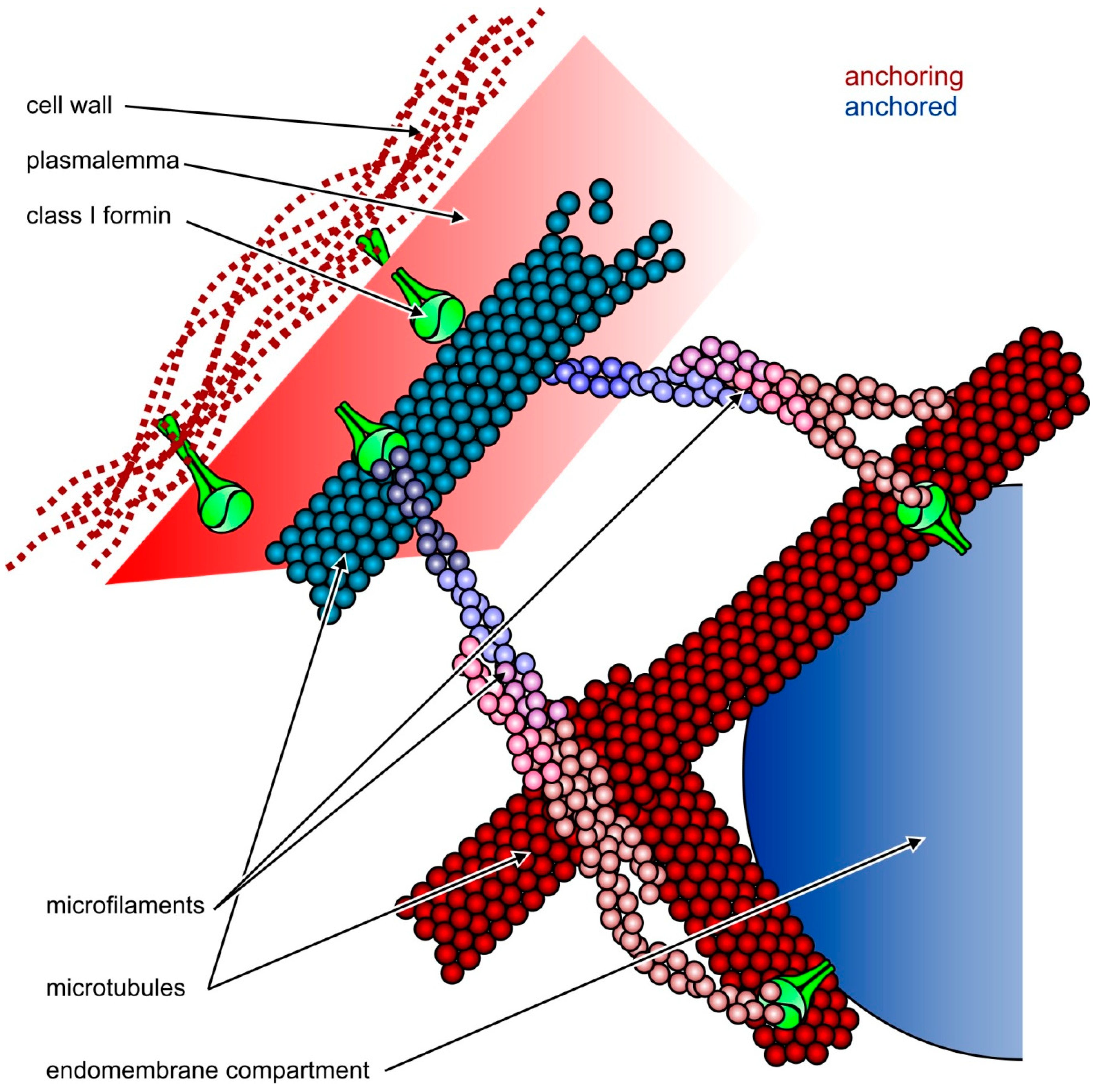
The interactions within the cell wall polymer network and the modification of these interactions provide insight into how the plant cell wall provides its dual function. The important cytoskeleton functions are mentioned below: They constantly undergo remodeling to fulfill their roles in supporting cell division, enlargement, and differentiation. Cytoskeleton in a plant cell diagram. Plant cells house highly dynamic cytoskeletal networks of microtubules and actin microfilaments.
 Source: brainly.in
Source: brainly.in
The eukaryotic cytoskeleton is a dynamic filamentous network with various cellular and developmental functions. Prokaryotic cells are less complex, with no true nuclei or. It is important to distinguish between cell graviperception and cell gravisensing. It holds different cell organelles in place. The plant actin cytoskeleton controls the position of the nucleus (see above), around which the ppb is generally formed.
 Source: blog.udemy.com
Source: blog.udemy.com
The functions of these actin structures are unclear. The plant cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic and versatile intracellular scaffold composed of microtubules and actin microfilaments and plays an important role in many aspects of plant cell growth and development, including such fundamental processes as cell division, cell expansion, and intracellular organization and. It is a complex network of interlinking. The cytoskeleton in a cell is involved in several functions such as mechanical support, motility. The important cytoskeleton functions are mentioned below:
 Source: marysrosaries.com
Source: marysrosaries.com
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, excluding bacteria and archaea. The assembly of this matrix is regulated and. 13 how does cytoskeleton help cells move? They constantly undergo remodeling to fulfill their roles in supporting cell division, enlargement, and differentiation. The actin cytoskeleton plays an essential role in several biological processes in plants, including cell division, cell.
 Source: aflam-neeeak.blogspot.com
Source: aflam-neeeak.blogspot.com
It extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. The cytoskeleton supports the cell, shapes the organelles, organizes and teters them, and plays a role in molecule transport, cell division and cell signaling. In eukaryotes, it is composed of three main components, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and. It has been demonstrated recently that the actin cytoskeleton and its associated elements provide a key target in many signaling events. The functions of these actin structures are unclear.
 Source: wisegeek.com
Source: wisegeek.com
It assists in cell signalling. They constantly undergo remodeling to fulfill their roles in supporting cell division, enlargement, and differentiation. In addition, plant cells lack centrosomes, which leads to diffuse mt nucleation within the cell (si appendix, fig. Complete the table by matching the label to the function and then naming the appropriate part. The actin cytoskeleton in plant cells is mostly found within more central regions of the cytoplasm, notably within cytoplasmic strands that cross the vacuole and connect to the nucleus ( 28 ).
 Source: vhv.rs
Source: vhv.rs
Cytoskeleton in plant cell functions of cytoskeleton in plant cells involve cell support and shape. Cytoskeleton in a plant cell diagram. It has been demonstrated recently that the actin cytoskeleton and its associated elements provide a key target in many signaling events. The cytoskeleton is a complex network of fibers that supports the interior of a cell. It is important to distinguish between cell graviperception and cell gravisensing.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
There are eukaryotic cells in plants , animals , fungi and protists. The plant cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic and versatile intracellular scaffold composed of microtubules and actin microfilaments and plays an important role in many aspects of plant cell growth and development, including such fundamental processes as cell division, cell expansion, and intracellular organization and. A cell is the microscopic functional and structural unit of all living organisms. Collectively it is referred as the cytoskeleton. It assists in cell signalling.
 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
Plant cells house highly dynamic cytoskeletal networks of microtubules and actin microfilaments. With the recent characterization of plant mutants that show abe. There are considerable data that the plant cytoskeleton is reorganised in response to pcd, with remodelling of both microtubules and microfilaments taking place. 13 how does cytoskeleton help cells move? A plant cell diagram is.
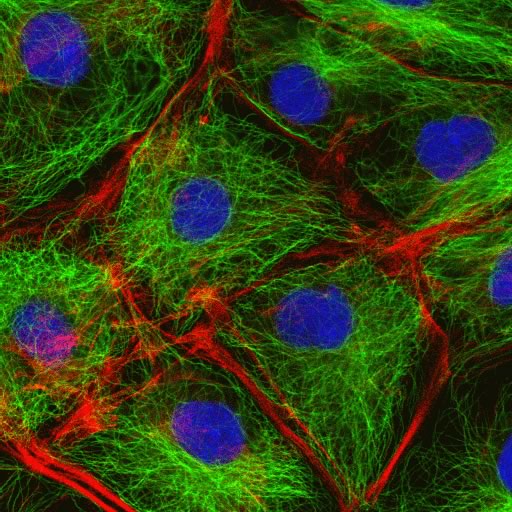 Source: lifeofplant.blogspot.com
Source: lifeofplant.blogspot.com
The cytoskeleton in a cell is involved in several functions such as mechanical support, motility. The important cytoskeleton functions are mentioned below: A cell is the microscopic functional and structural unit of all living organisms. There are eukaryotic cells in plants , animals , fungi and protists. Functions of cytoskeleton in plant cells involve cell support and shape.

The assembly of this matrix is regulated and. Why do plant cells have a cytoskeleton? The actin cytoskeleton in plant cells is mostly found within more central regions of the cytoplasm, notably within cytoplasmic strands that cross the vacuole and connect to the nucleus ( 28 ). The cytoskeleton supports the cell, shapes the organelles, organizes and teters them, and plays a role in molecule transport, cell division and cell signaling. It is found in all cells, though the proteins that it is made of vary between organisms.
 Source: cellstructure.pbworks.com
Source: cellstructure.pbworks.com
Cytoskeleton in a plant cell diagram. 13 how does cytoskeleton help cells move? The important functions of dynamic cytoskeletal networks have been indicated for almost every intracellular activity, from cell division to cell movement, cell morphogenesis and cell signal transduction. The important cytoskeleton functions are mentioned below: The plant cytoskeleton is the network of protein filaments, microtubules, and interconnecting filamentous bridges that give shape, structure and organization to the cytoplasm of the plant cell.
 Source: phys.org
Source: phys.org
The actin cytoskeleton in plant cells is mostly found within more central regions of the cytoplasm, notably within cytoplasmic strands that cross the vacuole and connect to the nucleus ( 28 ). 14 which of the following are features of the cytoskeleton in animal cells? The eukaryotic cytoskeleton is a dynamic filamentous network with various cellular and developmental functions. Virtually all eukaryotic cells, including plant cells, have a cytoskeleton. The important functions of dynamic cytoskeletal networks have been indicated for almost every intracellular activity, from cell division to cell movement, cell morphogenesis and cell signal transduction.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
11 do animal cells have cytoskeleton? The functions of these actin structures are unclear. It is a complex network of interlinking. There are eukaryotic cells in plants , animals , fungi and protists. It assists in cell signalling.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title cytoskeleton in plant cell by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.